Paying invoices blindly can be costly for you or your organization. At small scales, it might be unnoticeable, but as the frequency of invoices increases, you will need a layer of verification.
Fortunately, there is a basic way to check your invoice, it’s called 2-way matching.
In this article, we’ll talk about how to add a 2-way invoice matching for invoice processing and discuss why is it important.
What is 2-Way Matching?
Two-way matching is an automated process that checks for discrepancies between purchase orders and their associated invoices before invoices are approved and paid.
Also known as purchase order matching or PO matching, this method compares specific figures on both the purchase order and invoice to ensure they match within predefined tolerances.
By validating that the details of received invoices align with their corresponding purchase orders, 2-way matching helps prevent errors, overpayments, and fraud in the accounts payable process, ensuring accurate and efficient financial transactions.
Benefits of 2-Way Matching
2-way matching is a simple way for businesses to get started with matching their invoices and improve their financial operations without adding complexities.
With that, here are the advantages of two-way matching:
- Accuracy in Payments: Two-way matching ensures that the invoice amount matches the purchase order, reducing the chances of overpayments or underpayments.
- Fraud Prevention: By verifying that the invoice matches the original purchase order, two-way matching reduces the risk of fraudulent invoices being paid.
- Improved Financial Control: This process strengthens internal controls by ensuring that only authorized purchases are paid for, helping companies maintain better control over their finances.
- Simplified Verification: With 2-way matching, you streamline the verification process by comparing only two documents—the purchase order and the invoice.
- Streamlined Accounts Payable: Two-way matching simplifies the accounts payable process by automatically flagging discrepancies between POs and invoices. This reduces the time spent on manual verification and speeds up the payment cycle.
- Supplier Relationship Management: Ensuring accurate and timely payments through two-way matching can enhance relationships with suppliers, as it helps avoid payment delays and disputes.
- Cost Savings: By preventing errors and fraud, two-way matching can lead to significant cost savings. It also reduces the administrative burden of resolving discrepancies after payments have been made.
- Compliance and Audit Readiness: Two-way matching provides a clear audit trail, making it easier for companies to demonstrate compliance with internal policies and external regulations. This can be particularly important during financial audits.
- Fewer Blockers: In industries where services are frequently purchased, 2-way matching eliminates the need for a goods receipt, which can often be a blocker in the payment process. Without this requirement, your invoices don’t get stuck waiting for additional documentation. This ensures your accounts stay balanced, and your suppliers remain satisfied with prompt payments.
- Reduced Labor: Implementing 2-way matching significantly reduces the manual labor involved in invoice processing. Without the need to match a third document, your accounts payable team spends less time on each transaction. This decreases the workload and allows your team to focus on higher-value tasks.
- Faster Invoice Approval: One of the biggest issues accounts payable personnel face is slow invoice approval, with 47% complaining about its delay. With fewer documents to match, exceptions and discrepancies are less likely to occur, allowing invoices to move through the approval process more quickly.
- Significant Cost Savings: Overpayments are often caused by duplicate entries with 57% pointing it out to be significantly costly. By avoiding overpayments and quickly resolving discrepancies, 2-way matching can lead to substantial cost savings.
Overall, 2-way invoice matching is great for small businesses to get started with invoice matching, protect themselves from fraud, and improve their overall financial operations by having better control over finances.
How 2-Way Matching Works
2-way matching is the simplest of invoice matching methods and the easiest to apply, Here is how it works:
What You Need for 2-Way Matching

For two-way matching, you only need two things, the invoice and a purchase order.
- Purchase order: This is issued by the buyer. This is a request of the buyer to the vendor of the services or items they are requesting.
- Invoice: this is often provided by the supplier or the vendor. This contains all the items or services that are provided, with the respective amounts that are needed to be paid by the buyer
2-Way Matching Process
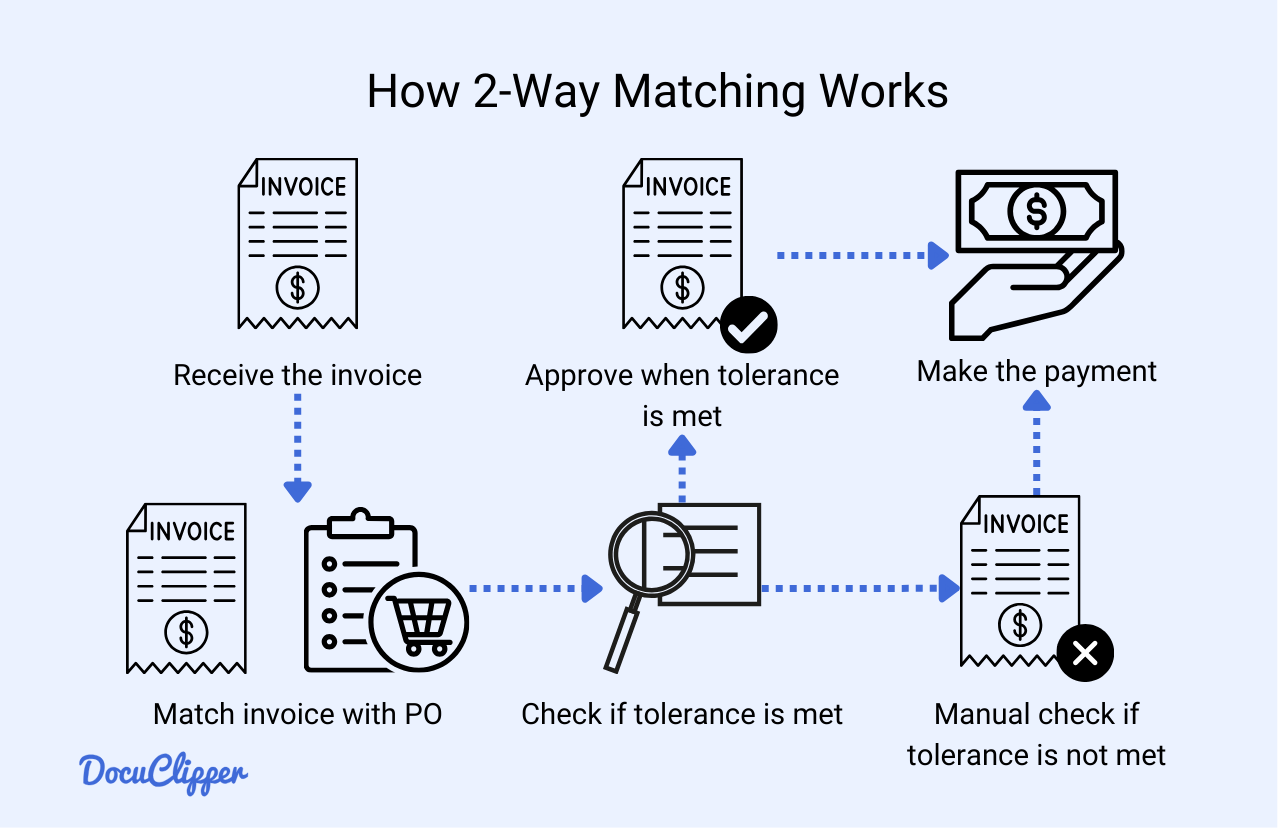
- Receive the invoice: A company receives an invoice from a vendor for the goods or services ordered via the purchase order. The invoice is then recorded in the accounting system for further verification.
- Match to purchase order: The invoice details are matched to the corresponding purchase order (PO). This involves verifying that the item descriptions, quantities, and prices on both documents are identical.
- Apply tolerance check: Tolerance values are predefined acceptable ranges of deviation between the invoice and the purchase order. If the discrepancies fall within this acceptable range, the invoice is automatically approved without further review. If the discrepancies exceed the tolerance levels, the invoice is flagged for manual review. This step ensures minor variations don’t unnecessarily delay payments while significant discrepancies are appropriately addressed.
- Contact the vendor if there are any inconsistencies: If inconsistencies are found, the invoice is held and not approved for payment. An invoice management personnel must manually address and resolve the issue with the vendor before the process can continue.
- Approve and process payment: Once any discrepancies are resolved and the invoice matches the purchase order, the invoice is approved manually. The payment is then scheduled, completing the transaction between the company and the vendor.
2 Examples of a 2-Way Match
Since you have a grasp of how a 2-way match works, here are practical examples:
Example 1: Logistics
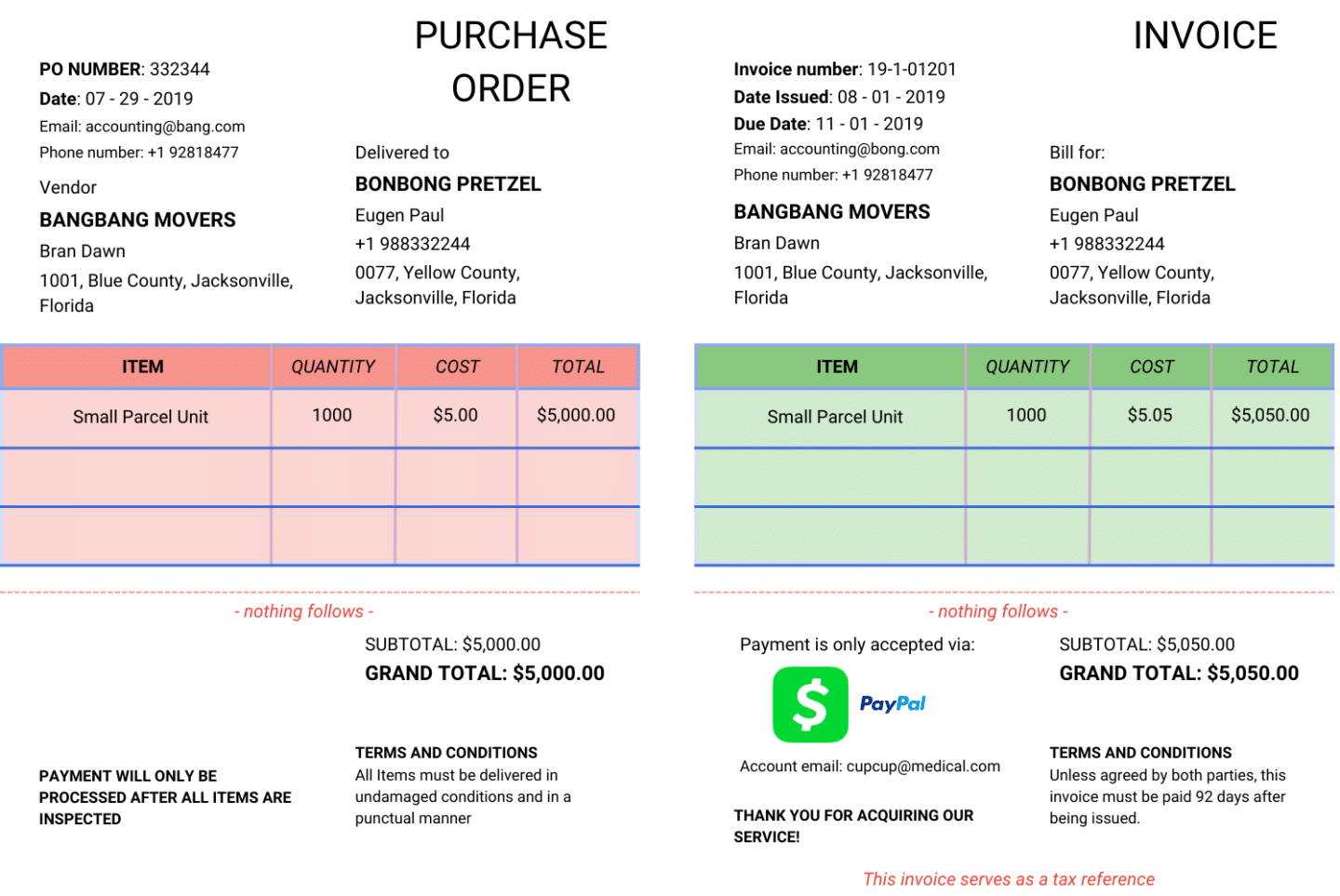
This example is in the logistics industry that has a satisfactory invoice match:
- Receive the invoice: A logistics company receives an invoice from a vendor for transportation services provided. The invoice details the transportation of goods from a warehouse to a distribution center.
- Match to purchase order: The accounts payable department matches the invoice to the corresponding purchase order (PO). The PO had specified the transportation of 1000 units of product at a rate of $5 per unit.
- Apply tolerance check: The tolerance check allows for a minor variance of up to 2% in the total cost. The invoice states the transportation cost as $5050, which is within the acceptable tolerance range (2% of $5000 is $100). Thus, the invoice is approved without further review.
- Resolve discrepancies: In this case, no discrepancies are found, so the invoice is not held and moves to the next step.
- Approve and process payment: The invoice is approved manually, and the payment is scheduled according to the company’s payment terms, completing the transaction between the logistics company and the vendor.
Example 2: Auto Parts
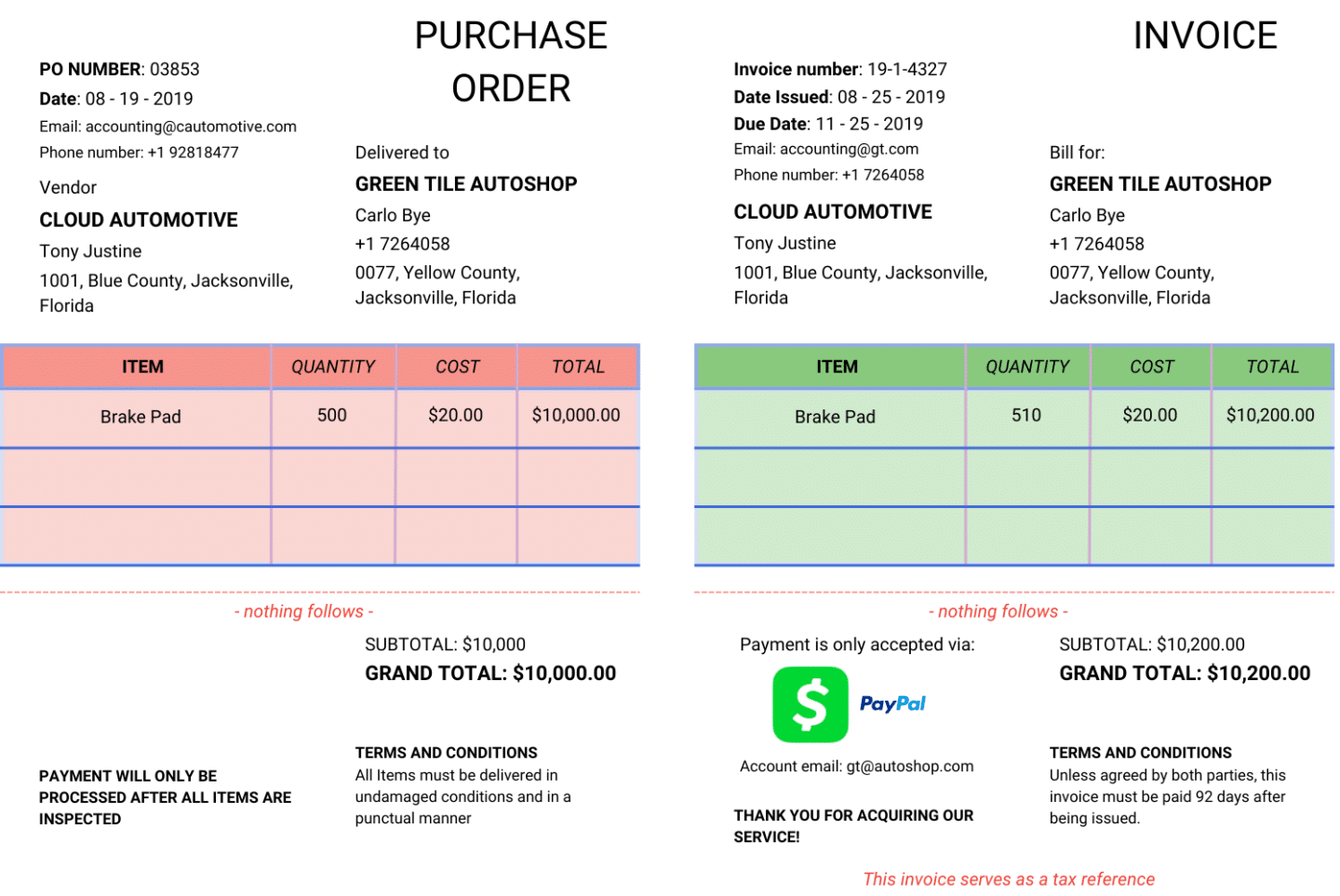
This example is in the automotive industry which has a significant margin of discrepancy:
- Receive the invoice: An auto parts retailer receives an invoice from a supplier for a shipment of brake pads. The invoice details 500 brake pads at $20 each.
- Match to purchase order: The accounts payable department matches the invoice to the corresponding purchase order (PO). The PO had specified an order of 500 brake pads at $20 each.
- Apply tolerance check: The tolerance check allows for a minor variance of up to 1% in the total quantity. However, the invoice states the quantity as 510 brake pads at $20 each, totaling $10,200, which exceeds the 1% tolerance (1% of 500 is 5 pads, so up to 505 pads would be acceptable).
- Resolve discrepancies: Since the quantity discrepancy exceeds the tolerance limit, the invoice is placed on hold. The accounts payable manager must manually review the discrepancy, contact the supplier to resolve the issue, and adjust the invoice or PO as necessary.
- Approve and process payment: Once the discrepancy is resolved and the invoice matches the purchase order, the invoice is approved manually. The payment is then scheduled according to the retailer’s payment terms, completing the transaction between the auto parts retailer and the supplier.
How to Extract Data from the Invoices
Extracting data from invoices, especially when dealing with hundreds each month, can be daunting. While comparing a single invoice to a purchase order is straightforward, managing this process at scale requires robust strategies to avoid errors and delays.
Established companies often rely on both manual and automated methods to ensure data accuracy and consistency.
Manual data extraction methods
In manual data extraction, key fields such as the purchase order (PO) number, invoice number, quantity, and price are identified and recorded.
This approach requires consistent attention to detail to prevent errors and maintain consistency across all records.
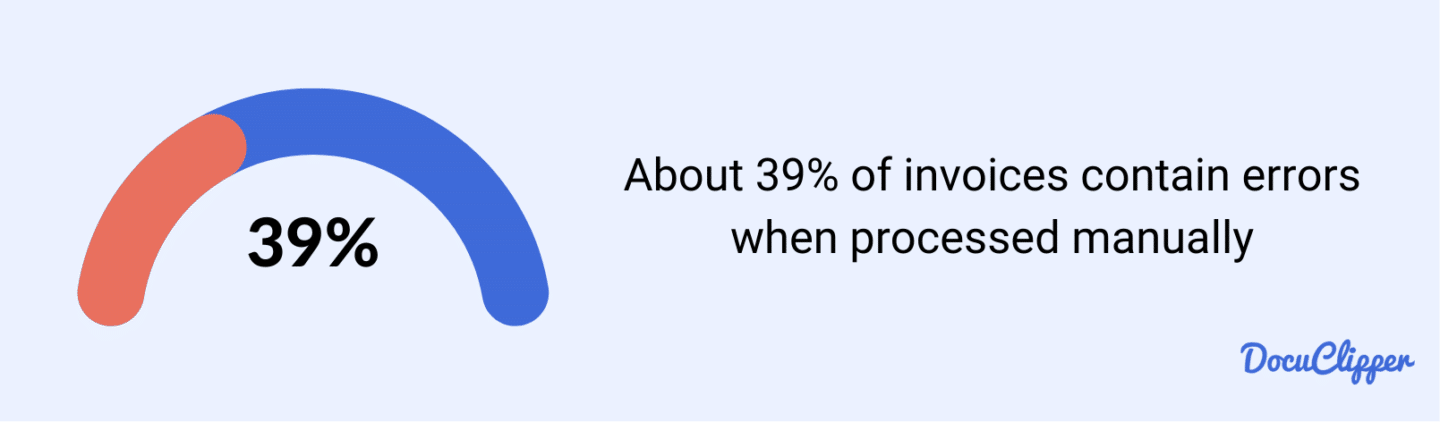
However, the manual data entry process can be time-consuming and prone to mistakes. In fact, About 39% of invoices contain errors.
Automated data extraction tools
To enhance efficiency of your invoice data extraction, many businesses automate data entry by using tools such as Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology.
OCR software scans invoices, extracts relevant data, and compiles it into a spreadsheet or it can directly be imported to an ERP or accounting software. Personnel then matches it with purchase orders, significantly reducing the time and effort involved.
The automation not only speeds up the process but also minimizes human error, ensuring more accurate and consistent data entry.
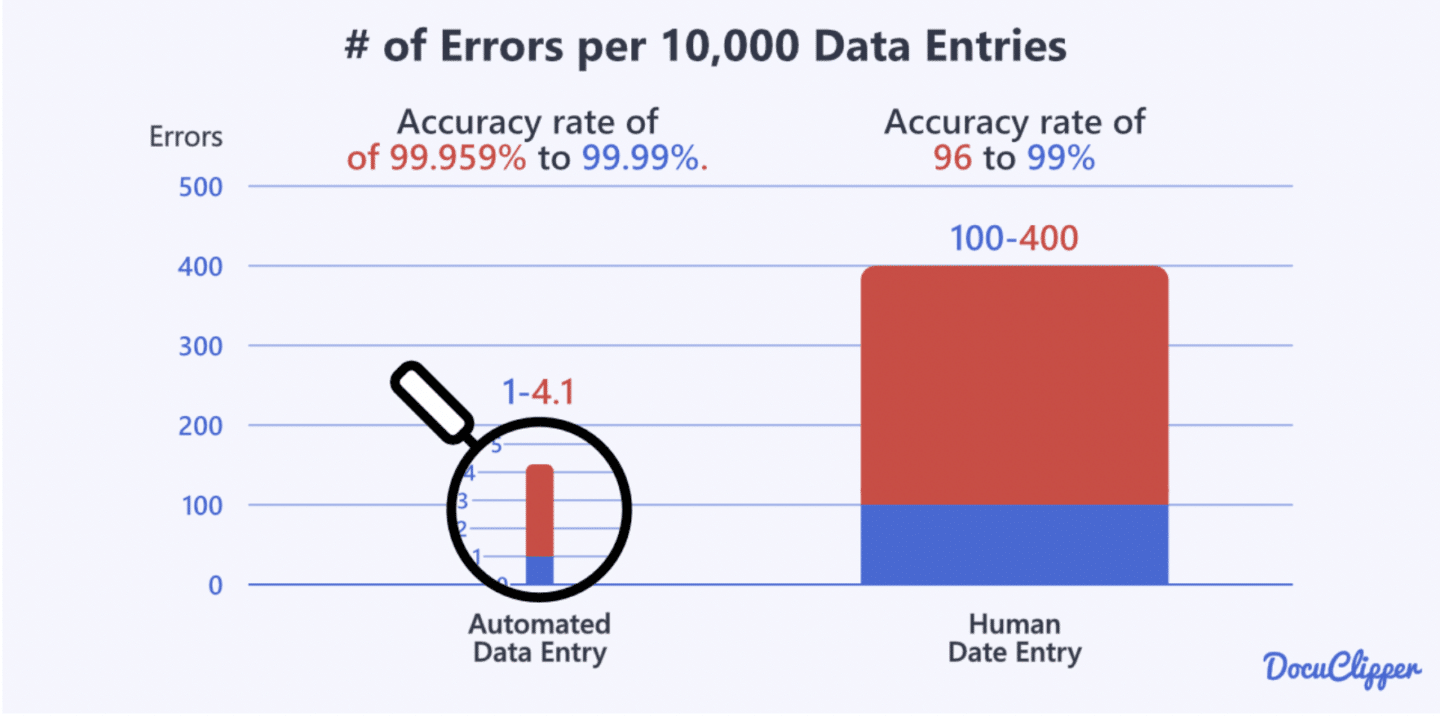
Typically, automated data entry boasts an accuracy rate of 99.959% to 99.99%. In contrast, the accuracy rate for human data entry ranges from 96% to 99%.
How to Implement 2-Way Matching for Your Business
When you decide that you can start a 2-way matching process for your business, here are some necessary steps:
- Assess Current Accounts Payable Process: Evaluate your existing accounts payable (AP) process to identify inefficiencies and areas prone to errors or fraud. Document how invoices are currently received, recorded, and approved for payment. Understanding the baseline process helps pinpoint where 2-way matching can bring improvements.
- Develop and Train on New Procedures: Design new procedures for incorporating 2-way matching into the AP process. This involves defining the steps for creating detailed purchase orders, receiving and recording invoices, and performing the matching process. Conduct training sessions for your AP team to ensure they understand the new procedures and the importance of accurate data entry and verification.
- Implement Technology and Tools: Invest in accounting software that supports 2-way matching. Ensure the software can automate the matching of purchase orders and invoices, applying predefined tolerance checks. Integrate the software with your existing systems to streamline data flow and minimize manual intervention.
- Monitor, Adjust, and Optimize: After implementing 2-way matching, continuously monitor the process to ensure it is functioning as intended. Collect feedback from the AP team and make necessary adjustments to improve efficiency and invoice accuracy. Regularly review the system’s performance and update tolerance levels, procedures, and training as needed to optimize the process and adapt to any changes in business operations or vendor relationships.
Types of Invoice Matching
There are more ways to match your invoices, here are some examples:
2-Way Matching
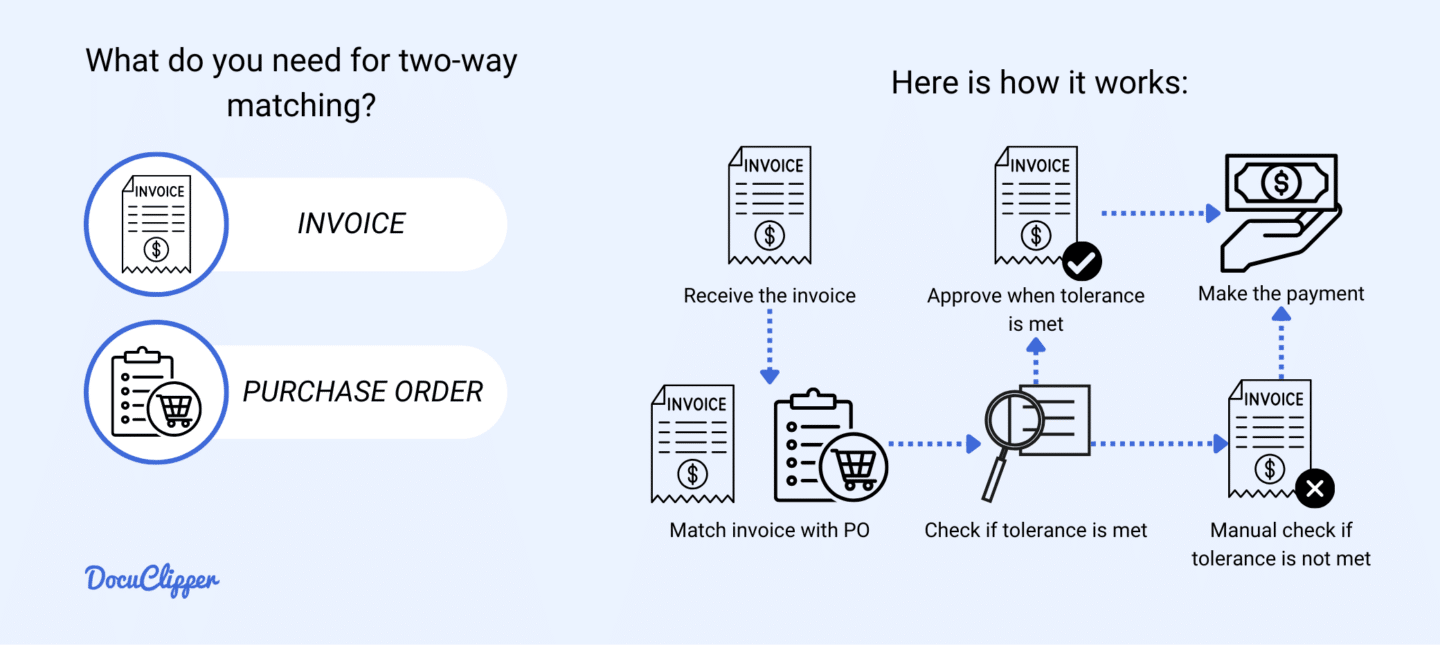
Two-way matching, also known as purchase order matching, is a process that checks for discrepancies between the invoice and the purchase order (PO). This method ensures that the details on the invoice, such as item descriptions, quantities, and prices, match the PO.
If the discrepancies fall within predefined acceptable limits, the invoice is approved for payment; otherwise, it is flagged for review. This process reduces the risk of human error and speeds up the invoice verification process.
3-Way Matching
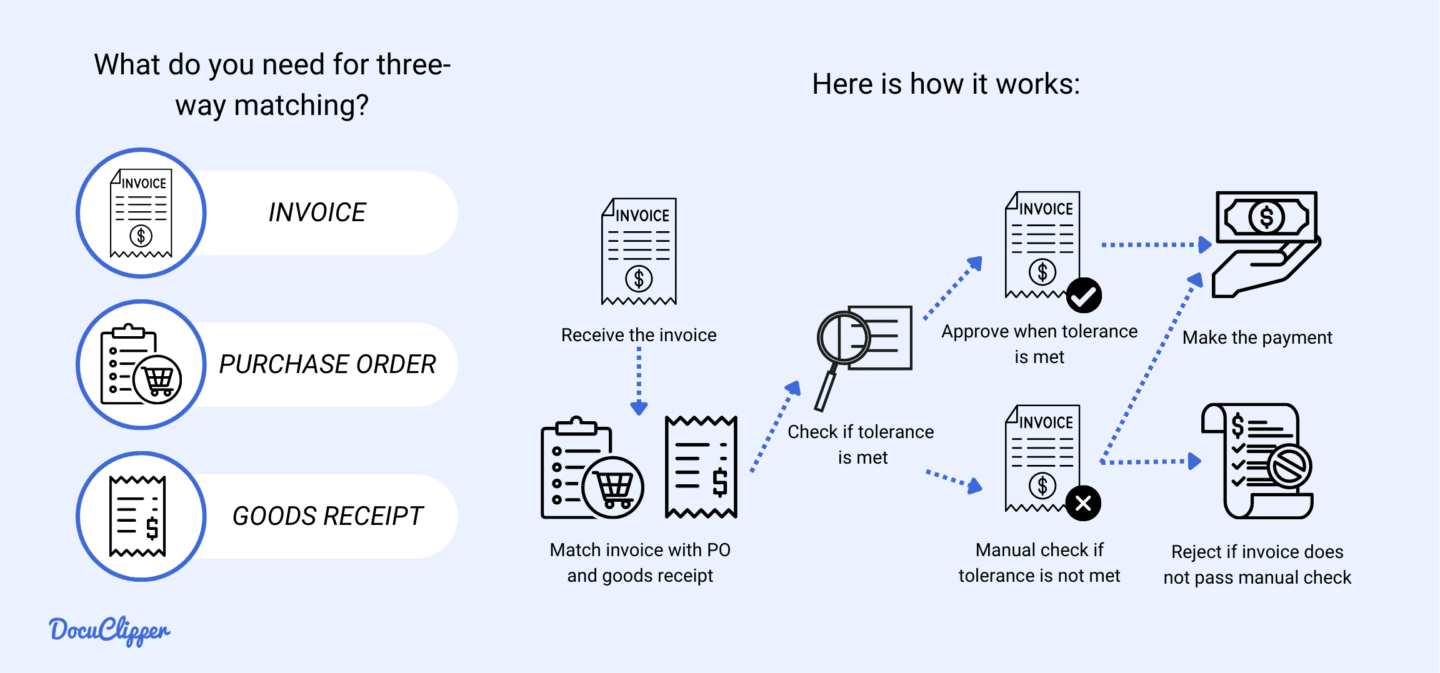
Three-way matching is an advanced process that compares the invoice and purchase order to the goods receipt note (GRN). It involves verifying that the goods or services billed in the invoice match both the PO and the GRN, confirming that the items were received as ordered.
This method provides greater assurance that the invoice reflects actual goods or services received, reducing the risk of overpayment and fraud. However, it is more time-consuming and requires accurate and timely recording of goods receipts.
4-Way Matching
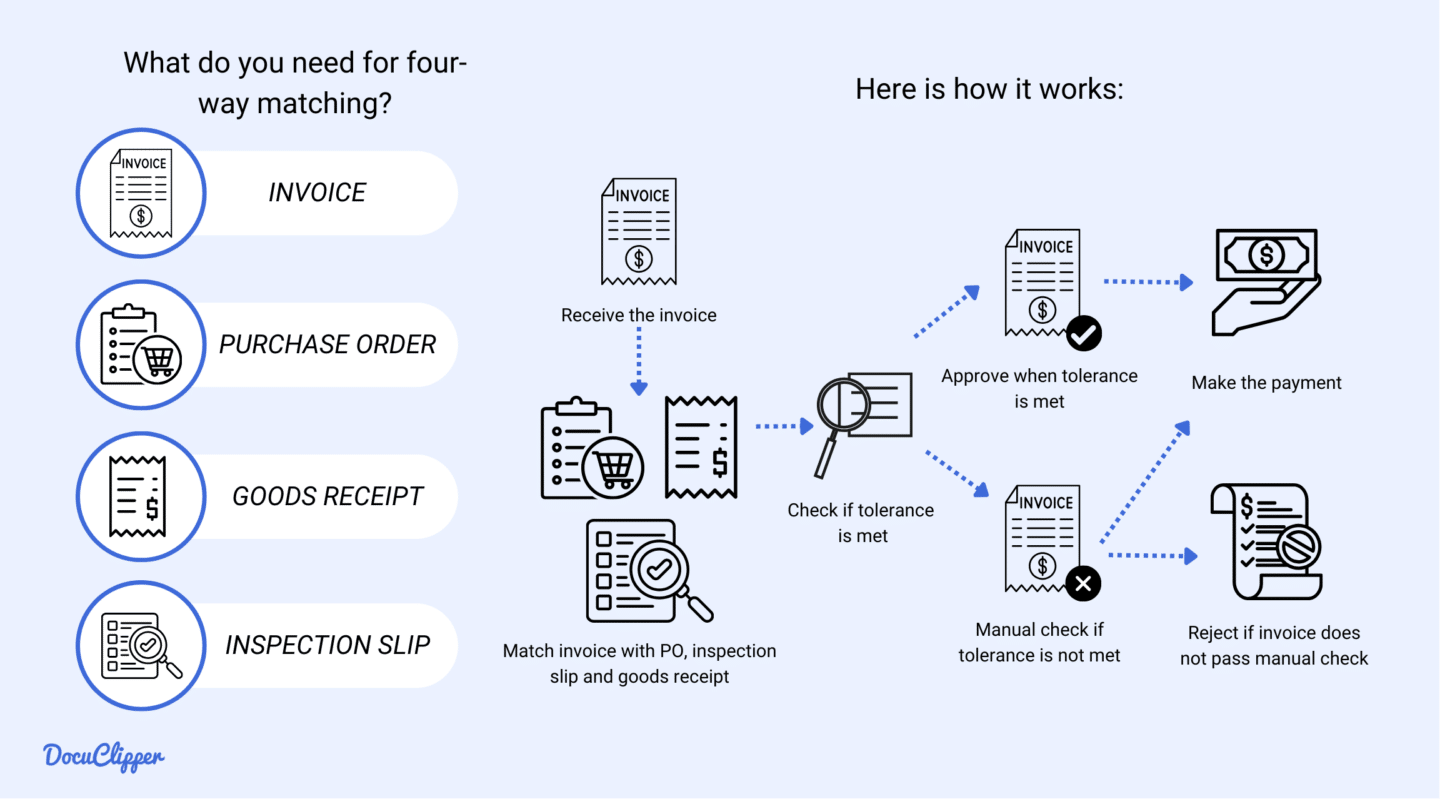
Four-way matching is the most comprehensive invoice matching process, adding an inspection step to the verification. This method involves comparing the invoice, purchase order, goods receipt note, and inspection slip that verifies the quality and quantity of the received items.
The invoice is approved for payment only if all documents match within acceptable limits. This method ensures the highest level of accuracy and fraud prevention but is the most time-consuming and requires coordination across multiple departments.
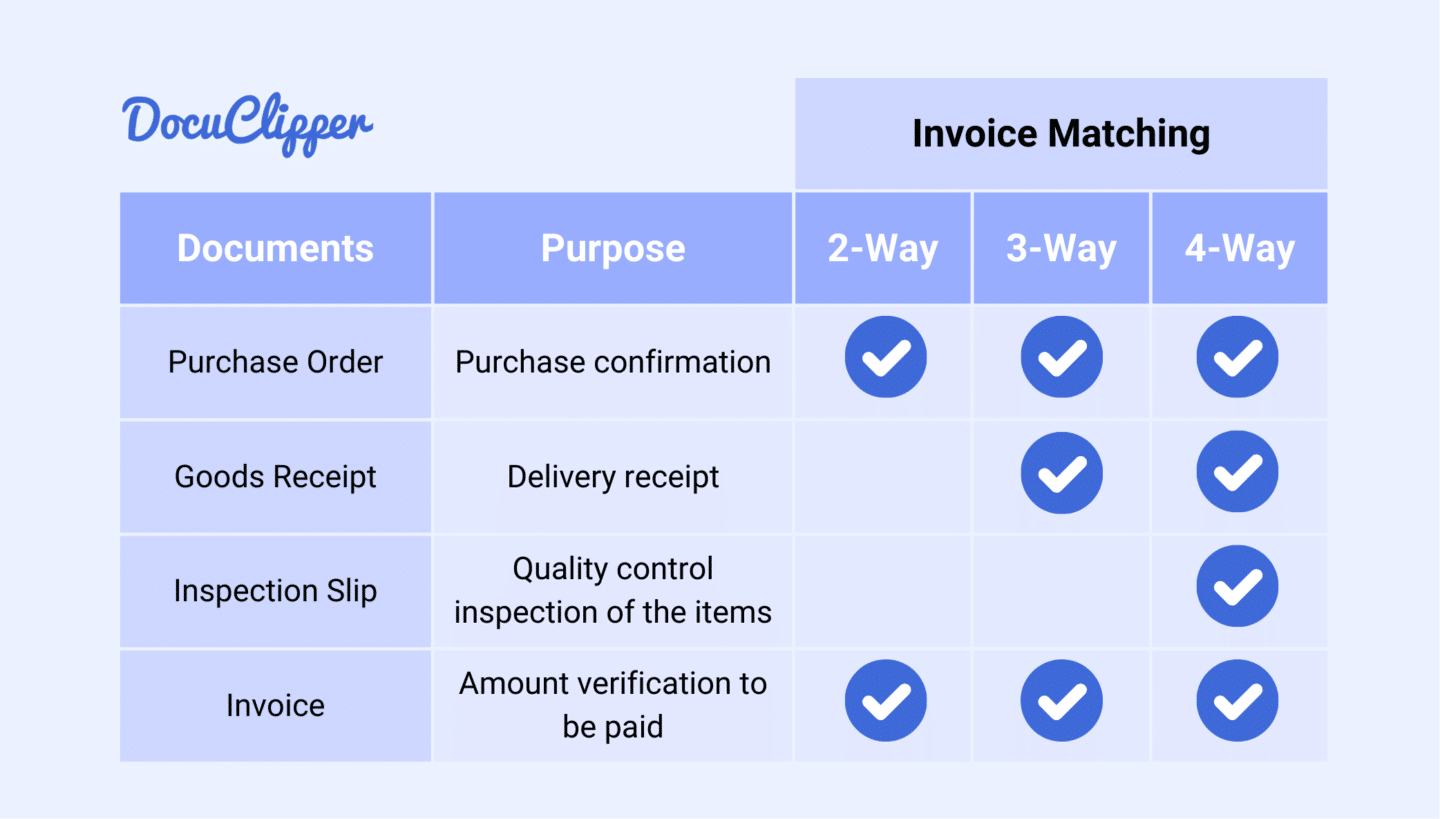
2-Way vs 3-Way vs 4-Way Matching
2-way matching is the simplest and quickest method, suitable for repetitive transactions from clients with a good relationship, with a lower risk of discrepancies. It compares the invoice to the purchase order, ensuring basic accuracy and reducing human error.
In contrast, 3-way matching adds another layer of verification by including the goods receipt note, making it ideal for transactions where confirming receipt of goods is crucial. This method significantly reduces the risk of overpayment and fraud but it takes more steps.
4-way matching takes it a step further by incorporating an inspection slip to verify both the quantity and quality of received goods, providing the highest level of accuracy and security. However, it is the most complex and time-consuming method, requiring thorough coordination and documentation.
Conclusion
Two-way matching is a vital process for ensuring accuracy and efficiency in invoice processing. By comparing purchase orders and invoices, this method helps businesses avoid costly errors such as overpayments and fraud.
The simplicity of two-way matching, coupled with its ability to streamline operations and reduce manual labor, makes it an essential tool in accounts payable management.
Whether dealing with high volumes of invoices or seeking to improve vendor relationships, implementing two-way matching can significantly enhance your financial processes and contribute to better overall business performance.
FAQs about 2-Way Matching
In this section, we’re going to answer common questions about 2-way matching:
What is the 2 way match issue?
The 2-way match issue refers to discrepancies that arise when the details on the invoice do not align with the purchase order. This can happen due to differences in quantities, pricing, or other specifications, requiring manual intervention to resolve the mismatch before payment can be approved.
Who is responsible for a 2 way match?
The buyer is typically responsible for ensuring the accuracy of the 2-way matching process. This involves verifying that the purchase order and invoice details match before approving the invoice for payment. The accounts payable department often handles this task, ensuring that only authorized payments are made.
What is the main goal for a two-way match?
The primary goal of a two-way match is to ensure that the invoice accurately reflects the goods or services ordered and received. By comparing the purchase order with the invoice, businesses can verify that they are only paying for what was actually ordered, thus preventing errors and fraud.
Why is the 2-way match considered an internal control?
Two-way matching is considered an internal control because it provides a check against unauthorized payments. By verifying that invoices match purchase orders, this process helps prevent fraudulent activities and ensures that the company’s financial transactions are accurate and legitimate.
Which document typically triggers the two-way match?
The purchase order typically triggers the two-way match. When an invoice is received, it is compared to the purchase order to ensure that the details match. Only when the invoice aligns with the purchase order is it approved for payment, thus completing the two-way matching process.