All businesses start small, even the ones that receive a large investment from donors. Small businesses are always in a fragile state and they need to keep track of business expenses or else they face disaster.
You might not have automated bookkeeping set up yet for your financial management, so this blog will talk about the most common business expense categories that every small business should track so they can effectively manage their finances.
What is a Business Expense Category?
A Business Expense Category refers to the classification of expenses incurred during the operation of a business.
These categories help in organizing financial transactions for better management, analysis, and reporting.
These categories can either be operational expenses, utilities, payroll, legal fees, and many more. The more specific a category is, the better it is for financial management as it does put information on the tracked funds and can easily be flagged or pointed out.
Simplify Your Money Management – Get Our Transaction Categorization Spreadsheet Today
What Are Tax-Deductible Business Expenses?
Tax-deductible business expenses are those costs that a business can legally deduct from its income on its tax return, thereby reducing the taxable income and the amount of tax owed.
These expenses must be both ordinary (common and accepted in the business’s industry) and necessary (helpful and appropriate for the business). Examples include rent, salaries, utilities, and office supplies, among others.
Different jurisdictions have specific rules about what constitutes a tax-deductible expense. It depends on the federal or national government and state and local governments on which types of expenses they consider tax-deductible.
Why are Business Expense Categories Important?

The importance of categorizing business expenses might be different from one business to another but here are the main reasons why they are necessary:
- Financial Analysis and Management: By categorizing expenses, businesses can more easily analyze their financial performance, identify trends, and make informed decisions.
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Categories help in creating more accurate budgets and forecasts by understanding where money is being spent.
- Tax Preparation: Proper categorization simplifies tax preparation, ensuring that businesses maximize their deductions and comply with tax laws.
- Cost Control: By identifying where expenditures are going, businesses can pinpoint areas where they can reduce costs.
Types of Business Expense Categories
Breaking down business expenses into more specific categories, particularly within Operating and Non-operating Expenses, provides a clearer view of how a business allocates its resources.
These categories can vary by industry, but the following gives a broad overview of common types within each.
Operating Expenses

Operating expenses (OPEX) are the costs required for the day-to-day maintenance and administration of a business. These expenses are essential for the core business activities and include:
- Rent or Lease Payments: Costs associated with leasing office space, retail space, or equipment necessary for business operations.
- Salaries and Wages: Payments to employees, including salaries, wages, bonuses, and commissions.
- Utilities: Essential services such as electricity, water, gas, and internet that are necessary for operations.
- Insurance: Premiums are paid for various types of insurance, including property, liability, and health insurance for employees.
- Supplies and Materials: The cost of goods or materials needed for the production of products or services.
- Advertising and Marketing: Expenses related to promoting the business, including advertising, marketing materials, and website maintenance.
- Repair and Maintenance: Costs to maintain or repair business equipment or property.
- Travel Expenses: Costs associated with business travel, including transportation, lodging, and meals.
- Professional Fees: Fees for services provided by lawyers, accountants, consultants, and other professionals.
Non-operating Expenses
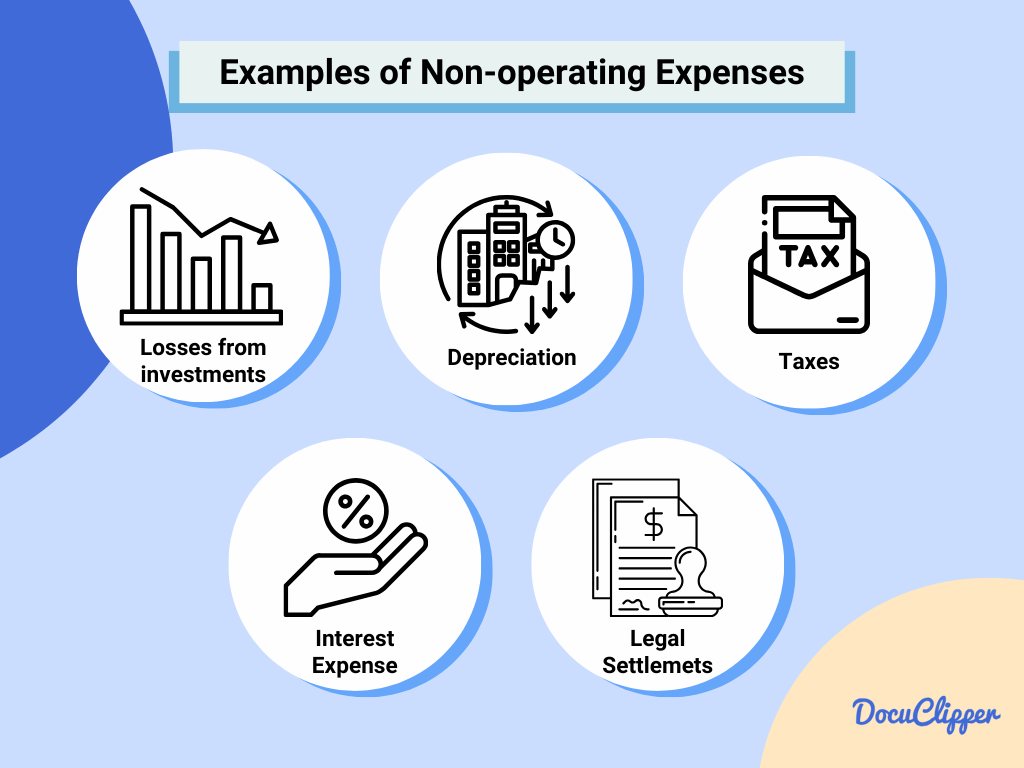
Non-operating expenses (NOPEX) are costs that are not directly tied to the primary activities of the business.
These are incurred outside the core business operations and include:
- Interest Expense: Interest paid on borrowed funds, such as loans or lines of credit.
- Depreciation and Amortization: The systematic allocation of the cost of tangible and intangible assets over their useful lives. While not a cash expense, it represents the wearing out or consumption of these assets.
- Taxes: Income taxes and other taxes not directly related to the core business activities.
- Losses from Investments: Losses incurred from investments outside the normal business operations, such as losses from the sale of assets or investments in other companies.
- Legal Settlements: Costs associated with legal disputes and settlements that are not part of the day-to-day business operations.
Understanding the difference between regular business costs and unexpected ones is key. It helps people see how well the business is doing, separates everyday expenses from unusual ones, and aids in making smart choices by focusing on the main parts of the business.
50 Business Expense Categories for Small Businesses and Startups
Here are some categories that small businesses and start-ups should keep in mind:
Advertising and Marketing
Costs for promoting your business, including online ads, print materials, and marketing campaigns. These expenses are crucial for attracting new customers and maintaining visibility in the market.
Bank Fees
Charges from financial institutions for managing your accounts, including monthly fees, overdraft charges, and transaction fees. Keeping an eye on these can help manage operating costs effectively.
Charitable Contributions
Donations made by the business to charity organizations. These contributions can sometimes be tax-deductible and also reflect positively on the company’s social responsibility efforts.
Commission and Fees
Payments made for services or to salespersons as commissions. These are often variable costs that depend on the company’s sales performance or usage of third-party services.
Computer and Internet Expenses
Costs associated with technology use, including purchasing computers, software, and internet service fees. This category is essential for maintaining the technological infrastructure of the business.
Consulting Services
Fees paid to consultants for specialized advice and services. Consulting can help in areas such as strategy, finance, marketing, and technology.
Continuing Education
Expenses related to professional development courses, workshops, and seminars. Investing in continuing education keeps skills relevant and enhances business capabilities.
Credit Card Processing Fees
Fees for accepting credit card payments from customers. These fees are a part of doing business in today’s digital and cashless society.
Depreciation
The allocation of the cost of tangible assets over their useful lives. Depreciation reflects the wear and tear on assets like buildings, equipment, and vehicles.
Dues and Subscriptions
Membership fees for professional organizations and subscriptions to industry publications. These expenses help businesses stay informed and connected in their industry.
Employee Benefits (health, retirement, etc.)
Costs for health insurance, retirement plans, and other employee benefits. Offering competitive benefits is key to attracting and retaining quality employees.
Employee Education and Training
Investments in training and development programs for employees. This category is crucial for skill enhancement and workforce productivity.
Environmental Compliance
Expenses related to adhering to environmental regulations and laws. Compliance ensures the business operates sustainably and avoids legal penalties.
Equipment Rental
Fees for renting necessary equipment instead of purchasing it. Rental can be a cost-effective option for short-term needs or to save on upfront costs.
Event Sponsorship
Costs to sponsor events, which can increase brand visibility and community engagement. Sponsorships are a strategic marketing and networking tool.
Freight and Shipping Costs
Expenses for shipping goods to customers or receiving inventory. Efficient management of these costs can significantly affect product pricing and margins.
Furniture and Fixtures
Purchases of office furniture and fixtures to create a functional work environment. These are essential for comfort and productivity in the workplace.
Gifts
Business gifts to clients, employees, or partners. These gestures can help strengthen relationships and enhance business reputation.
Health and Safety Equipment
Investments in equipment to ensure a safe workplace. This category is vital for employee well-being and to comply with safety regulations. These can be protective equipment in the construction, medical, and chemical industry.
Import Duties
Taxes on goods brought into the country. Understanding and managing these costs is important for businesses involved in international trade.
Insurance (liability, property, health)
Premiums for liability, property, and health insurance. Insurance protects the business from various risks and potential financial losses.
Interest Expense
Interest paid on business loans or lines of credit. Managing debt wisely is crucial for financial health and sustainability.
Inventory Purchases
Costs for buying inventory that the business will sell. Effective inventory management can improve cash flow and profitability.
Legal and Professional Fees
Fees for services provided by lawyers, accountants, and other professionals. These services are essential for compliance, financial management, and legal advice.
License and Permit Fees
Costs for necessary business licenses and permits. Staying compliant with local, state, and federal regulations is essential for legal operation.
Maintenance and Repairs
Expenses for keeping equipment and property in good condition. Regular maintenance prevents larger expenses down the line.
Meals and Entertainment
Business-related dining and entertainment expenses. While offering networking opportunities, careful tracking is necessary for tax purposes.
Office Decor
Costs to enhance the appearance and atmosphere of the office. A well-designed office can improve employee morale and impress clients.
Office Supplies and Expenses
Purchases of supplies needed for daily operations, such as stationery and cleaning products. Keeping these costs in check is essential for budget management.
Packaging and Containers
Costs for materials needed to package products for sale. Effective packaging can enhance product appeal and protect items during shipping.
Payroll Expenses
Payroll expenses encompass the total amount spent on employee compensation, including salaries, wages, bonuses, and taxes withheld. This category is critical for managing the largest cost for many businesses and ensuring compliance with tax and labor laws.
Petty Cash
Petty cash refers to a small amount of cash on hand used for covering minor expenses, such as office supplies or small repairs. Keeping track of petty cash helps maintain accurate financial records and prevents misuse of funds.
Postage and Delivery
This category covers the costs associated with mailing and delivering goods, including postage, courier, and freight charges. Effective management of these expenses can lead to significant savings, especially for businesses that rely heavily on shipping.
Printing and Reproduction
Expenses for printing and reproducing documents, marketing materials, and other business needs fall into this category. It’s essential for businesses to monitor these costs to avoid unnecessary expenditure on printing services.
Professional Memberships
Fees paid for memberships in professional organizations or industry associations are categorized here. These memberships can provide networking opportunities, industry insights, and access to professional development resources.
Rent on Business Property
This includes lease payments for office space, retail locations, warehouses, or any other property used for business operations. Rent is a significant fixed expense for many businesses, making it crucial to negotiate favorable terms.
Research and Development
R&D expenses cover the costs associated with developing new products or services, including materials, labor, and testing. Investing in research and development can be essential for innovation and staying competitive in the market.
Salaries and Wages
Payments to employees for their services, including salaries for salaried employees and wages for hourly workers, are recorded here. Fair and competitive compensation is vital for attracting and retaining talent.
Software Subscriptions
This category includes the costs for software licenses and subscriptions necessary for business operations, such as accounting software, project management tools, and industry-specific applications.
Taxes (payroll, sales, property)
Businesses incur various taxes, including payroll, sales, and property taxes. Proper management and understanding of tax obligations are crucial for avoiding penalties and optimizing tax positions.
Telephone and Communication Expenses
Costs for business communication, including landline, mobile phone services, and internet connectivity, are accounted for in this category. Efficient communication tools are essential for operations, customer service, and collaboration.
Tools and Equipment
Expenses for purchasing or maintaining tools and equipment necessary for business operations are included here. Regular maintenance and timely upgrades can prevent costly downtimes.
Training and Staff Development
Investments in employee training and development programs to enhance skills and knowledge are captured in this category. Continuous learning opportunities can improve team performance and job satisfaction.
Travel Expenses
This covers all costs related to business travel, such as flights, hotels, car rentals, and meals. Monitoring travel expenses closely can help businesses control costs while still supporting necessary travel.
Utilities (electricity, water, gas)
Utility expenses include payments for electricity, water, gas, and other essential services. Efficient utility usage and cost management can contribute to reducing operational expenses.
Vehicle Expenses
Costs associated with business vehicles, including purchase, lease, maintenance, and fuel, are categorized under vehicle expenses. Effective management of vehicle expenses can lead to significant savings, especially for businesses that rely on transportation.
Warranties and Service Contracts
This category encompasses the costs for warranties and service contracts for equipment, machinery, or technology. These contracts can protect against unexpected repair costs and ensure equipment reliability.
Waste Removal
Expenses for trash collection and disposal services required for business operations are included here. Proper waste management is not only essential for compliance with regulations but also reflects a business’s commitment to sustainability.
Web Hosting and Domain Fees
Costs for maintaining a business’s online presence, including website hosting and domain name registration, are captured in this category. A reliable and accessible website is crucial for marketing, sales, and customer engagement.
Workwear and Uniforms
This includes expenses for purchasing and maintaining workwear or uniforms required for employees. Uniforms can enhance professionalism and brand identity, making them a worthwhile investment for many businesses.

How Many of These Categories Do I Need?
The number of expense categories you need depends on your specific business requirements. Not every category will fit your operations, as the common categories vary widely across industries.
Choose only business expense categories relevant to your financial tracking needs.
The industry also determines what type of expenses you have to sort out. You won’t need any freight expenses if you are in finance tech. Specify and eliminate the unnecessary categories as these create confusion.
It’s recommended that you get accounting help to correctly identify what business expense categories you should be tracking.
How to Categorize Business Expenses
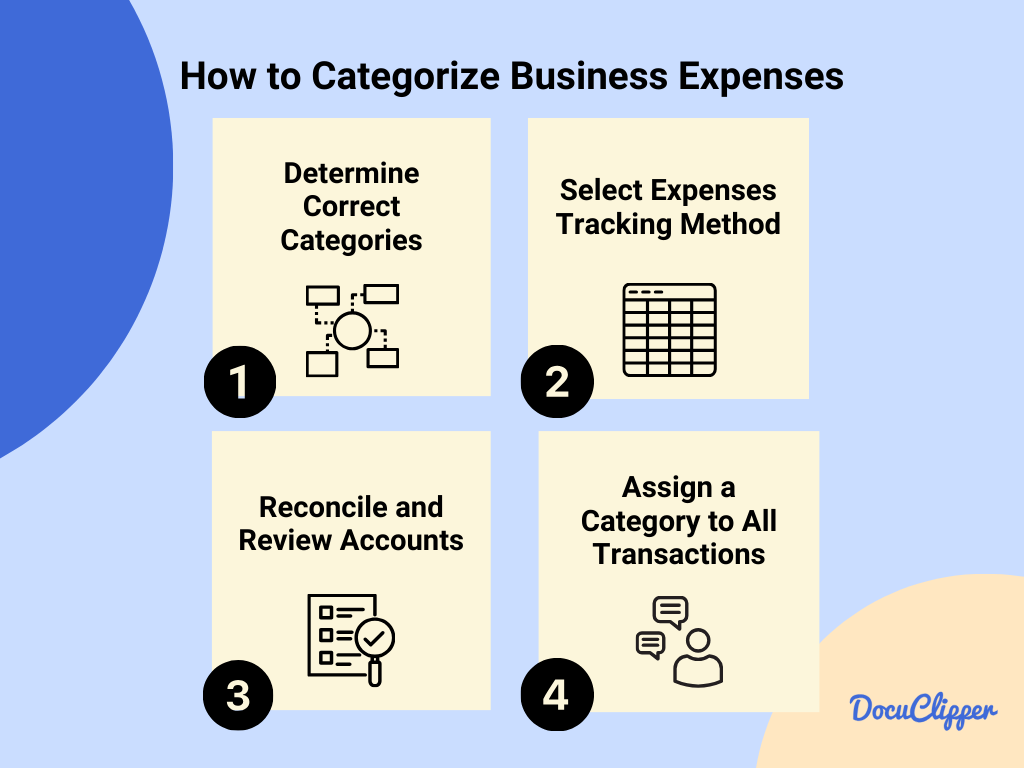
Here are some steps on how to categorize business expenses:
- Determine Correct Categories for Your Specific Business: Begin by identifying the categories that reflect your business activities. This might include direct costs, like inventory purchases, and indirect costs, such as marketing and utilities.
- Select Business Expense Tracking Method: Choose how you’ll track these expenses. Options range from manual entry in spreadsheets to using sophisticated accounting software that automates much of the process.
- Reconcile and Review Your Financial Accounts on Schedule Basis: Regularly, perhaps monthly or quarterly, review your accounts to ensure that all transactions are recorded correctly and reconcile any discrepancies.
- Assign a Category to All Transactions: As you are conducting a transaction categorization, assign each to its appropriate field. This practice helps in generating more meaningful financial reports.
How to Categorize Bank Transactions from PDF Statements
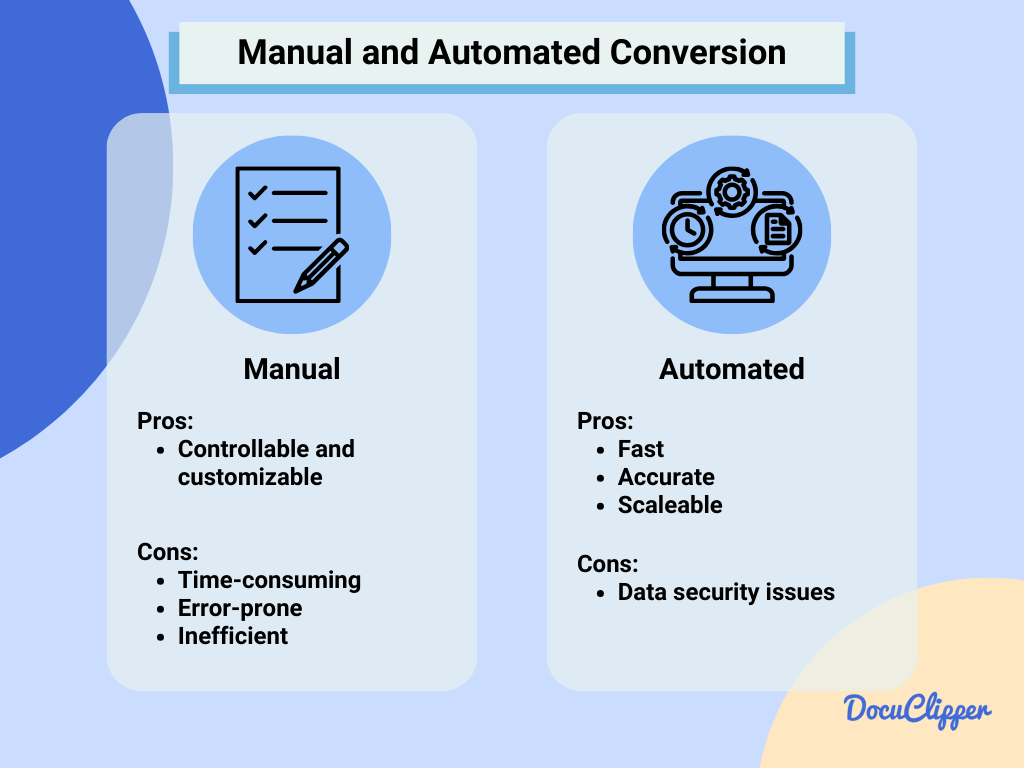
In some instances, bank feeds, or downloading bank transactions to CSV sheet is not available and you’ll need to extract bank transactions from PDF bank or credit card statements.
In this case, you will need to enter your bank transactions into a spreadsheet and then upload them to your accounting, expense tracking software or where you track your expenses.
And there are two ways to enter your bank transactions from PDF statements:
- Manual: Very tedious, prone to errors, time-consuming, and only good if you have very few transactions. Some businesses categorize bank transactions and expenses in Excel as they are manually inputting data, making it double the work.
- Automatic: Processing bank statements using a bank statement converter such as DocuClipper will get you all your bank transactions in spreadsheets in seconds. This method is the best if you do this regularly and have many bank transactions on your bank/credit card statement.
Once you have your spreadsheet then you can upload your bank transactions to wherever you tracking your expenses and continue the process as normal. If you think reading bank statements is a little complicated for you and have it piling up, check these articles:
How to Keep Track of Business Expenses
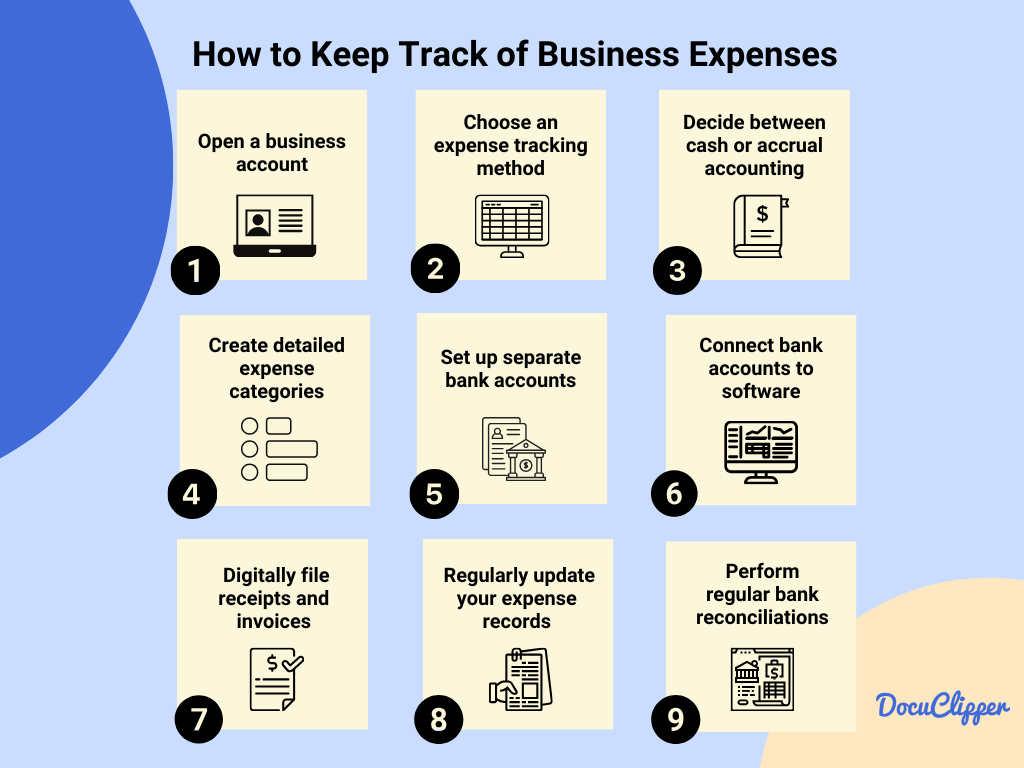
Here is a simple way how to keep track your business expenses as you are running a small business or a start-up:
1. Open a business account that fits your needs like savings or checking. This helps manage money better and offers monthly statements for tracking.
2. Choose an expense tracking method that works for you, from simple spreadsheets to advanced accounting software. It’s all about finding the right tool to keep track of spending.
3. Decide between cash or accrual accounting. Cash is simpler, recording expenses when paid. Accrual gives a fuller picture, recording expenses when incurred, which is great for bigger businesses.
4. Create detailed expense categories to see where the money goes. This helps in understanding your spending better and managing finances effectively.
5. Set up separate bank accounts for different business needs to avoid confusion and get a clear picture of your finances.
6. Connect bank accounts to software or convert PDF credit cards or bank statements for easier expense tracking. Tools like DocuClipper can help with converting statements into useful formats.
Here are some articles where you can use OCR to convert PDF statements into CSV, XLS, and QBO or through your bank feeds:
7. Digitally file receipts and invoices to keep a good record for taxes and financial analysis. Converting documents to digital format can save time and reduce errors.
8. Regularly update your expense records to keep your financial information current. Whether it’s automatic updates or manual entry, staying on top of this is key.
9. Perform regular bank reconciliations and audits to ensure your financial records are accurate and to catch any issues early. This keeps your business’s financial health in good shape and makes tax time easier.
Conclusion
As you are starting your business no matter how small, tracking your expenses is a significant task to stay afloat and to be aware of the status of your venture.
Being aware of the expense categories you have allows you to focus on where you have losses and in which part of your business can still improve.
How DocuClipper Can Help?
Doing things manually can be problematic in terms of time and money. It is also prone to mistakes and might give you wrong insights into the financial status of your business.
DocuClipper is an OCR bank statement converter that streamlines the process of managing business finances by efficiently converting PDF bank and credit card statements into actionable data.
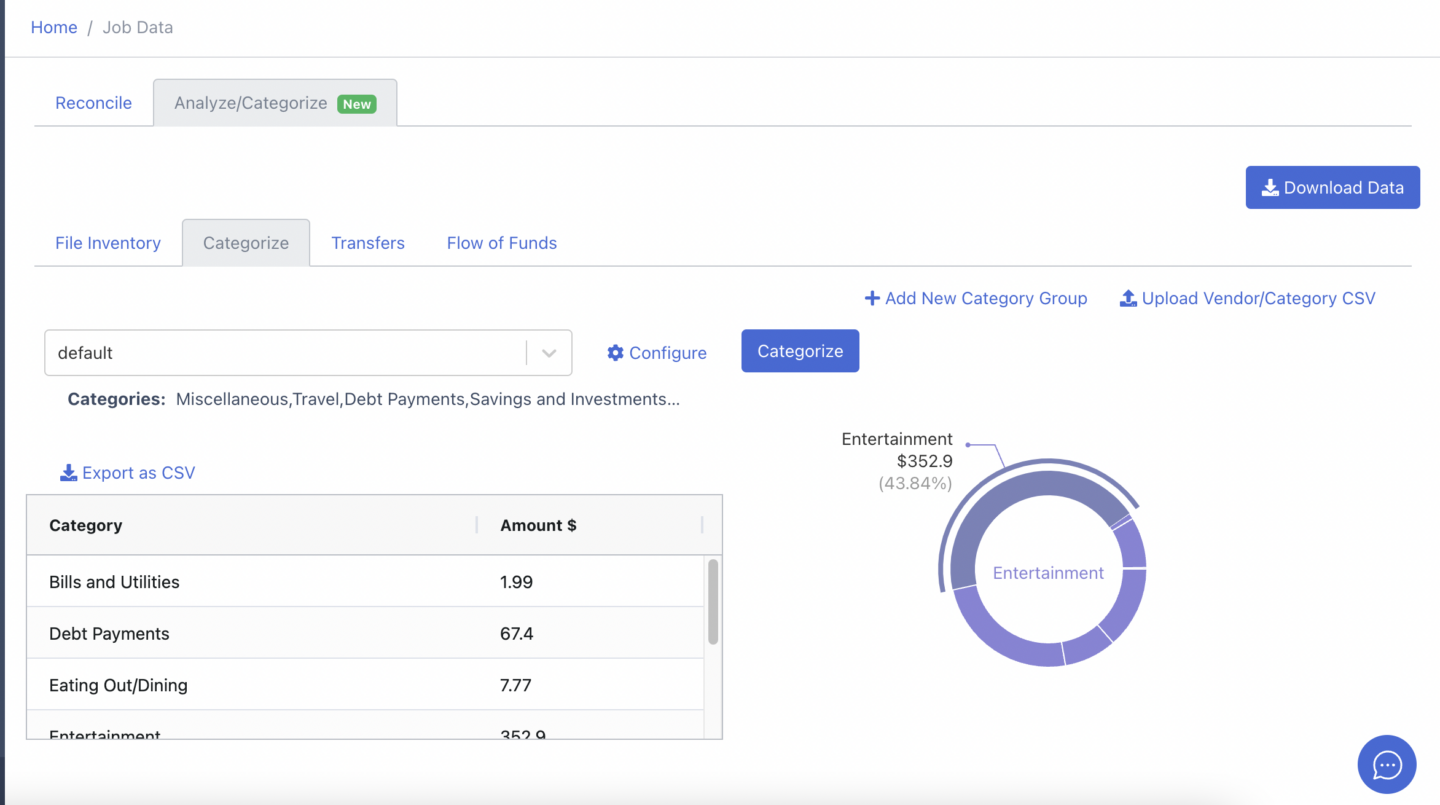
It not only automates the categorization of bank transactions but also offers flexibility in creating custom categories to meet specific needs, whether for personal use or client management. This tool is a valuable asset for anyone looking to simplify the financial tracking and analysis process
FAQs about Business Expense Categories
Here are some frequently asked questions about making business expense categories:
What is classified as a business expense?
A business expense is any cost incurred in the operation of a business. This includes rent, salaries, office supplies, and any other costs necessary for the business to function and generate revenue.
How do you organize expense categories?
Expense categories can be organized by grouping similar expenses together. Common methods include categorizing expenses by function (e.g., marketing, operations), nature (e.g., fixed, variable), or according to tax deduction categories.
How do you group business expenses?
Grouping business expenses involves creating categories that reflect how your business operates. For example, all costs related to producing goods might go under “Cost of Goods Sold,” while office-related expenses could be grouped under “Office Expenses.”
How do I organize my business expenses?
Start by identifying every type of expense your business incurs and categorize these expenses into logical groups that reflect how your business operates. Finally, utilize accounting or expense tracking software to consistently record and oversee these expenses.
What are the 4 types of expenses in accounting?
In accounting, expenses are typically categorized into four types: fixed, variable, accrued, and operational. Each type has its characteristics and ways of being managed within the financial records of a business.
What is miscellaneous expenses?
Miscellaneous expenses refer to costs that don’t neatly fit into any specific category of business spending. They are often infrequent or minor expenses that are not part of the regular business operations, such as one-off repairs or small office needs.