Businesses nowadays handle millions of transactions daily. Yet, the invoicing process for many businesses still needs to be updated, probably your business also relies on printed or PDF invoices that require manual verification and data entry.
This method of processing invoices consumes a lot of time and is prone to errors, especially during the pre-accounting phase when data is manually entered. These inefficiencies can affect business operations and be frustrating for both businesses and customers.
Fortunately, e-invoicing is changing the game. By digitizing your invoicing process, you can make it more accurate, efficient, and less costly.
This makes your accounts payable system much faster for payments, improved efficiency, better financial data accuracy, and happier customers.
In this article, I’ll walk you through what e-invoicing is, how it works, and why it’s quickly becoming a must-have for businesses aiming to stay competitive in today’s dynamic marketplace.
What is E-Invoice?
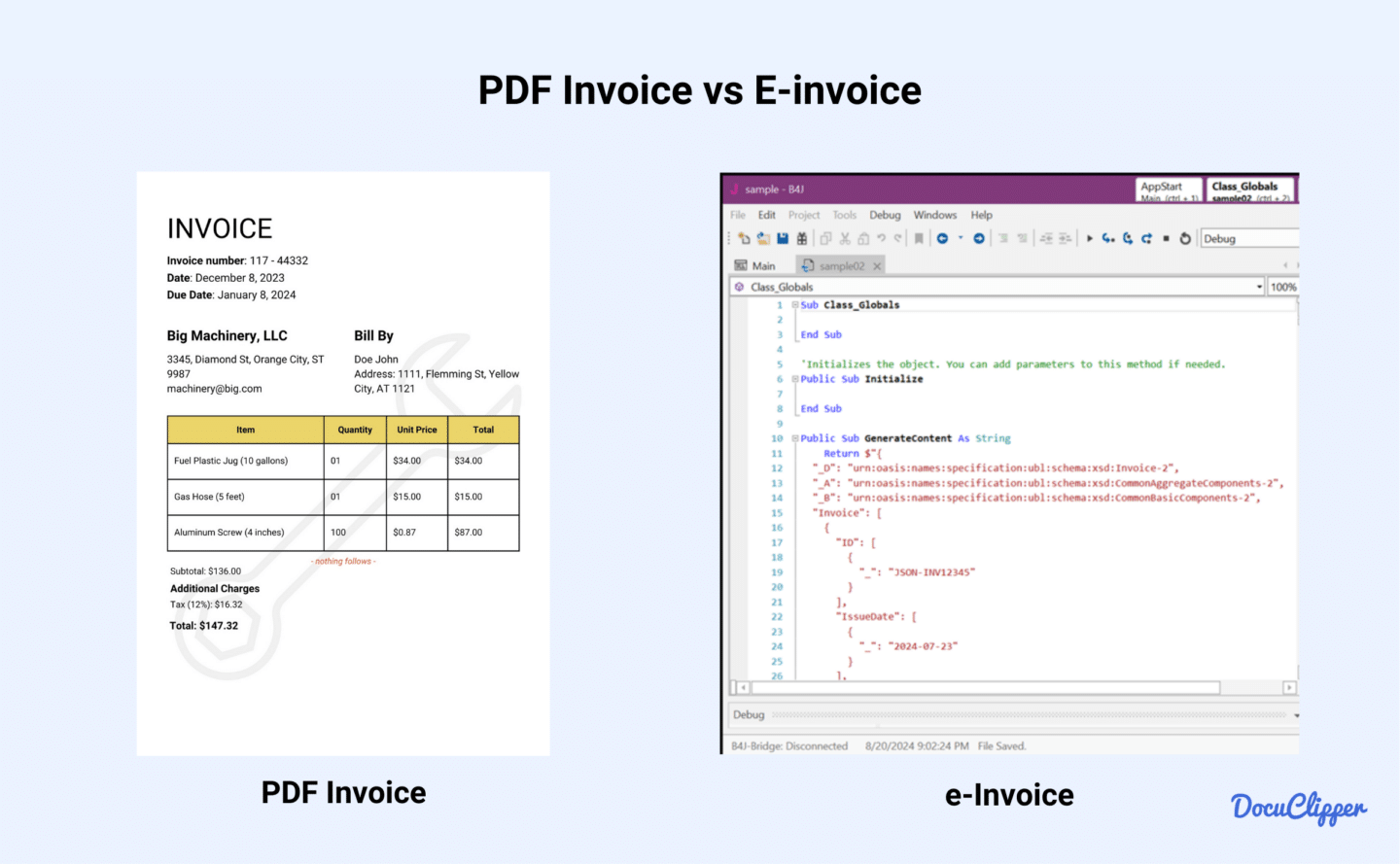
An e-invoice, short for electronic invoice, is a digitally formatted billing document exchanged between a buyer and seller.
Unlike traditional invoices, e-invoices are created, sent, and processed using a structured electronic format, such as XML. This allows software to communicate between systems, allowing data to be shared and processed automatically without manual intervention.
E-invoices include all the details of a traditional invoice, such as supplier information, invoice number, payment terms, and tax details, but in a standardized format designed for automated workflows.
This makes it more accurate, fast, and compatible across different accounting or ERP systems.
E-invoicing is becoming prevalent as many governments mandate its use to enhance tax compliance and reduce fraud.
What E-Invoice is Not
An e-invoice is not a simple PDF invoice as it is usually confused because PDFs are “electronic” in layman’s terms.
Unlike PDFs, which are static and require manual invoice processing, e-invoices use a structured data format (e.g., XML) designed for automated invoice processing.
While PDFs are human-readable documents, e-invoices are coded for them to be read easily by accounting systems, eliminating manual entry and reducing errors.
Benefits of E-Invoicing
Here are some of the reasons why you should consider putting your business on the e-invoicing track:
- Speeds up payments: You can send e-invoices instantly, avoiding postal delays and reducing your invoice processing time. Since they integrate directly into accounting systems, there’s no need for manual data entry, which significantly accelerates your invoice approval workflow and payment cycles.
- Reduces processing costs: By eliminating PDF invoices from your workflow, you can reduce your dependence on data entry workers typing the information for you. Automation also reduces the need for additional staff to manually verify and input data, saving time and resources.
- Minimizes errors: E-invoices, often coded in formats like XML, are auto-generated and populated directly from the software, eliminating manual errors during both the pre-accounting and post-accounting stages.
- Enhances account invoice reconciliation: E-invoicing syncs directly with your ERP systems, checking the invoice without any extra layer. This real-time integration eliminates bottlenecks and makes it smoother for your AP team.
- Adds fraud protection: Features like digital seals and audit trails safeguard your invoice authenticity. It makes this tamper-proof and makes it easy for you to possibly track who attempted.
- Simplifies compliance: This allows your invoices to be formatted to what your national or local government requires. It is also easier to store and reserve for audits.
- Strengthens business relationships: Real-time tracking of invoices improves transparency between your buyers and suppliers. Faster approvals and reduced disputes build trust, encouraging stronger, more collaborative partnerships for your business.
E-Invoicing vs Traditional Invoicing
When comparing e-invoicing to traditional invoicing, you’ll notice significant differences in how each handles the billing process.
In e-invoicing, invoices are delivered instantly and integrate directly with your accounting systems without passing through any extra layer like an employee.
When you are doing it in the traditional way, you have to rely on manual creation and mailing, which slows down the entire billing cycle.
Traditional invoicing can also lead to more errors since depending on someone’s typing are windows to mistakes and they could potentially tamper vital information.
E-invoicing, on the other hand, offers safeguards like digital seals and encryption to prevent fraud and tampering.
Additionally, you’ll find that digital storage simplifies everything during audits, unlike paper invoices, which take up physical space and risk damage.
Regulations and Compliance for E-Invoicing
E-invoicing regulations are still in their early stages, but governments worldwide are gradually establishing standards to encourage adoption.
These regulations often define specific formats and requirements for different business sectors, including B2G (business-to-government), B2C, and B2B transactions.
Here’s how countries are approaching compliance and regulation:
United States
In the United States, you are not required to comply with e-invoicing for B2B or B2C transactions at the federal level. However, there are efforts to encourage its adoption in B2G interactions and you will have to adjust.
Federal initiatives, such as the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) Memorandum 15-19, required all federal agencies to transition to e-invoicing for procurement by 2018. This is something you need to keep in mind when you are doing transactions with a federal agency.
You might also see e-invoicing getting used much often through efforts like the Business Payments Coalition (BPC) and the Federal Reserve’s e-Invoice Exchange Market Pilot, launched in 2021. This pilot aims to create a standardized e-invoicing network across the U.S.
On a state level, if you have a business in California, you have to comply with its 2018 mandate requiring state contractors to submit e-invoices through the Cal eProcure platform.
Canada
If your business is in Canada, e-invoicing is legal but not mandatory. However, since 2018, public body providers have been required to accept e-invoices.
Canada has standardized the use of the UBL format for e-invoicing making it a must for making e-invoices.
As a business, you’re also obligated to retain electronic invoices for at least six years.
United Kingdom
In the UK, e-invoicing is not mandatory except for transactions involving public entities like the National Health Service (NHS).
The 2015 Small Business, Enterprise, and Employment Act grants ministers the authority to regulate e-invoicing for public procurement in England, though Northern Ireland, Scotland, and Wales have their own rules.
If you’re considering e-invoicing for B2B transactions, you need to follow HMRC standards. Customers must agree to receive e-invoices, and you need to ensure these documents are authentic, intact, and readable.
To comply, you can use certified electronic signatures, EDI systems, or business controls that maintain a clear audit trail for your invoices.
Australia
In Australia, the Australian Taxation Office (ATO) oversees e-invoicing as the Peppol Authority, setting standards and managing invoice specifications.
Since July 2022, all Commonwealth agencies have been required to adopt Peppol e-invoicing for B2G transactions, marking a significant step toward digital transformation in public procurement.
For B2B transactions, e-invoicing remains voluntary, but the government has proposed a phased implementation. From July 2023, large companies must support Peppol e-invoicing upon request, followed by medium-sized businesses in July 2024.
Public entities are also mandated to accept e-invoices if a supplier opts to send them, ensuring broader compatibility and adoption.
The Rest of the World
When you are operating in the rest of the world, here is some extra information:
- Europe: If you operate in Europe, Directive 2014/55/EU requires all EU member states to adopt e-invoicing for public procurement.
- In Italy, e-invoicing is mandatory for all B2B and B2G transactions, managed through the Sistema di Interscambio (SDI).
- France and Germany are also advancing e-invoicing adoption with their national standards, such as XRechnung in Germany.
If your business deals with cross-border transactions, you’ll benefit from the widespread adoption of PEPPOL, this allows you to easily access the information within the EU.
- Latin America: In Latin America, e-invoicing is a well-established practice to improve compliance and reduce tax evasion.
- If you are in Mexico, you’ll use the CFDI system for invoicing. In Brazil, businesses rely on the Nota Fiscal Eletrônica (NF-e) for real-time reporting to tax authorities.
Chile has taken a comprehensive approach by mandating e-invoicing nationwide.
- Middle East: In the Middle East, e-invoicing is gaining momentum to enhance tax compliance. If you’re in Saudi Arabia, you’ll need to comply with the FATOORAH system, which mandates real-time reporting for all businesses.
- In the UAE, you will have to prepare because mandatory e-invoicing is set to roll out by 2026. This initiative aims to simplify both B2B and B2G transactions, making financial processes more efficient and aligned with global standards.
How to Get Started with E-Invoicing
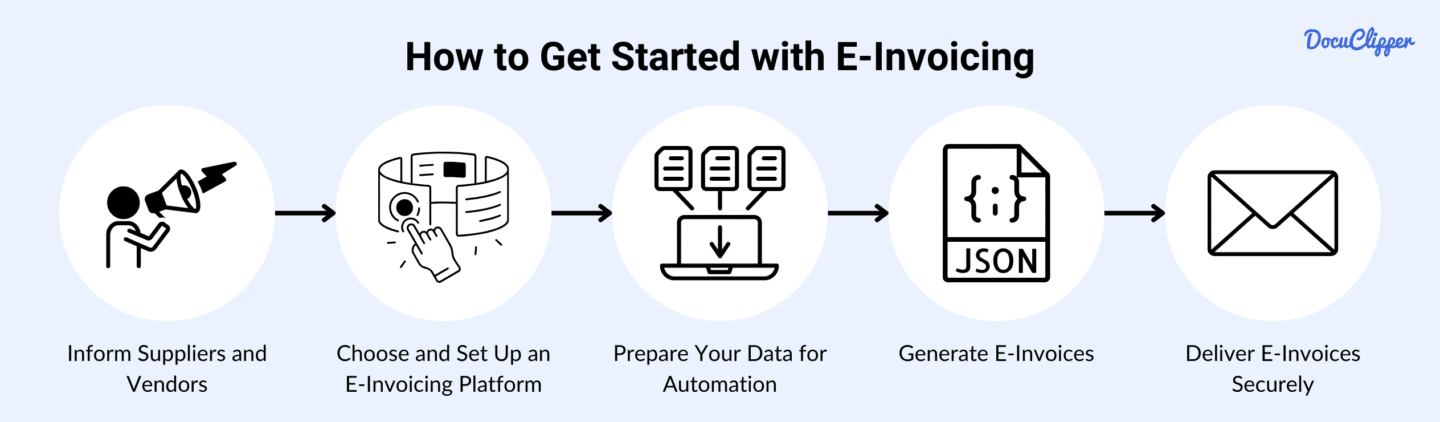
Here are the steps when you are planning to transition from traditional invoicing to e-invoicing.
- Inform Suppliers and Vendors: Begin by reaching out to your business partners on your e-invoicing transition. Verify their contact details and prepare them to be compatible with your invoicing system.
- Choose and Set Up an E-Invoicing Platform: Select an e-invoicing platform that aligns with your business needs and complies with your country’s regulatory requirements.
- Prepare Your Data for Automation: Clean and standardize your existing invoicing data to ensure it integrates smoothly with the e-invoicing system.
- Generate E-Invoices: Use your platform to create e-invoices in the required format, such as XML or UBL.
- Deliver E-Invoices Securely: Send invoices through the agreed-upon method, whether via email, a secure portal, or direct integration with your clients’ systems.
Automate Invoice Processing with DocuClipper
E-invoicing is still in its early stages and has not yet been universally adopted. Many businesses rely on PDF or paper invoices, as government mandates for e-invoicing are limited.
This challenge when processing invoices requires manual invoice data entry into spreadsheets or ERP systems which is very costly and takes time.
Fortunately, tools like DocuClipper provide a solution. DocuClipper is an OCR-based invoice converter that transforms PDF invoices into manageable formats like as XLS, CSV, and QBO.
It’s highly scalable and capable of processing hundreds of invoices in seconds at top accuracy. These converted files can then be seamlessly imported into your ERP or accounting software, saving time, improving invoice accuracy, and streamlining your workflow.
FAQs about E-Invoicing
Here are some frequently asked questions about e-invoicing:
Is e-invoicing mandatory in the US?
E-invoicing is not mandatory in the United States for B2B or B2C transactions. However, it is required for certain B2G transactions, as federal agencies must use e-invoicing for procurement. While not widely enforced, initiatives like the e-Invoice Exchange Market Pilot aim to encourage broader adoption across businesses.
What is the rule for e-invoicing?
The rules for e-invoicing vary by country and sector. Generally, e-invoicing must follow government-defined standards, such as specific formats like XML or UBL, to ensure compatibility and compliance. Businesses may also need to maintain invoice integrity, authenticity, and readability for regulatory and audit purposes.
Who needs to file an e-invoice?
The requirement to file an e-invoice depends on local regulations. Typically, businesses dealing with government entities (B2G) or operating in countries with e-invoicing mandates, like Italy or Brazil, must file e-invoices. Some regions also extend this requirement to large corporations or specific industries.
When to start e-invoicing?
The right time to start e-invoicing depends on your region’s regulations and business needs. Begin if your country mandates e-invoicing, your trading partners request it, or you want to improve efficiency. Early adoption helps streamline processes and ensures compliance with evolving global standards.
What is the downside to electronic billing?
The downside to electronic billing includes potential cybersecurity risks, as sensitive data could be targeted by hackers. Initial setup costs for e-invoicing software and integration may also be high. Additionally, businesses with incompatible systems or partners unwilling to adopt e-invoicing may face implementation challenges.
What happens if an e-invoice is not made?
If an e-invoice is not made where it is legally required, businesses may face penalties, fines, or compliance issues. Missing e-invoices can delay payments, disrupt operations, and lead to complications during audits or tax assessments, potentially harming the company’s financial and regulatory standing.
Are emailed invoices legal?
Emailed invoices are generally legal but may not meet the standards of e-invoicing. While they are acceptable for record-keeping and payment purposes, true e-invoices require a structured format (e.g., XML) for automated processing and regulatory compliance in certain regions. Always verify local requirements.