Not all invoices are created equal Whether they’re traditional paper invoices or e-invoices as there are many types of invoices and they vary in design and format based on legal requirements and vendor preferences.
However, reading them is straightforward, and identifying key information is easier than you might think.
In this article, we’ll guide you through how to read an invoice, emphasize the important parts to look for, and explain how to use this information effectively in your accounting process.
Understanding these elements will help you manage your finances more efficiently and ensure accurate record-keeping.
It can also help you make an efficient way to extract data from invoices and process them efficiently.
1. Invoice Header
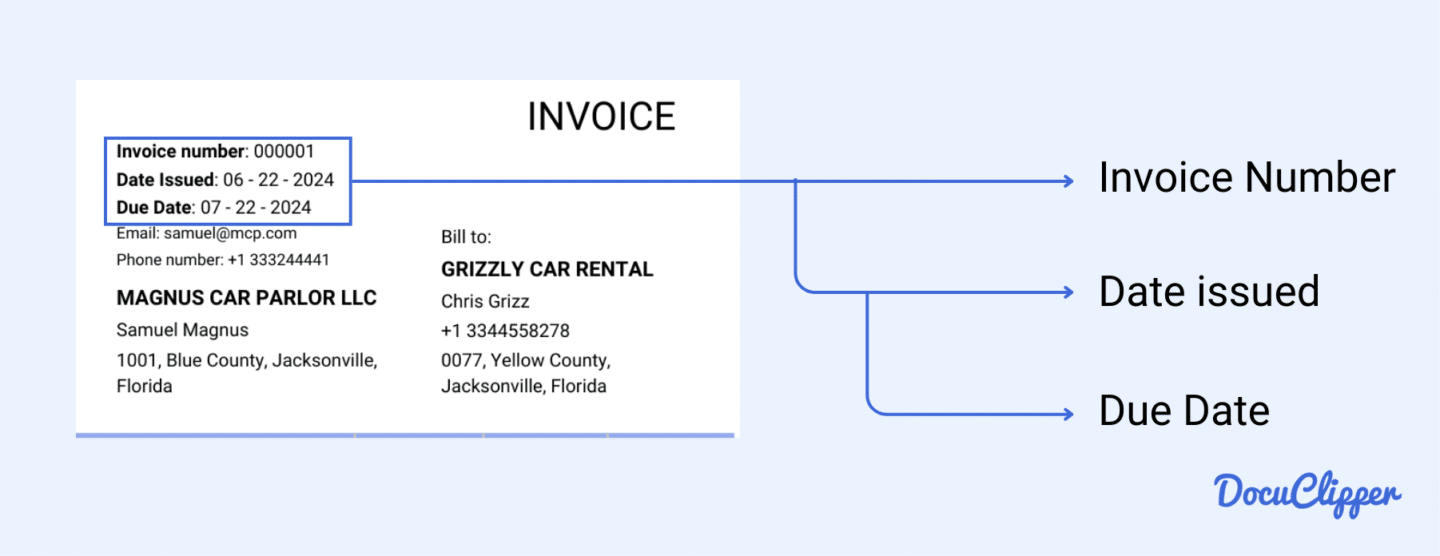
The invoice header contains all the basic and essential information, making it the most crucial part of the invoice. This section tracks the invoice’s unique classification and important dates.
- Invoice Title: Clearly labeled as “Invoice,” so you know it’s a request for payment.
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the invoice. No two invoices should share the same number. Vendors or suppliers use this number to track all their issued invoices.
- Invoice Date: The date when the invoice is issued, indicating when the purchase was made or the supply was delivered.
- Due Date: The date by which payment should be made. Late payments can incur serious penalties, depending on your agreement with the vendor or supplier, and may strain your business relationship.
2. Seller’s Information
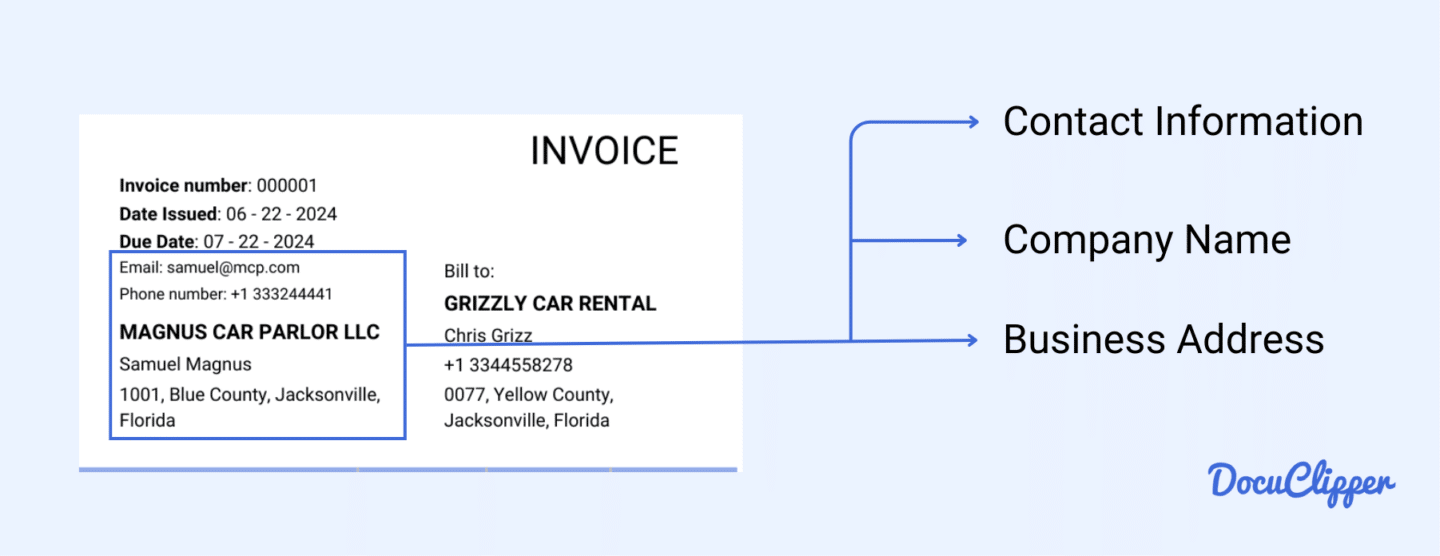
In this section, you’ll find all the information related to the seller. It’s crucial to have contact details in case you need to verify any information or resolve issues.
- Company Name: The name of the company or individual issuing the invoice. This helps you identify who the invoice is from.
- Address: The full address of the seller, usually the business office location. Knowing the address is important for records and potential correspondence.
- Contact Details: This includes the phone number, email, and website (if applicable). These details are essential for reaching out to the seller with any questions or clarifications regarding the invoice.
3. Buyer’s Information
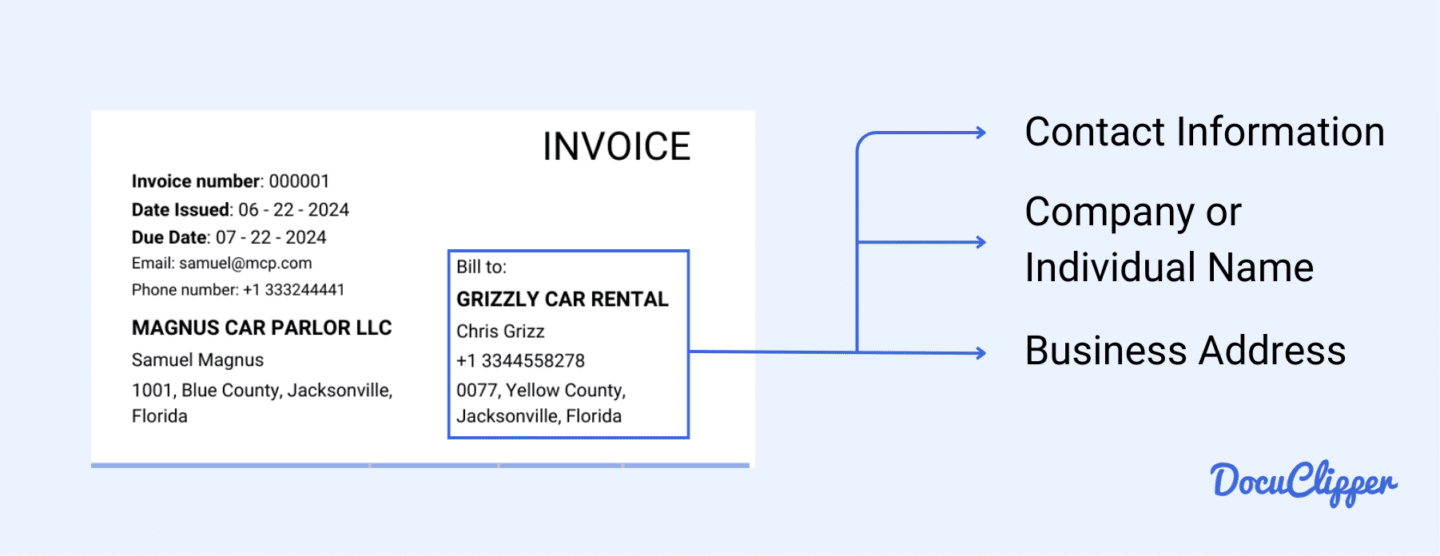
This section contains all the information about the buyer, mirroring the details provided for the seller.
- Company/Individual Name: The name of the company or individual being billed. This helps identify who is responsible for the payment.
- Address: The full address of the buyer, whether it’s the business address or the residential address for personal transactions. This information is essential for accurate record-keeping and potential correspondence.
- Contact Details: The buyer’s phone number and email are included. This allows the seller to contact you if they need to clarify anything regarding the purchase.
4. Line Items
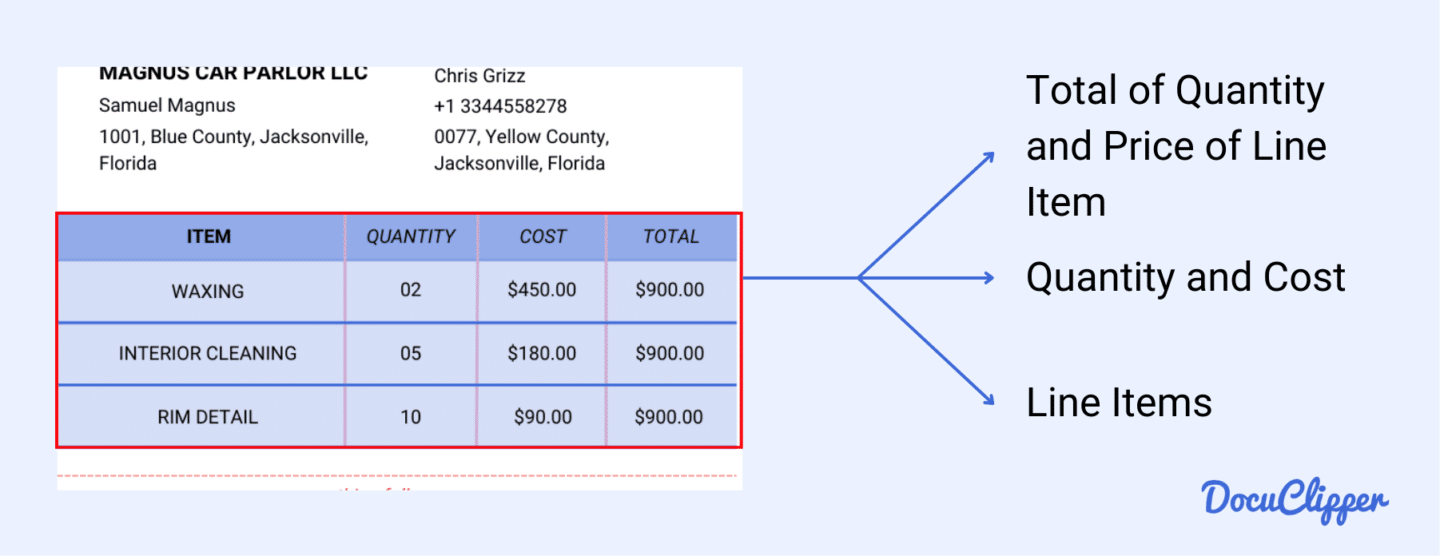
This section provides detailed information about the items or services being purchased. Disputes often arise here over price, quantity, and calculations and it’s the most important part of your invoice reconciliation.
This is also where invoice data extraction software gathers the most important data.
- Description of Products or Services Provided: This is where the seller lists the types of items or services they provided. Descriptions can range from detailed to general, giving you a clear understanding of what you’re being billed for.
- Quantity: The number of items being purchased is noted here. For services, it might indicate the number of hours or sessions committed.
- Unit Price: This lists the cost per unit, hour, or session, helping you understand the rate being charged.
- Total Amount per Item: This is the untaxed total of the quantity multiplied by the unit price, showing the cost for each line item.
5. Amounts & Total
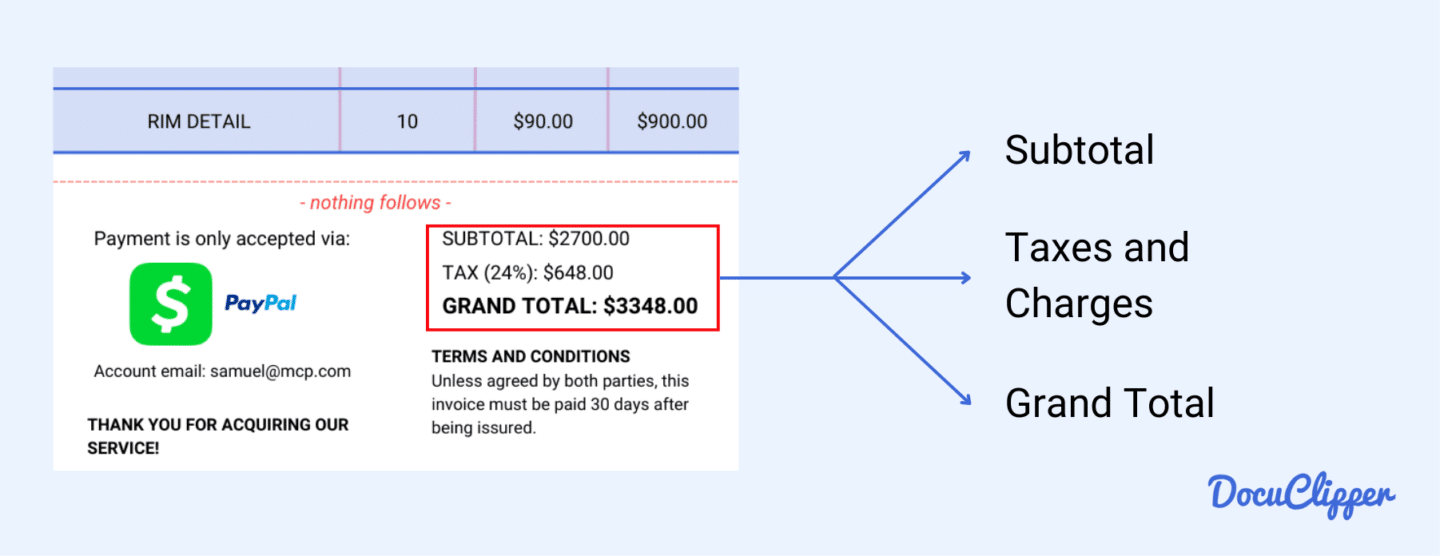
This section provides a collective summary of all the line items and the total amount you’ll need to pay.
- Subtotal: This is the total cost of all items or services before any taxes or additional fees are applied. It gives you a clear view of the base amount being charged.
- Taxes and Other Fees: Taxes vary by country or state and are added to the subtotal. Additional fees might include delivery charges or special services. Knowing these fees helps you understand the extra costs involved.
- Grand Total: This is the final amount you owe, including the subtotal and all applicable taxes and fees. Some sellers may also include extra charges for deliveries or special services, so it’s important to review this section carefully.
6. Payment Terms
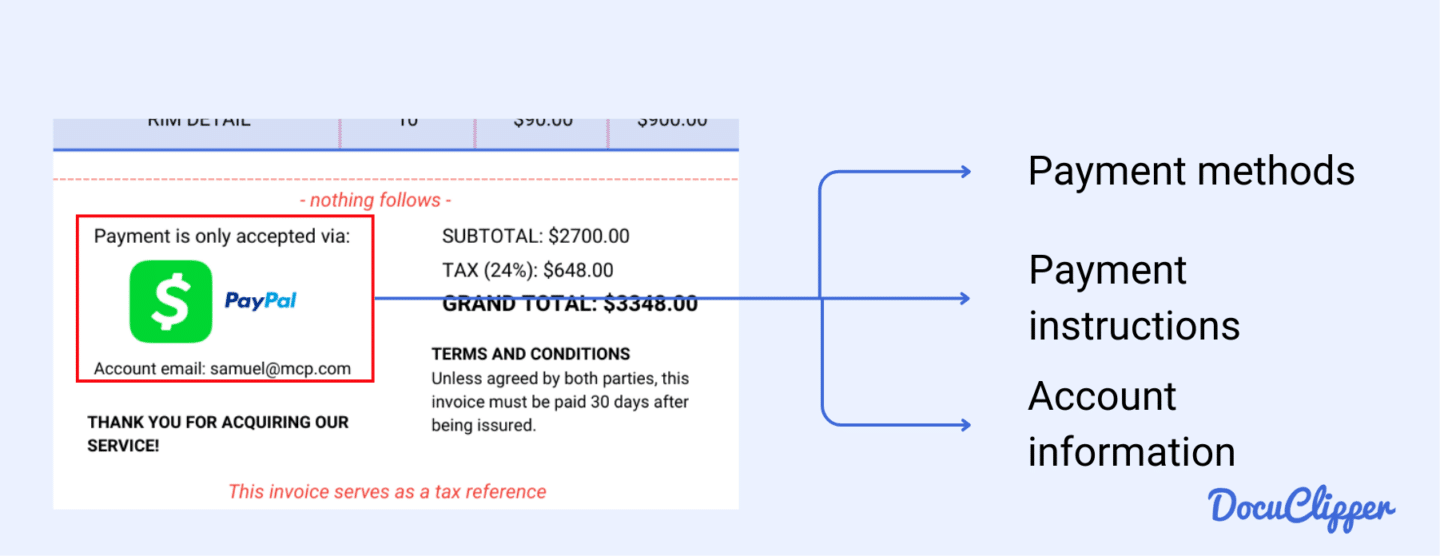
This section outlines the payment instructions, which can vary in detail depending on the seller’s preferences.
- Payment Methods: This lists the accepted payment methods, such as credit card, bank transfer, or PayPal. Knowing these options helps you choose the most convenient way to pay.
- Bank Details: If a bank transfer is preferred, the seller will provide their bank account information here. Sometimes, e-wallet accounts are listed as an alternative.
- Payment Instructions: This includes any specific instructions or notes regarding the payment, such as reference numbers to include or steps to follow for certain payment methods.
7. Additional Notes
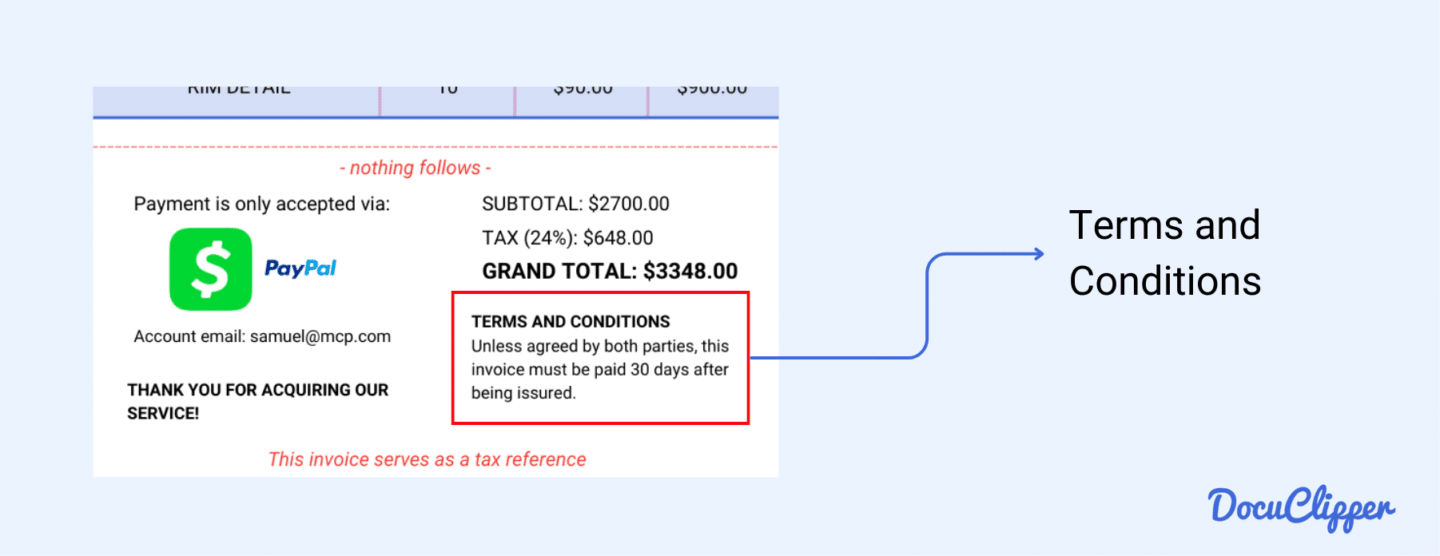
This section contains extra notes from the seller, which can include terms and conditions or a personal message.
- Terms and Conditions: This outlines any additional terms or conditions related to the sale. It could cover return policies, warranty information, or specific agreements made between you and the seller. Reviewing these terms ensures you understand all aspects of the transaction.
- Thank You Note: Many sellers include a thank you note to show appreciation for your business. It’s a small gesture that can enhance your relationship with the seller and reflect their commitment to customer service.
8. Footer
The footer section of an invoice may include regulatory statements and contact information, often required by state laws.
- Legal Information: This includes any legal disclaimers or mandatory information that must be provided by law. It ensures compliance with local regulations and helps protect both you and the seller in legal matters.
- Contact Information: The footer also reiterates contact details for any queries regarding the invoice. This usually includes the seller’s phone number, email, and possibly their website, making it easy for you to reach out with any questions or concerns.
What is an Invoice?
An invoice is a document the seller gives you to request payment for goods or services. It includes the cost of the products purchased or services rendered.
Essentially, it’s a business record listing products sold or services performed, sent before payment is made.
By invoicing, the seller is providing a legally enforceable document requesting payment, ensuring both parties have a clear and formal record of the transaction.
How to Extract Data from PDF Invoice?
Extracting data from PDF invoices can be done in two ways, each with different requirements and efficiency.
- Manual Invoice Processing: This traditional method involves manually typing all necessary information, such as dates, invoice numbers, line items, quantities, prices, and totals into a spreadsheet. While straightforward, it is prone to errors and very time-consuming, making it less efficient for large volumes of invoices.
- Using OCR: Optical Character Recognition (OCR) software offers a modern and efficient alternative. OCR software can quickly extracts data from PDF invoice and extract all relevant data in seconds, compiling it into a spreadsheet. This method significantly reduces the likelihood of errors and saves time, making it ideal for handling large numbers of invoices.
Conclusion
Understanding how to read an invoice is crucial for managing your finances and ensuring accurate record-keeping. By familiarizing yourself with the invoice header, seller and buyer information, line items, amounts, payment terms, and additional notes, you can streamline your accounting process and avoid potential disputes. Efficient invoice reading and processing are essential for maintaining good business relationships and financial stability.
FAQs about How to Read an Invoice
Here are some frequently asked questions about invoices and understanding them:
How should an invoice read?
An invoice should clearly list the seller’s and buyer’s information, including names, addresses, and contact details. It should include the invoice number, date of issue, due date, and a detailed list of items or services provided, with quantities, unit prices, and total amounts. Payment terms and methods should be clearly stated to avoid any confusion.
How to read invoice terms?
Invoice terms outline the conditions of the sale and payment. These terms typically include the payment due date, acceptable payment methods (such as credit card, bank transfer, or PayPal), and any late payment penalties. Understanding these terms is crucial to ensure timely payments and to avoid any additional fees or disputes with the vendor.
How to check invoice details?
To check invoice details use invoice reconciliation to verify that the invoice number is unique and matches your records. Ensure the dates are correct, and the seller’s and buyer’s information is accurate. Review the line items for correct descriptions, quantities, and prices. Confirm that the subtotal, taxes, and grand total are correctly calculated. This process helps prevent errors and discrepancies.
Learn more about invoice matching:
What is the rule for invoice numbers?
Invoice numbers should be unique for each invoice issued by a seller. This unique identifier helps both the seller and buyer track and reference specific transactions. It’s crucial for maintaining organized records, preventing duplication, and ensuring accurate bookkeeping.
How should an invoice be numbered?
Invoices should be numbered sequentially, often using a combination of numbers and letters (e.g., INV-1001, INV-1002). This system helps maintain an organized record of all invoices issued, making it easier to track and reference past transactions. Sequential numbering also helps identify any missing invoices, ensuring comprehensive record-keeping.