An invoice is a legal document that records a transaction between a buyer and seller, detailing the goods or services provided, their cost, and payment terms.
It includes essential information like invoice number, payment due date, and contact details, and serves as a vital record for businesses.
What’s the Main Purpose of an Invoice?
The main purpose of an invoice is to formalize the sale of goods or services and request payment from the buyer provided by the vendor or seller.
It provides a clear record of the transaction, detailing products/services, prices, and payment terms, while also serving as a legal agreement, aiding in financial record-keeping, and ensuring timely payments.
Key Elements of an Invoice
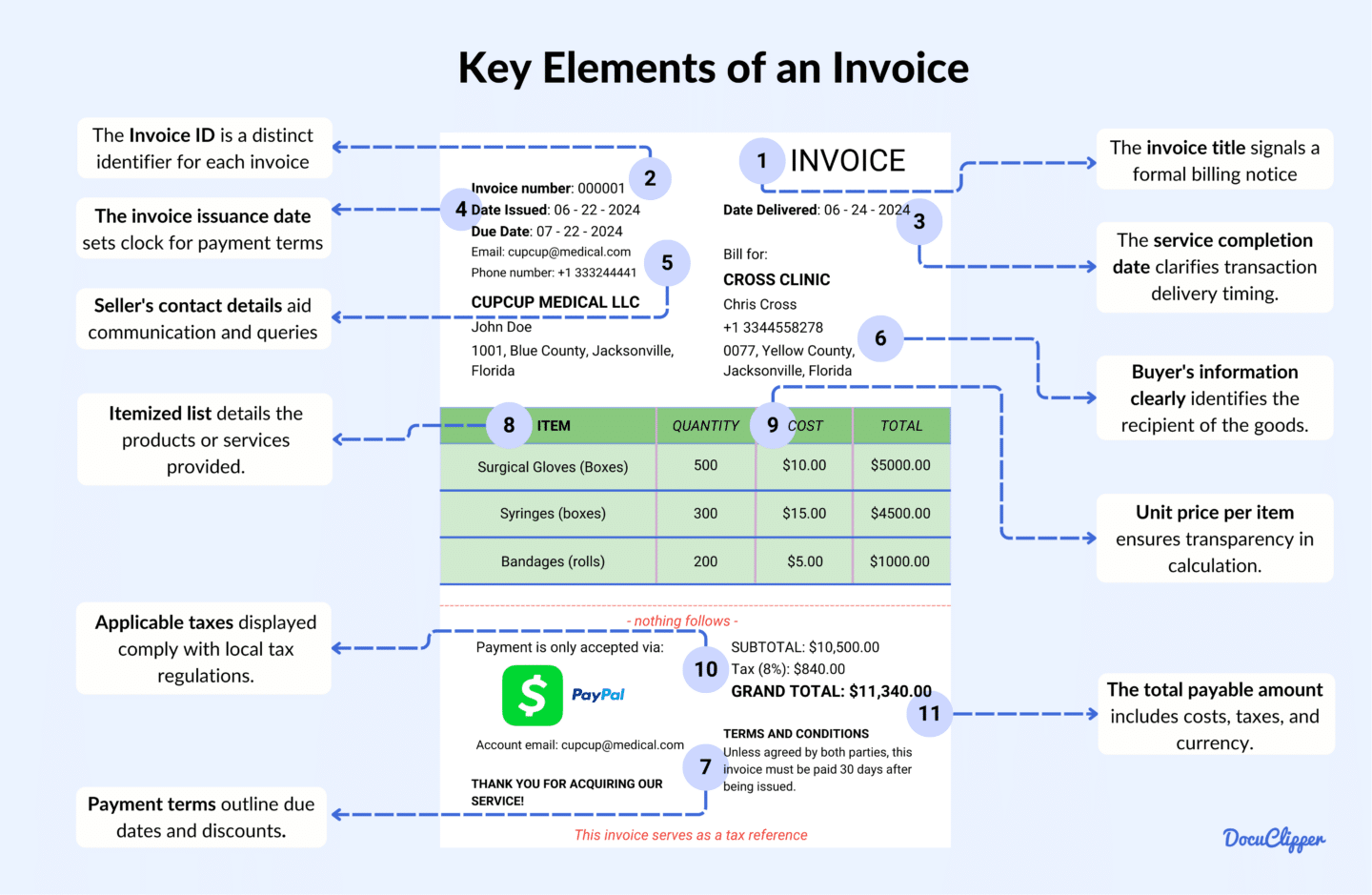
An invoice contains many parts each holding necessary information often established by law as requirements.
Here is a detailed list of its parts:
- Invoice Title: The invoice title is prominently displayed at the top, signaling that this document is a formal billing notice. It often includes the company’s logo to maintain a professional look.
- Unique Invoice ID: This is a distinct identifier assigned to each invoice, ensuring it is easily tracked and differentiated from others. It aids in payment monitoring and avoids duplication.
- Service Completion Date: The service completion date specifies when the goods or services were delivered to the client. It provides clarity on the timing of the transaction.
- Invoice Issuance Date: This is the date the invoice was officially created and sent to the client. It sets the clock for the payment terms and due dates.
- Seller’s Contact Information: This section provides the name, address, and contact details of the seller or service provider. It ensures the buyer knows whom to reach out to for questions or payment.
- Buyer’s Details: The invoice should include the buyer’s name and contact information to clearly identify the recipient of the goods or services. This aids in record-keeping and transaction verification.
- Payment Terms and Policies: This part outlines the agreed-upon payment conditions, including the due date, possible late fees, and any discounts for early payment. Clear terms help avoid misunderstandings.
- Itemized List of Products/Services: Each product or service provided is listed in detail, with a brief description. This breakdown helps the buyer understand what they are being charged for.
- Unit Price for Each Item: The price per item or service is specified in this section. It provides transparency and explains the calculation of the total amount owed.
- Applicable Taxes: This part shows the taxes being charged, such as VAT or sales tax, in accordance with local laws. Properly displaying tax rates ensures compliance with tax regulations.
- Total Payable Amount with Currency: This is the final amount the client needs to pay, including all costs and taxes. Stating the currency avoids confusion in international transactions.
Why Invoices are Important in Business?
There are several reasons that businesses consider invoices as an important part of their accounting:
- Ensure Timely Payments: Invoices ensure timely payments by clearly outlining the services rendered, the amount owed, and payment deadlines. They serve as a legal document, reducing the risk of payment disputes and revenue loss.
- Track Business Income: Invoices help businesses track their income by documenting every sale or service transaction. This ensures accurate financial reporting and assists with tax preparation.
- Enhance Client Trust: Well-structured invoices enhance client trust by providing clarity and transparency in billing. Clients appreciate detailed breakdowns of charges, which can foster long-term business relationships.
- Prevent Payment Disputes: Proper invoicing helps prevent payment disputes by clearly outlining terms, services, and costs. This reduces the chances of misunderstandings or delays in payment.
- Tax Compliance: Invoices play a crucial role in tax compliance by documenting sales, expenses, and applicable taxes. They simplify tax filing and ensure adherence to government regulations.
- Streamline Business Operations: Automating invoicing processes can streamline business operations by reducing manual errors and speeding up payment collection. It allows businesses to focus on growth rather than administrative tasks.
- Improves Financial Planning: Invoices help businesses with financial planning by providing insight into cash flow and sales trends. This information is essential for budgeting and making informed business decisions.
- Improve Supplier Relationships: Proper invoicing improves supplier relationships by ensuring timely and accurate payments. It also helps businesses take advantage of early payment discounts.
Types of Invoices
There are several types of invoices, each serving a specific purpose in business transactions. Here are the most common types:
- Standard Invoice: This is the most common type of invoice used for a basic sale of goods or services. It includes details such as the amount owed, due date, and payment terms.
- Proforma Invoice: A preliminary bill of sale sent to buyers in advance of a shipment or delivery of goods. It outlines the terms of the transaction but is not a request for payment.
- Recurring Invoice: Used for ongoing services or subscription-based businesses, this invoice is issued regularly (weekly, monthly, etc.) for repetitive transactions.
- Commercial Invoice: Used in international trade, it includes details about the shipment of goods, including the cost, quantity, and type of goods, for customs purposes.
- Credit Invoice (Credit Memo): Issued when a refund or discount is given to the buyer. It shows a reduction in the amount owed by the customer.
- Debit Invoice (Debit Memo): Used to indicate an increase in the amount owed by the customer, often due to additional services or adjustments.
- Timesheet Invoice: Commonly used by professionals or freelancers who bill clients based on hours worked, such as consultants or contractors.
- Mixed Invoice: This invoice includes both debits and credits, typically used when adjustments need to be made to an original invoice.
- Final Invoice: Issued once all work has been completed, this invoice provides the final breakdown of costs, including any outstanding balances from previous payments.
- Past Due Invoice: Sent when a customer has failed to pay by the due date, reminding them of the outstanding balance and possibly including late fees.
How to Create an Invoice
Making an invoice is very easy and can be done quickly.
Here is a quick rundown of how to create an invoice:
1. Identify the Parties: Clearly identify both your business and the client by including the full name, contact information, and address of each party. This ensures both parties know who is involved in the transaction and aids in future communications.

2. Describe What’s Being Exchanged: Provide a detailed description of the products or services being exchanged, including quantities, rates, and any additional notes. This transparency helps clients understand exactly what they are paying for.
3. Give the Payment Details: Clearly state the total amount owed, the payment due date, and accepted payment methods. Ensuring clarity here helps avoid delays and facilitates faster payment processing.

How to Send an Invoice
When it comes to sending invoices, there are essentially three methods you can use:
- Mail: Sending an invoice by mail was traditionally the standard method. It remains popular with some businesses, but it has drawbacks such as slow delivery, the potential for lost mail, and the chance that addresses may change.
- Email: Sending invoices via email is faster and allows for easier delivery to the appropriate person or department. As long as the recipient’s email system is well-managed, invoices are less likely to be lost.
- Invoicing Software: Using invoicing software automates the process and often includes payment links, enabling customers to pay directly online. This method can speed up the payment process and reduce the need for manual follow-ups.
How to Pay an Invoice
Paying invoices is a standard routine in businesses, but because it’s so widely used, many scammers are taking advantage of businesses often paying invoices without double-checking what they’re paying for.
In this section we’re going to show you step by step process of how to pay for invoices to avoid paying fraudster invoices:
- Review the Invoice for Received Goods and Services: Carefully examine the invoice to ensure it accurately reflects the goods or services you received. Verifying the details helps avoid discrepancies and ensures you’re paying for what was provided.
- Note the Payment Due Date: Take note of the payment due date to ensure timely payment and avoid any late fees. Being aware of the deadline helps you plan your cash flow effectively.
- Choose Your Payment Method: Select a payment method that is accepted by the vendor, such as a credit card, bank transfer, or online payment. Choosing the most convenient option helps you settle the invoice efficiently.
- Add the Invoice to Your Payment Schedule: Schedule the payment by adding the invoice to your accounting system or calendar. This ensures you won’t miss the payment and helps keep your financial records organized.
- File Payment Confirmation Details: Once the payment is made, store the confirmation details for your records. Keeping proof of payment ensures you have documentation in case of any future disputes or verification needs.
How Much Does It Cost to Process an Invoice?

In the United States, processing an invoice can cost you anywhere from $13.11 to as much as $40, depending on your business size, according to reports from Ardent Partners and Adobe. Top performers, however, have significantly lowered their costs, with some spending as little as $1.42 per invoice by 2022, compared to $6 for bottom performers.
In the UK, you could be paying between £4 and £25 per invoice, but costs can climb to £50 for more manual processes. Automating your system can help you reduce these expenses by 60-80%, bringing your average cost down to £5 or less.
In Australia, traditional methods such as handling paper or PDF invoices can cost between $27 and $30, but switching to eInvoicing could lower your costs to $9.18 per invoice, as suggested by the Australian Taxation Office and Deloitte Access Economics.
Functions of Invoice
Here are the main functions of an invoice and its purpose why businesses always record, issue, and archive it:
- Legal Protection: Invoices serve as legally binding documents that can be used in disputes to prove the delivery of goods or services and the agreed-upon payment terms. They provide businesses with legal protection in case of non-payment or other contract violations.
- Records Management: Invoices act as essential records of transactions, helping businesses maintain accurate financial records for audits, reporting, and future reference. Proper records and invoice management ensure that all financial data is organized and accessible when needed.
- Payment Tracking: Invoices allow businesses to track payment statuses, ensuring that customers pay on time and any overdue accounts are easily identified. This helps maintain a steady cash flow and reduces the risk of outstanding debts.
- Easy Tax Filing: Invoices simplify tax filing by providing a clear record of income, expenses, and VAT or sales tax collected. This documentation is essential for accurate tax reporting and deductions, reducing errors during tax season.
- Compliance: Invoices help businesses adhere to legal and regulatory requirements, such as tax laws and industry-specific standards. They ensure that all necessary details, such as payment terms and tax information, are properly documented.
- Business Analytics: Invoices provide valuable data for business analytics, offering insights into sales trends, customer behavior, and financial performance. This data helps businesses make informed decisions and identify areas for growth.
Invoice Management Best Practices
Here are some steps to manage invoices effectively, especially when your business grows in scale:
- Prioritize Invoices: Prioritizing invoices based on due dates and payment terms ensures that critical payments are handled promptly, helping businesses avoid late fees and maintain good supplier relationships.
- Prefer Digital Invoices: Opt for digital invoices to streamline processing, reduce paper usage, and minimize errors. Digital invoices are easier to store, manage, and retrieve for future reference.
- Payment Terms: Clearly define payment terms on invoices, including due dates, penalties for late payments, and any early payment discounts. This clarity helps avoid misunderstandings and encourages timely payments.
- Automate Invoice Processing: Implementing automation tools for invoice processing reduces manual labor, minimizes errors, and speeds up the entire workflow. Automation ensures invoices are processed efficiently and accurately.
- Avoid Duplicate Payments: Establish checks and systems to detect and prevent duplicate payments. This can include using unique invoice numbers, automated tracking systems, and regular audits.
- Standardize Invoice Approval Workflow: Create a standardized approval process that ensures consistency and reduces delays in invoice approvals. Clear guidelines help streamline the workflow and prevent bottlenecks.
- Invoice Tracking and Reminders: Use tracking and reminder systems to monitor unpaid invoices and send automated reminders to clients as due dates approach. This helps reduce late payments and improves cash flow.
- Create an Invoice Organization System: Develop an organized system for categorizing and storing invoices, whether digitally or physically. Proper organization aids in quick retrieval, audit preparation, and records management.
- Automate Invoice Data Extraction: Utilize tools for automating data extraction from invoices to reduce manual data entry and errors. Automation saves time and enhances accuracy in financial reporting.
- Regularly Reconcile Invoices: Conduct regular reconciliations to ensure that all invoices are correctly recorded, paid, and accounted for. This practice helps maintain financial accuracy and prevents discrepancies.
- Implement Invoice Matching: Use two-way or three-way matching to verify invoices against purchase orders and receipts. This process helps prevent overpayments, fraud, and discrepancies in billing.
Invoice vs Receipt: What are the Differences
An invoice is what you send to a customer to request payment after providing goods or services. It details the transaction and asks for compensation but doesn’t confirm payment. A receipt, on the other hand, is what you give to the customer after they’ve made a payment. It serves as proof that the transaction is complete.
Invoices are often used for credit transactions and business-to-business deals, while receipts are more common in cash transactions, retail sales, and official government dealings.
The key difference between the two is timing—an invoice comes before payment, requesting funds, whereas a receipt is given after payment to confirm it. An invoice helps you track the sales of your goods or services, while a receipt ensures both parties have a record of the completed transaction.
Learn more about invoice vs receipt.
Conclusion
Invoices play a critical role in business transactions by documenting the exchange of goods or services and formalizing the payment request.
They serve as essential legal and financial records, ensuring accurate tracking, timely payments, and compliance with tax and regulatory standards.
By automating and streamlining the invoicing process, businesses can reduce errors, improve cash flow, and enhance client relationships.
How Does DocuClipper Help with the Processing of Invoices?
DocuClipper is a tool designed to streamline invoice data extraction, allowing you to easily convert e-invoices in PDF format to Excel, CSV, and QBO files. Reconcile Invoices
The invoices can be quickly imported into QuickBooks, Xero, Quicken, Sage, or any of your accounting or ERP systems, and with DocuClipper’s API integration, you can fully automate the process.
For QuickBooks users, DocuClipper connects effortlessly, syncing invoice data automatically without any need for manual uploads or downloads. You can also extract invoice data directly from email attachments, a common method for receiving invoices.
In addition to invoices, DocuClipper handles receipts, bank statements, credit card statements, and brokerage statements with 99.5% accuracy. It also includes transaction categorization features, enabling you to easily organize and track each transaction, enhancing both the efficiency and precision of your financial management.