Extracting data from PDF invoices is a standard accounting, bookkeeping, and business operations procedure.
But when you’re running a business or have an accounting practice, you might deal with tens or hundreds of invoices which can take many days to process.
And taking a long with invoice data extraction can negatively affect the relationship with your vendors and your business performance.
So, in this blog, we’ll talk about how to do an efficient way of invoice data extraction and the types of information you can extract from an invoice.
What is Invoice Data Extraction?
Invoice data extraction is the process of retrieving key information from invoices and transferring it to databases like spreadsheets or accounting software.
This process is a super important component of pre-accounting work, setting the foundation for accurate financial record-keeping and ensures all relevant details such as dates, amounts, and vendor information are captured quickly and your invoice workflow is as easy and fast as possible.
Essential for expense management, this data aids in auditing and financial forecasting.
When businesses automate the data extraction process, they can save time, reduce errors, and improve financial accuracy.
Types of Data Extracted from Invoices
Various data types can be extracted from an invoice depending on your needs. Each serves distinct financial tracking and analysis purposes. Here are some examples:
- Vendor Details: The vendor is typically the one that provides the invoice, and within it is the relevant information about their establishment or business.
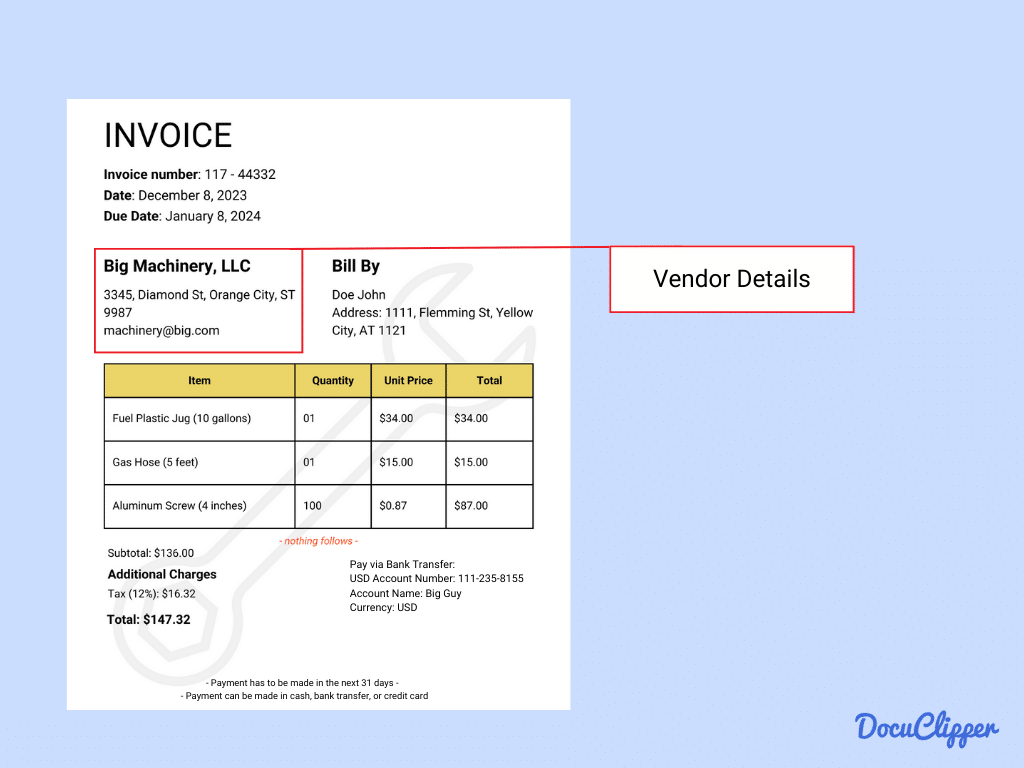
- Vendor Name: The official name of the company providing goods or services.
- Vendor Address: The physical or mailing address of the vendor.
- Vendor Contact Information: Includes the phone number and email address for direct communication.
- Vendor Tax Identification Number (TIN): A unique number used for tax purposes, essential for financial documentation and compliance.
- Customer Details: The customer is the one that acquires the invoice and basic information is placed for tracking.
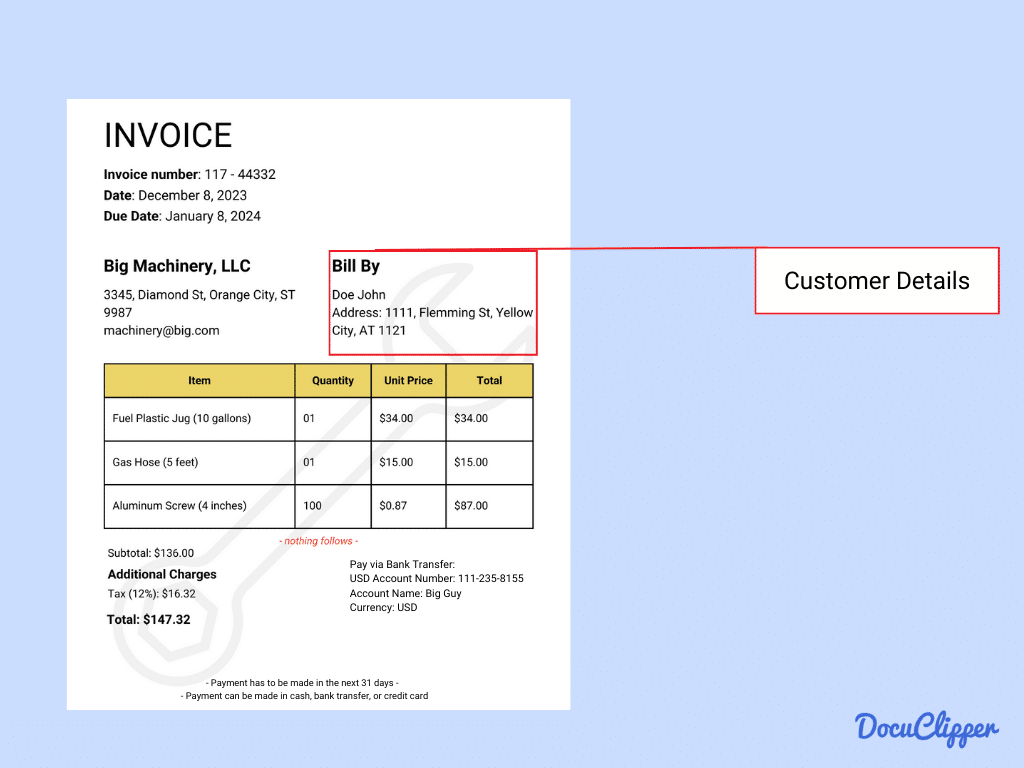
- Customer Name: The full legal name of the individual or entity purchasing the goods or services.
- Customer Address: The physical or postal address of the customer.
- Customer Contact Information: Includes essential details like phone number and email address for communication and service follow-ups.
- Invoice Specifics: Here are the details about the particular invoice that was sent.
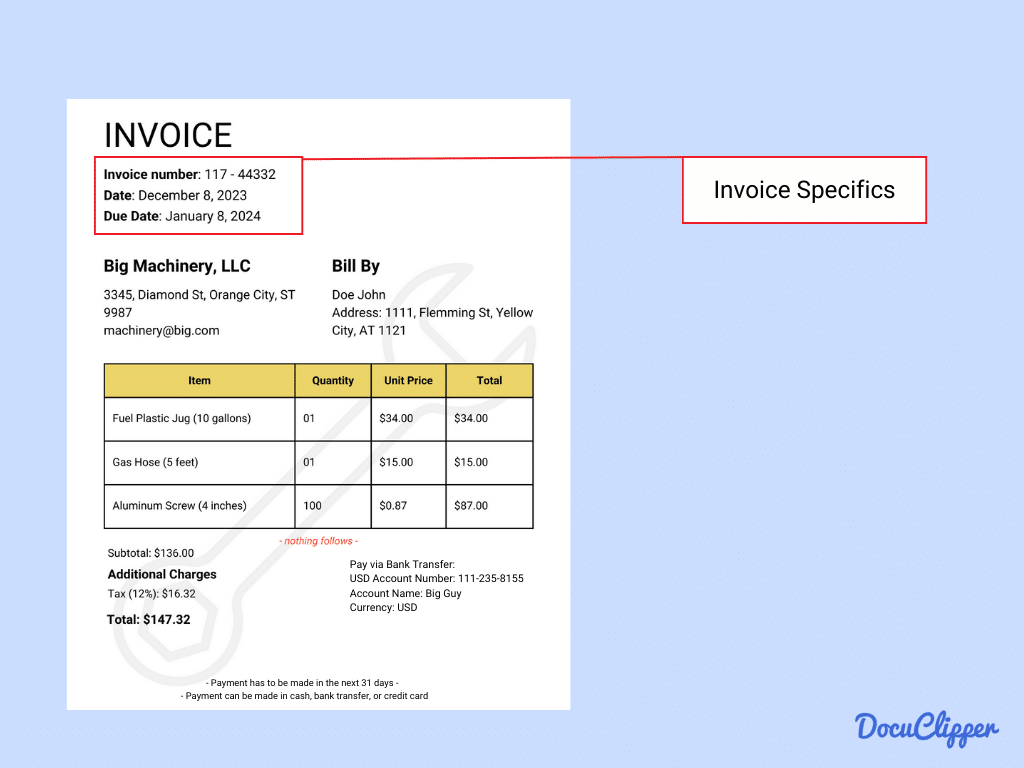
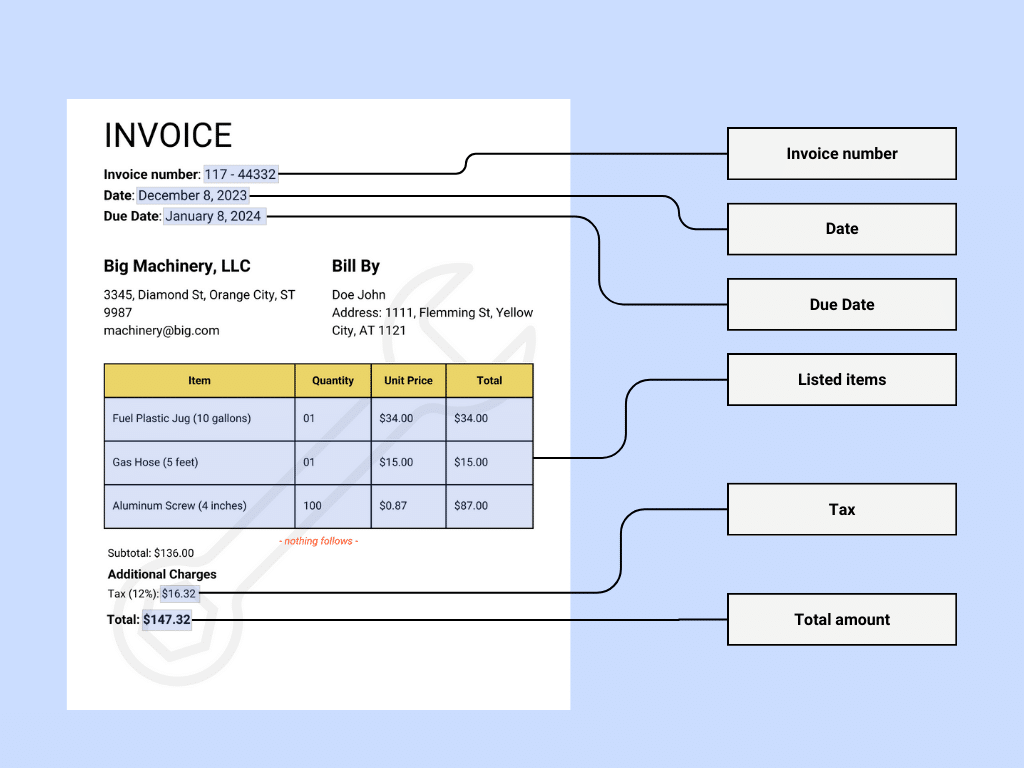
- Invoice Number: A unique code that helps track and reference the invoice.
- Invoice Date: The issue date of the invoice or when the invoice is given.
- Due Date: The deadline for payment or when the customer is expected to pay.
- Purchase Order Number (if applicable): Connects the invoice to a specific purchase order for easier tracking and processing.
- Line Items: Here is the breakdown of the charges within the invoice and each item or service listed.
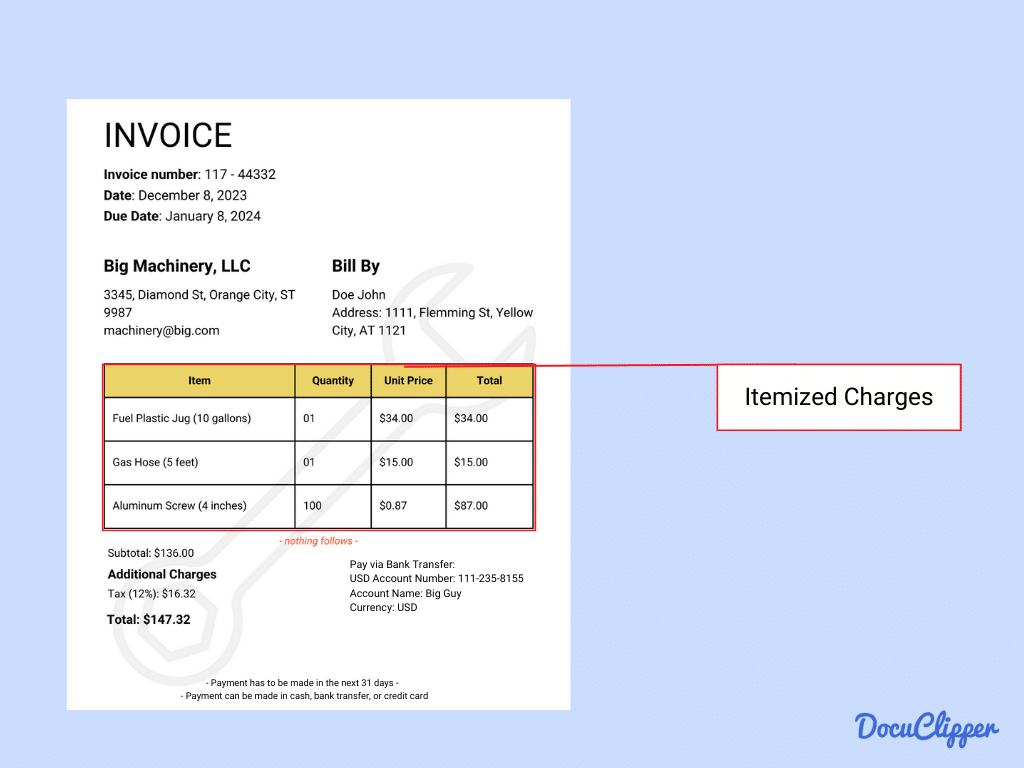
- Description: Details of what was purchased, including specifics about goods or services.
- Quantity: Lists how many of each item were bought.
- Unit Price: Shows the cost per individual item.
- Total Cost for Each Item: Calculates the total price for the quantity of each item purchased.
- Discount Applied (if any): Notes any reductions in price, enhancing transparency in billing.
- Totals: Here is the summary of the financial info combined.
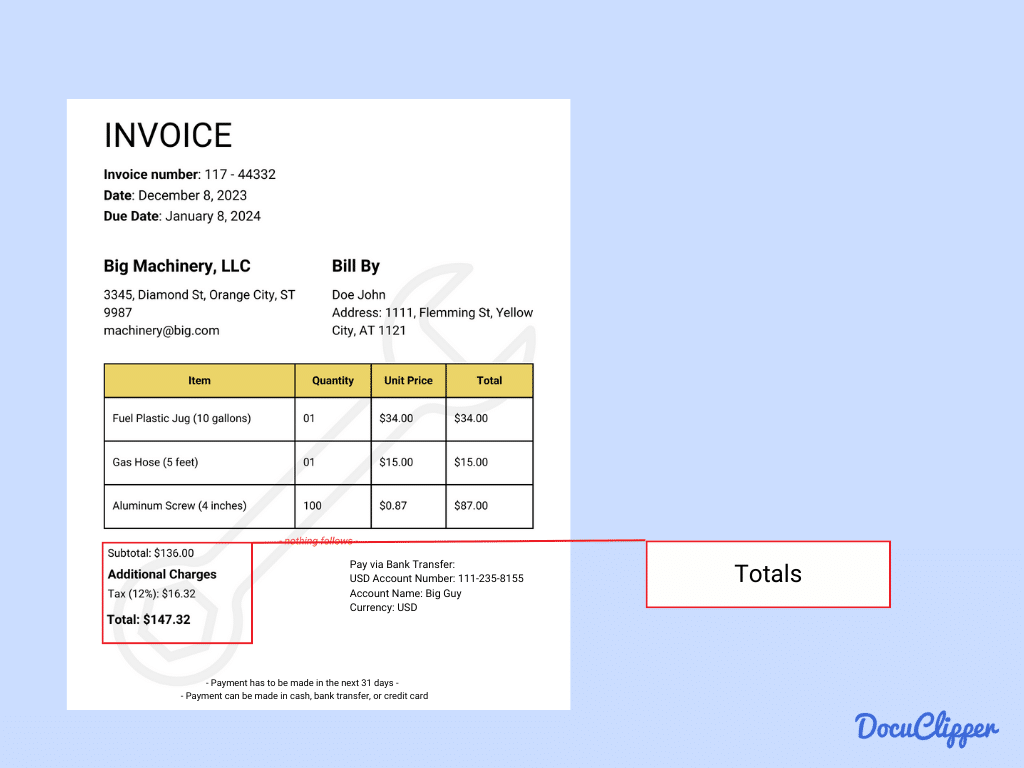
- Subtotal (before taxes and discounts): The total cost of all items before any taxes or discounts are applied.
- Tax Amount (breakdown of applicable tax rates): Lists the taxes charged, detailing different rates if applicable.
- Shipping and Handling Charges: Covers the costs associated with delivery and packaging of the goods.
- Grand Total (final amount due): The complete amount payable, including all charges and taxes.
- Payment Terms: This section shows how the customer can pay and the possible terms of the payment.
- Payment Method: Specifies how the payment was made, such as credit, debit, cash, or bank transfer.
- Payment Terms: Defines the timeframe for payment, like net 30 or net 60 days.
- Early Payment Discounts: Details any discounts offered for paying the invoice ahead of the due date.
- Banking Information (for wire transfers): When payments are done wirelessly, here is some information on where and how they can send the money.
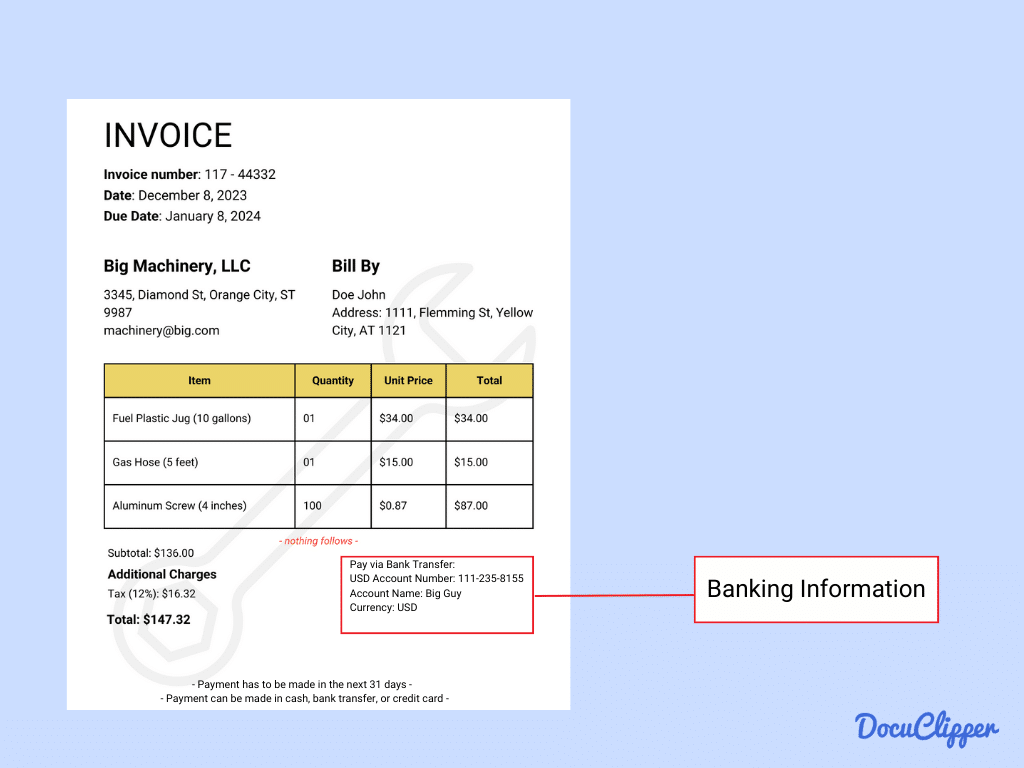
- Bank Name: The name of the financial institution where the account is held.
- Account Number: The unique identifier for the account used in transactions.
- Routing Number: The specific number used to identify the bank during electronic transactions.
- Currency: Invoices can run across different currencies especially when transactions are international.
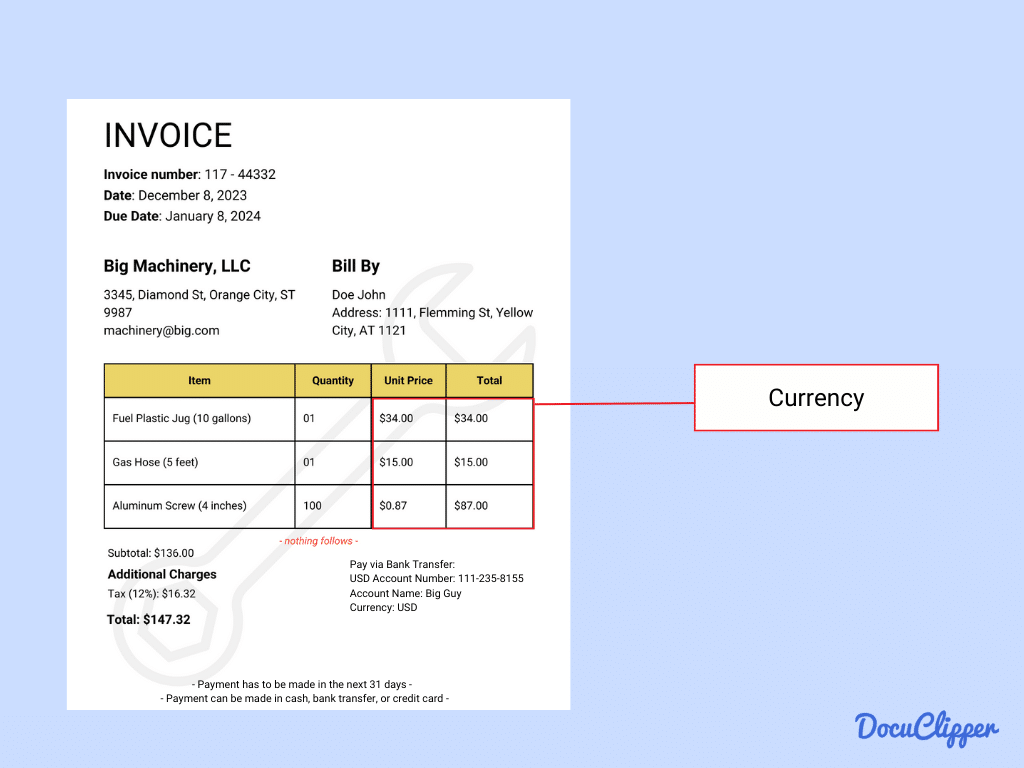
- Transaction Currency: Specifies the type of currency used to conduct the transaction, essential for international dealings and financial reporting.
- Additional Notes: Some useful auxiliary information.
- Special Instructions or Notes: Highlights any extra information or specific directions provided on the invoice, which may include delivery instructions, custom requests, or other pertinent details.
Learn more about how to read an invoice.
Challenges in Invoice Data Extraction
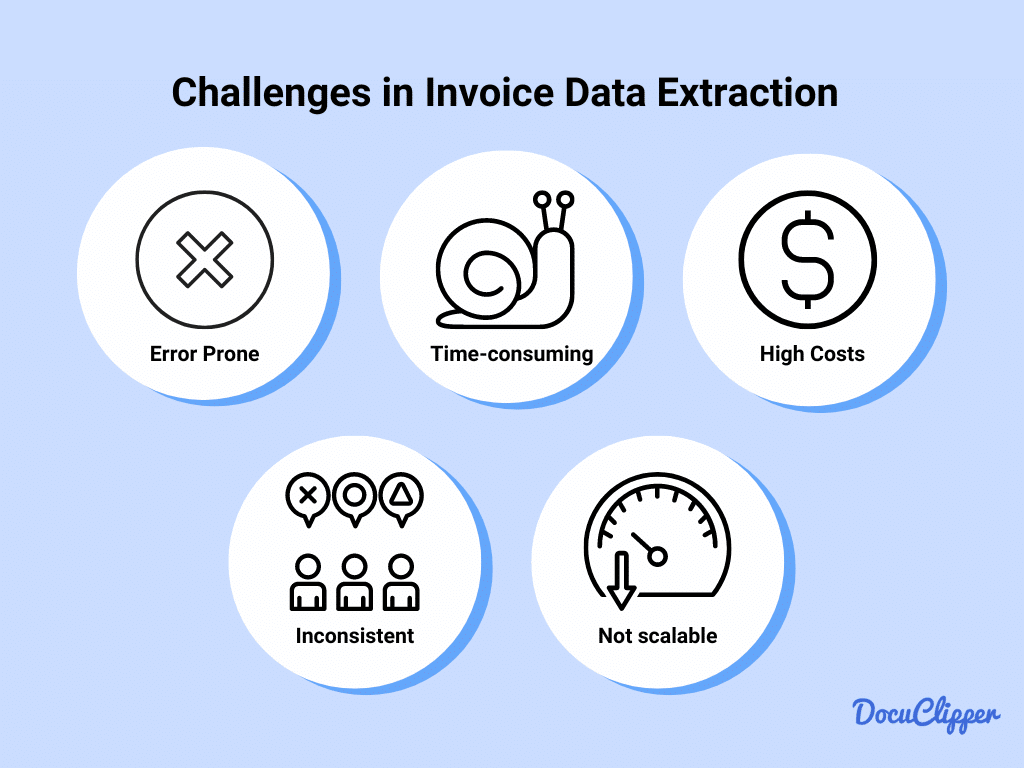
Extracting data from invoices, especially doing it manually can be quite challenging, time-consuming, and prone to errors.
And the more invoices you need to process the more the invoice data extraction is becoming complex.
So with that here are some of the challenges of invoice data extraction:
- Error Prone: Manual invoice processing and invoice data entry is susceptible to human errors, and it can have up to 4% error rates. Using OCR for invoice data extraction certainly reduces the possibility of errors.
- Time-Consuming: Processing invoices manually requires significant time and effort, especially for businesses that handle large volumes of invoices. Some employees spend 45% of their time on repetitive and manual tasks that can be automated.
- High Costs: Manual processing not only requires more time but also incurs higher labor costs. Outsourcing data entry costs $7 per hour while using OCR is around $40 for an entire month.
- Lack of Consistency: Different invoices may have different formats depending on the vendor, which can complicate the data entry process and lead to inconsistency in how data is recorded and processed.
- Scalability Issues: As a business grows, the volume of invoices also increases. Scaling manual processes is inefficient and can become a bottleneck for business operations.
Methods of Invoice Data Extraction
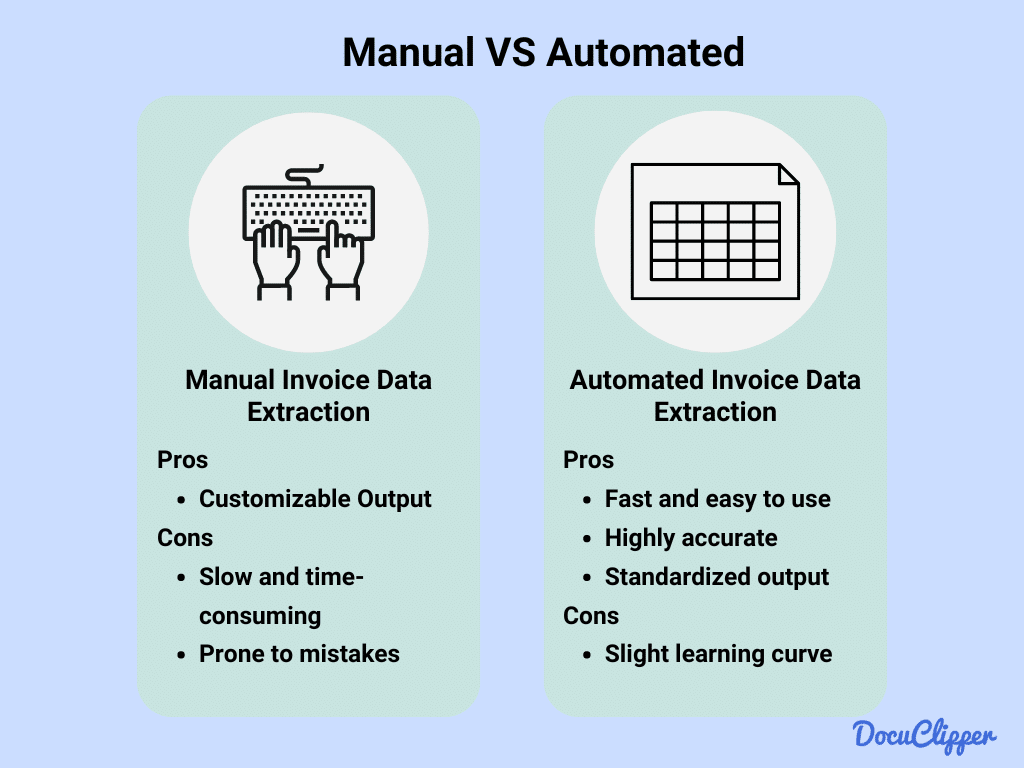
There are two methods of extracting data from invoices and both are widely used among accounting firms. They each have their benefits and downsides:
- Manual: Manual data extraction is time-consuming and error-prone, often requiring substantial resources. Few businesses still use this method due to the high risk of errors, which can lead to increased workload and potential liabilities for clients.
- Automated (OCR): Automated invoice processing uses OCR invoice scanning software. This method (using invoice parser) is widely adopted because it is fast, cost-effective, and generally more accurate than manual processing.
Automated Invoice Data Extraction
Automated invoice data extraction refers to the process of using technology, typically software based on Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and artificial intelligence (AI), to automatically capture and convert data from invoices into a structured digital format.
This paperless invoice processing eliminates the need for manual data entry and significantly streamlines the accounts payable and financial management processes within a company.
This technology eliminates the need for manual data entry and significantly streamlines the accounts payable and financial management processes within a company.
Here’s how it generally works and the benefits it provides:
- Scanning and Reading: The process begins with scanning paper invoices or importing digital invoices into the system. OCR technology then reads the text on these invoices.
- Data Identification and Extraction: Advanced OCR software can recognize and differentiate between various data fields on an invoice, such as vendor names, dates, invoice numbers, item descriptions, quantities, prices, and total amounts.
- Invoice Validation and Verification: The extracted data is then validated for invoice accuracy. The software might cross-reference the data against other documents or databases to ensure correctness and completeness or the user can manually review the extracted data comparing it with the original document.
- Data Integration: Once verified, the data is converted into a digital format that can be easily integrated into a company’s existing accounting systems. This streamlines ERP invoice processing and connects with other financial management systems.
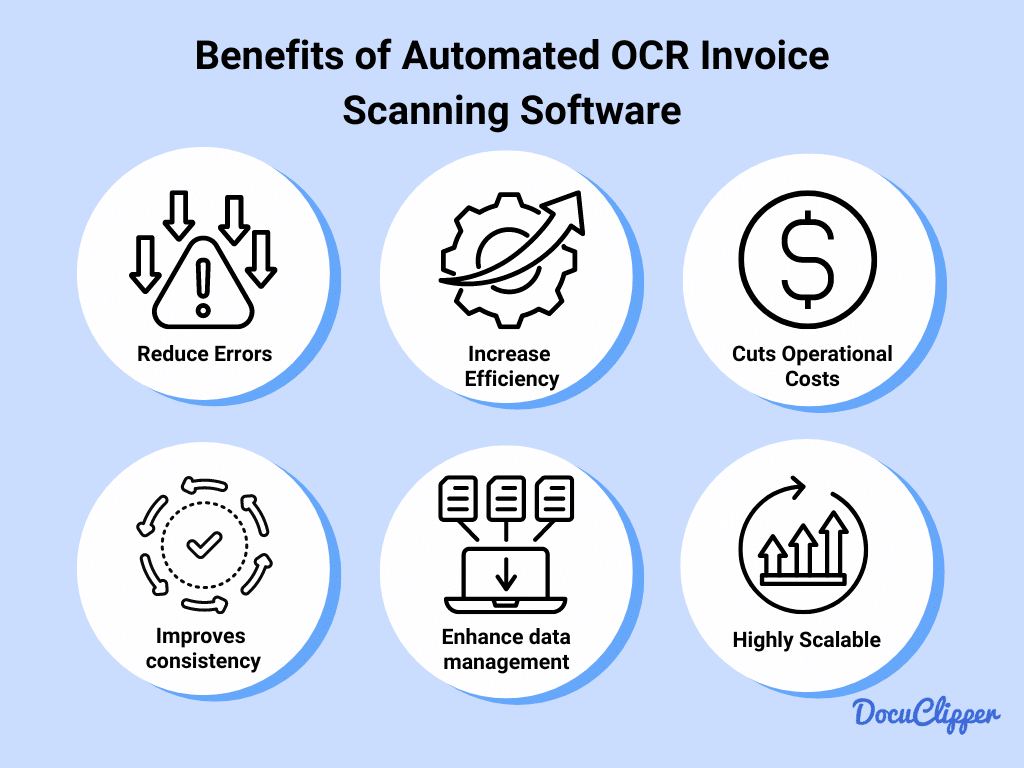
Benefits of Automated OCR Invoice Scanning Software
Luckily, all the common challenges of manually extracting data from invoices can be solved by using accessible invoice scanning software such as DocuClipper.
Using OCR you can automate parts of your invoice management and benefit from:
- Reduces Errors: OCR technology can significantly reduce errors by automating invoice data capture. The software is designed to accurately read and interpret text on invoices, regardless of slight variations in format.
- Increases Efficiency: OCR software can process large numbers of invoices quickly, saving time and allowing employees to focus on more strategic tasks rather than manual data entry which takes 40% of their time at work.
- Cuts Operational Costs: By automating the data entry process, businesses can reduce labor costs associated with manual entry. It costs $2.5 to $3.5 to outsource data entry to India, while it only costs around $40 for an OCR monthly subscription.
- Improves Consistency: OCR software can standardize data extraction from different invoice formats, ensuring consistent data handling. It can be programmed to identify specific fields regardless of where they appear on an invoice.
- Enhances Data Management: Digital data extraction makes it easier to store, search, and retrieve invoice data. This can improve overall document management and accessibility.
- Streamlines Post-accounting: By having accurately extracted and digitized data, post-accounting tasks like auditing and financial analysis become much more efficient.
- Scalability: Invoice OCR technology allows businesses to scale up their invoice processing without a corresponding increase in manual labor. OCR can process hundreds of invoices at once without issue but it’ll be difficult for only a single employee.
How to Extract Data from Invoices Using DocuClipper
Once you’ve decided to automate your invoice data extraction process, follow these straightforward steps with DocuClipper to start capturing invoice data efficiently:
Implementation Process
Step 1. Open Software: Launch DocuClipper and navigate to the “Invoices” and Receipts” section.
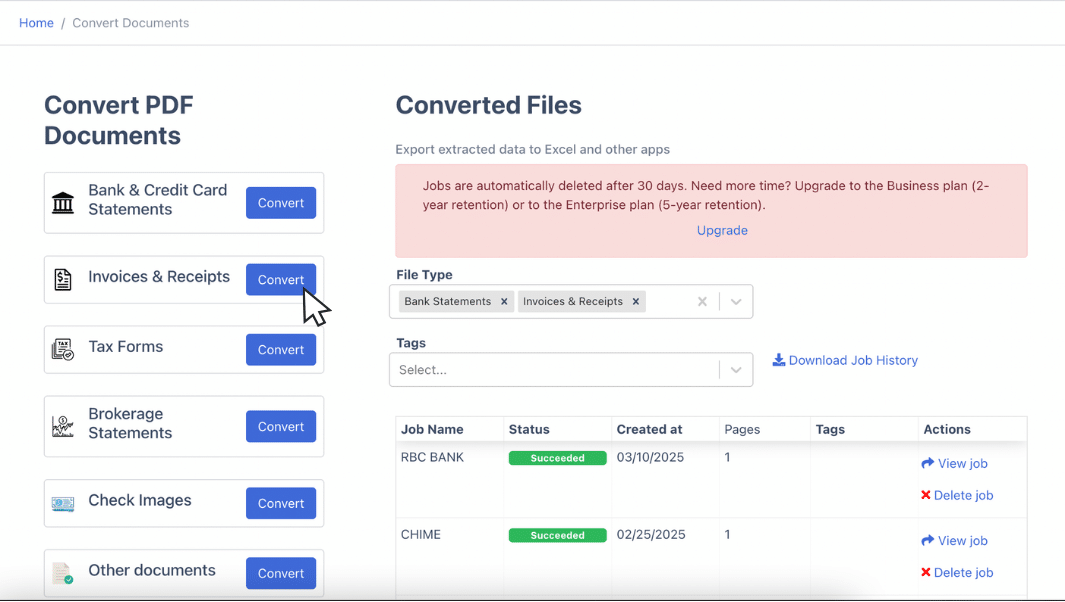
Step 2. Upload Files: Drag or upload your invoice files into the software. Assign a name to this job for easy tracking.
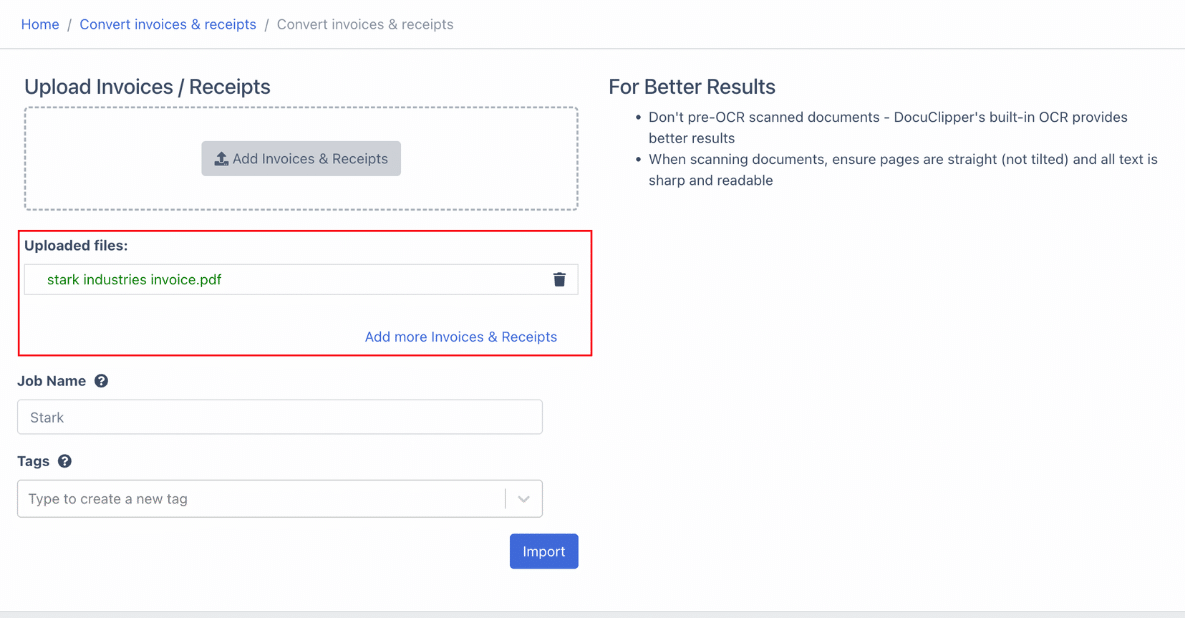
Step 3. Initiate OCR: Use DocuClipper’s Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to read the invoice text on scanned invoices. This technology allows for the processing of multiple invoices simultaneously. Click on “import” to begin.
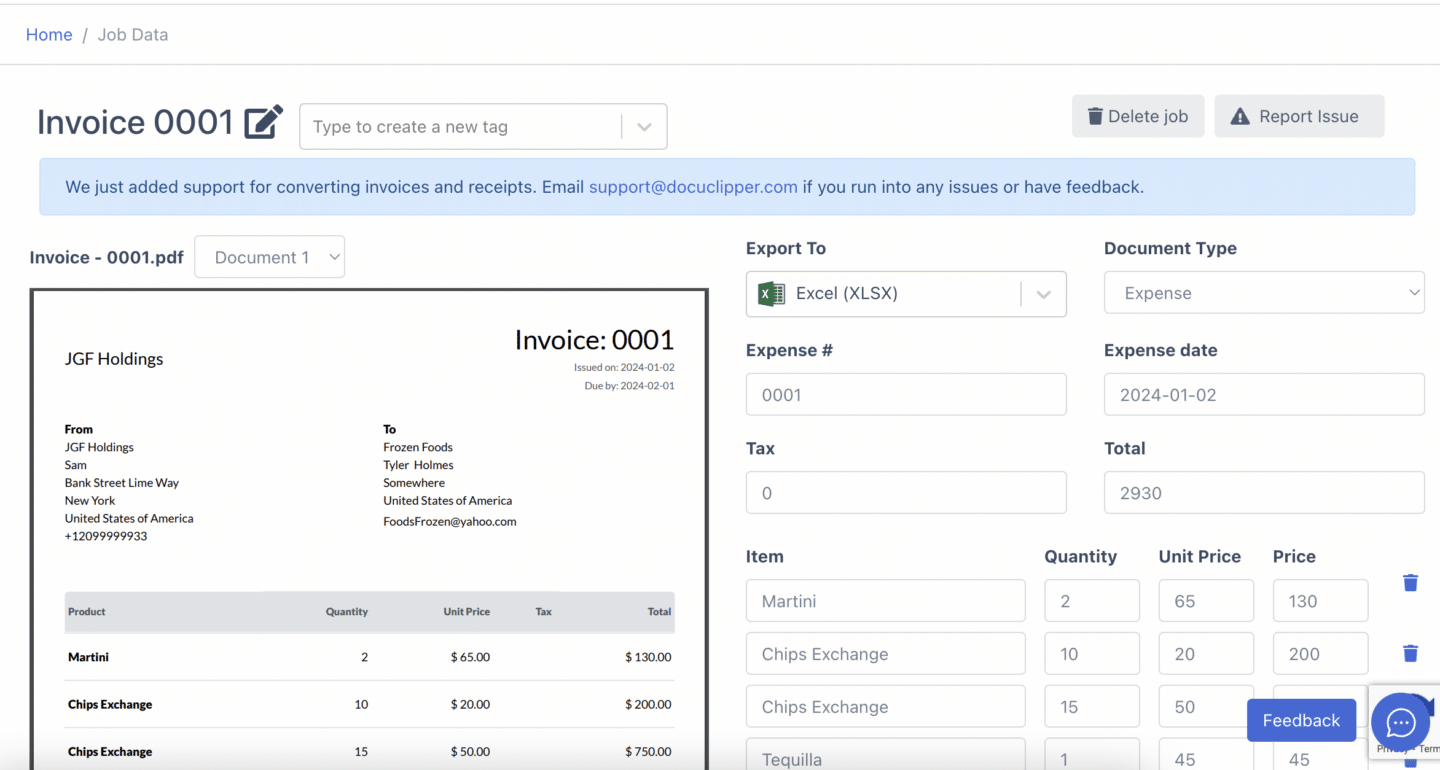
Step 4. Invoice Data Extraction: DocuClipper will automatically extract details such as item descriptions, subtotal, tax, total, and dates, from the invoices.
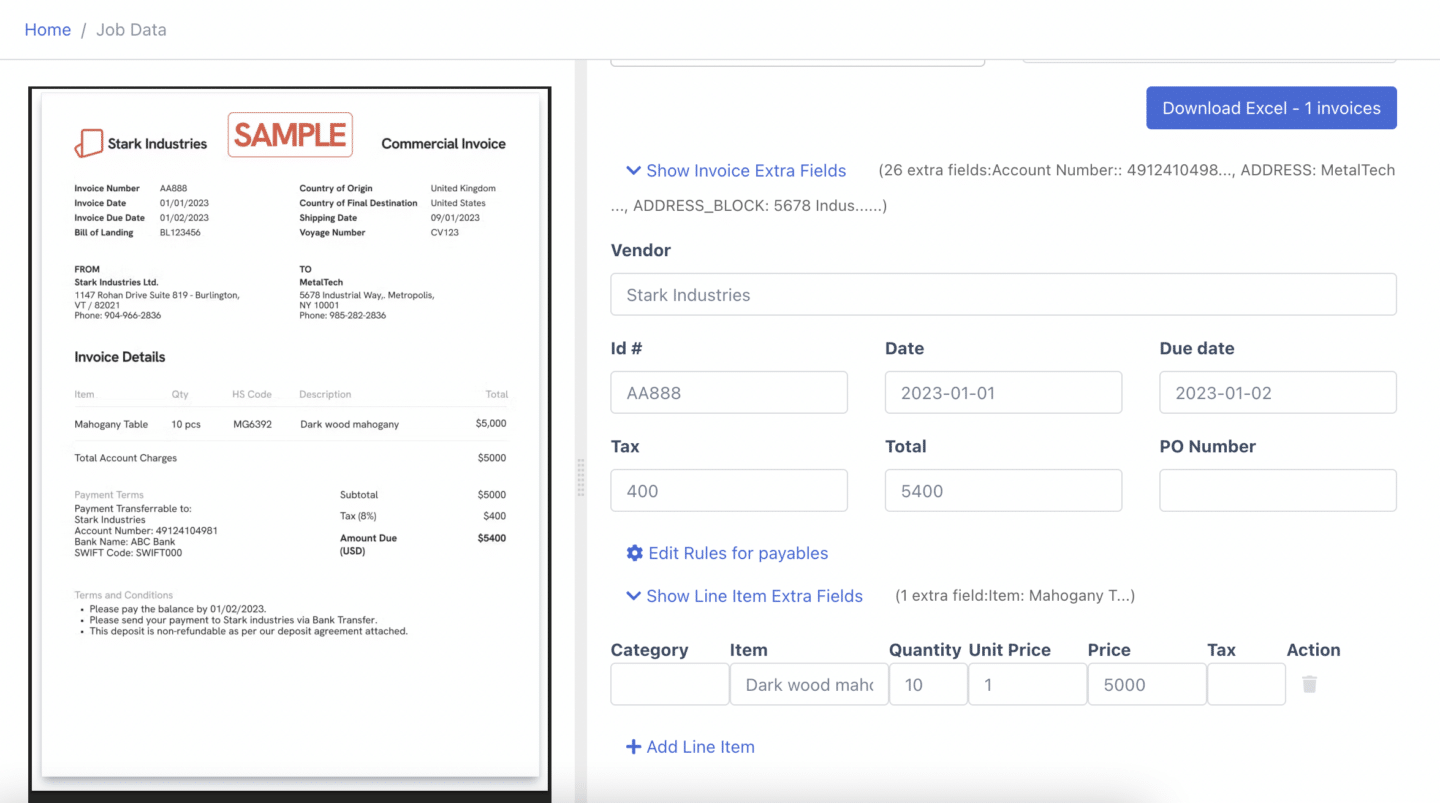
Step 5a. Preview and Export: Review a preview of the extracted data, including taxes, dates, and items. Decide the format for the output file—Excel, CSV, or QBO. Choose the desired format and click “Export” to complete the process.
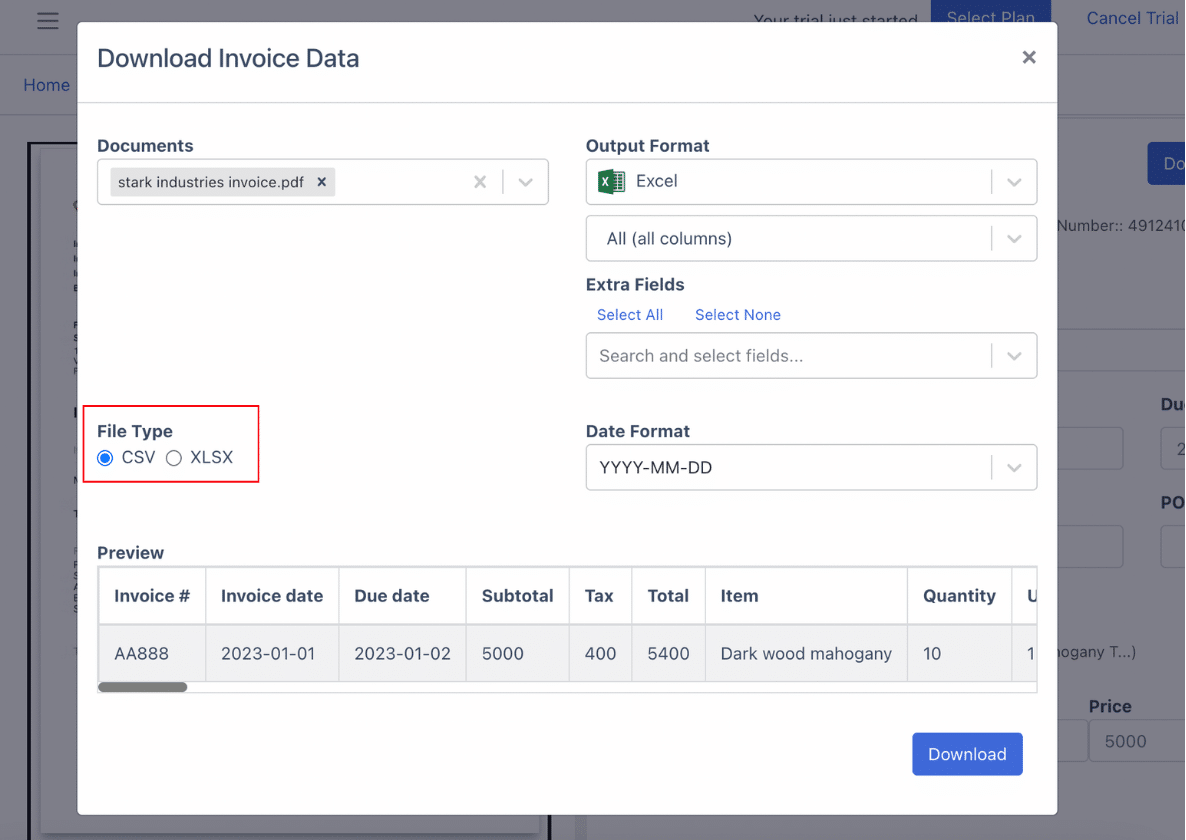
Step 5b. Import Invoices Into QuickBooks: Furthermore you can import extracted invoices into QuickBooks by connecting your QB account to DocuClipper.
Top 5 Invoice Data Extraction Software
Here are the top 5 invoice data extraction software that accounting firms use:
DocuClipper
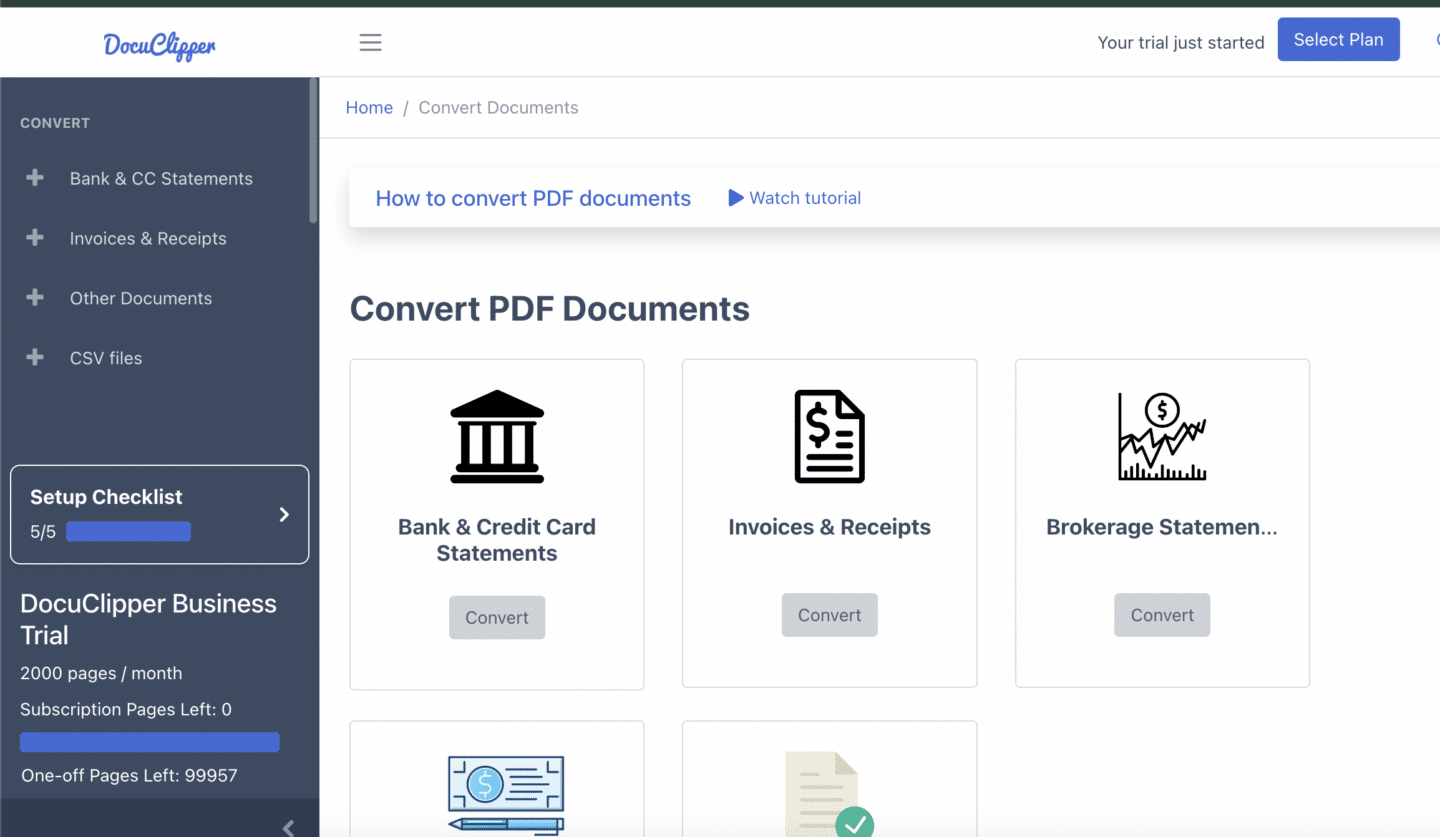
DocuClipper is the best invoice parser for extracting invoice data into structured information formats such as Excel, CSV, and QBO with a remarkable accuracy rate of 97%.
Furthermore DocuClipper can be synch with QuickBooks to quickly import your invoices.
Using advanced OCR technology, this software specializes in streamlining the invoice scanning process. It allows for batch processing, enhancing the efficiency of file conversion, and integrates through API with accounting platforms like QuickBooks, Xero, and Sage
AutoEntry
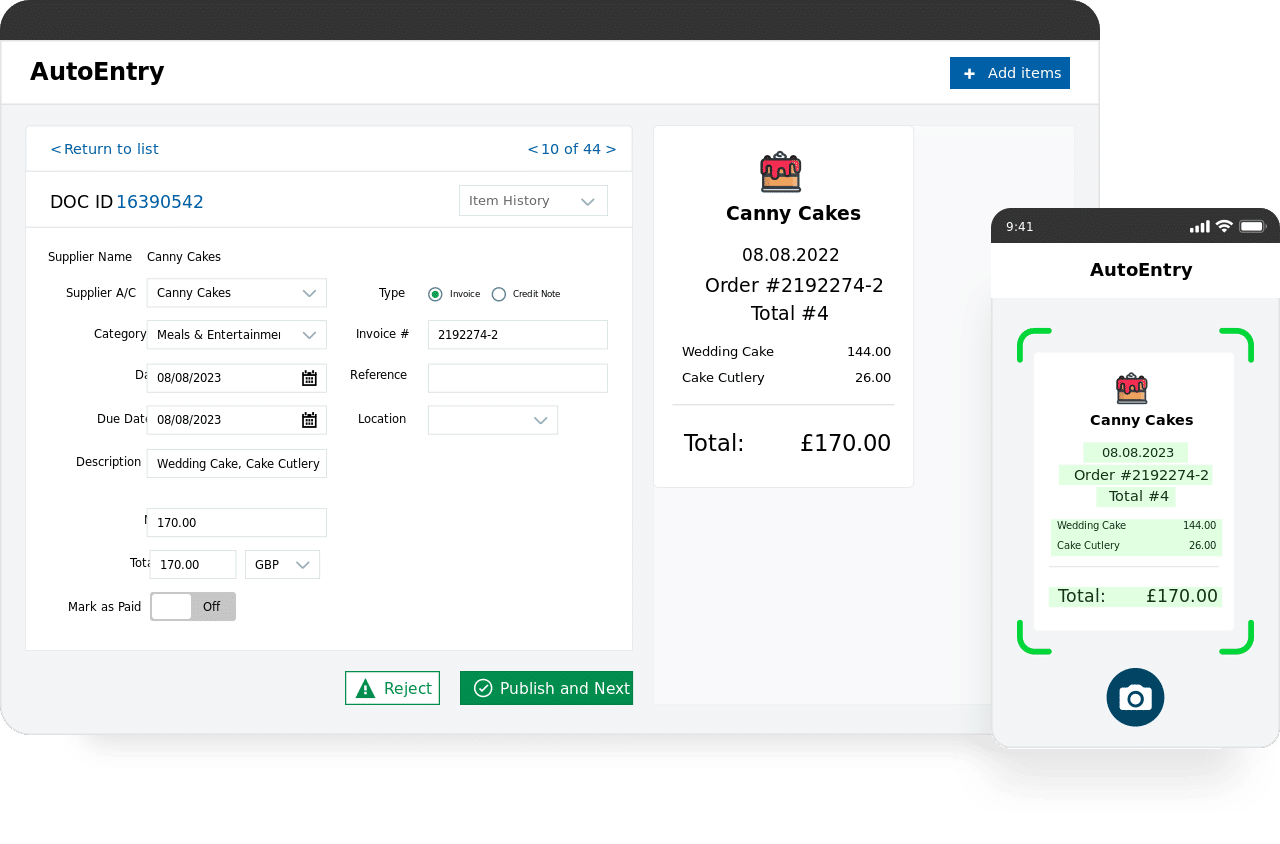
AutoEntry is a specialized data automation tool made for streamlining accounting processes by automating the extraction and publication of data to major accounting software platforms. It can also extract data from invoices for accounting use.
DextPrepare
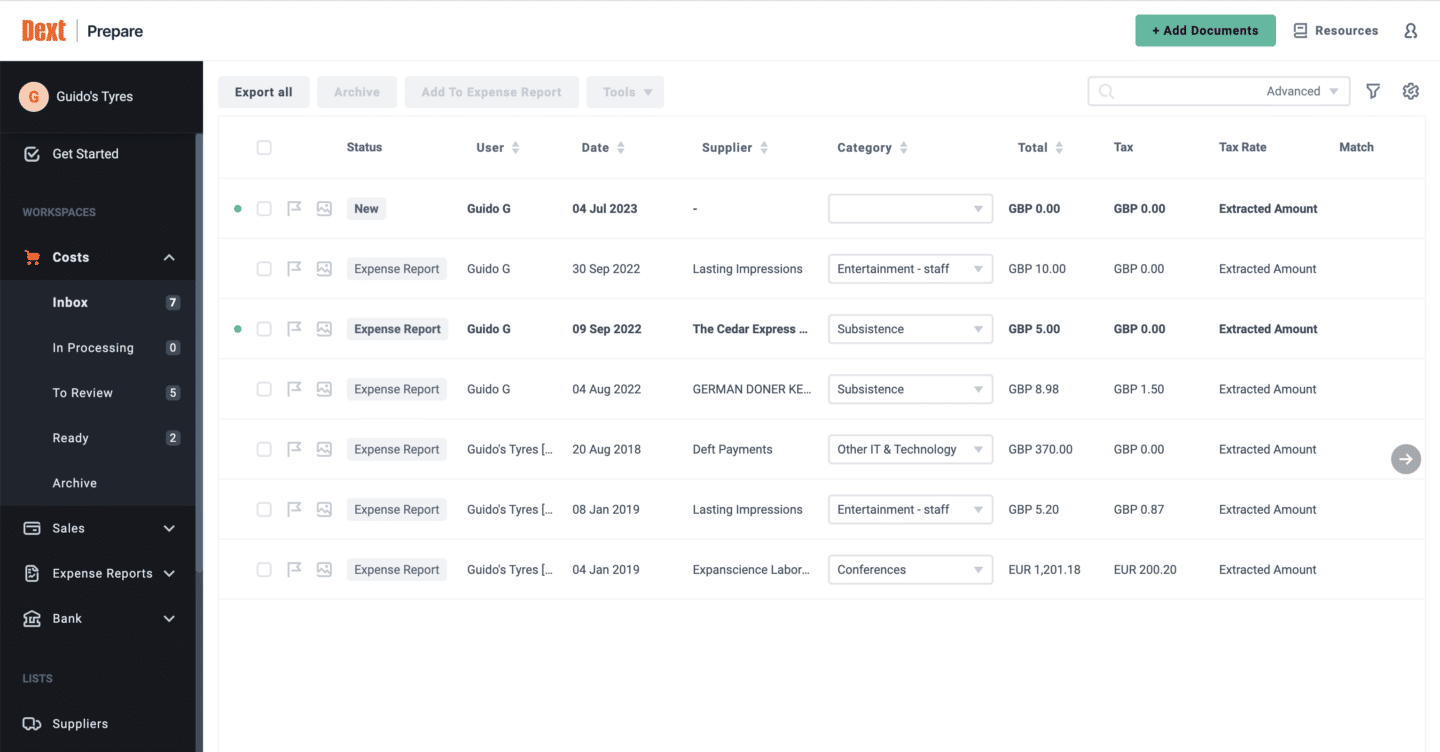
Dext Prepare is a specialized platform designed to enhance the productivity and profitability of accountants and businesses through superior data management and insights. It has tools that prepare, sort, and automatically publish invoices and receipts,
Klippa
Klippa is a comprehensive expense management solution designed to optimize the way businesses handle their expenses. It automates the submission and processing of business expenses, like invoices and receipts.
Nanonets
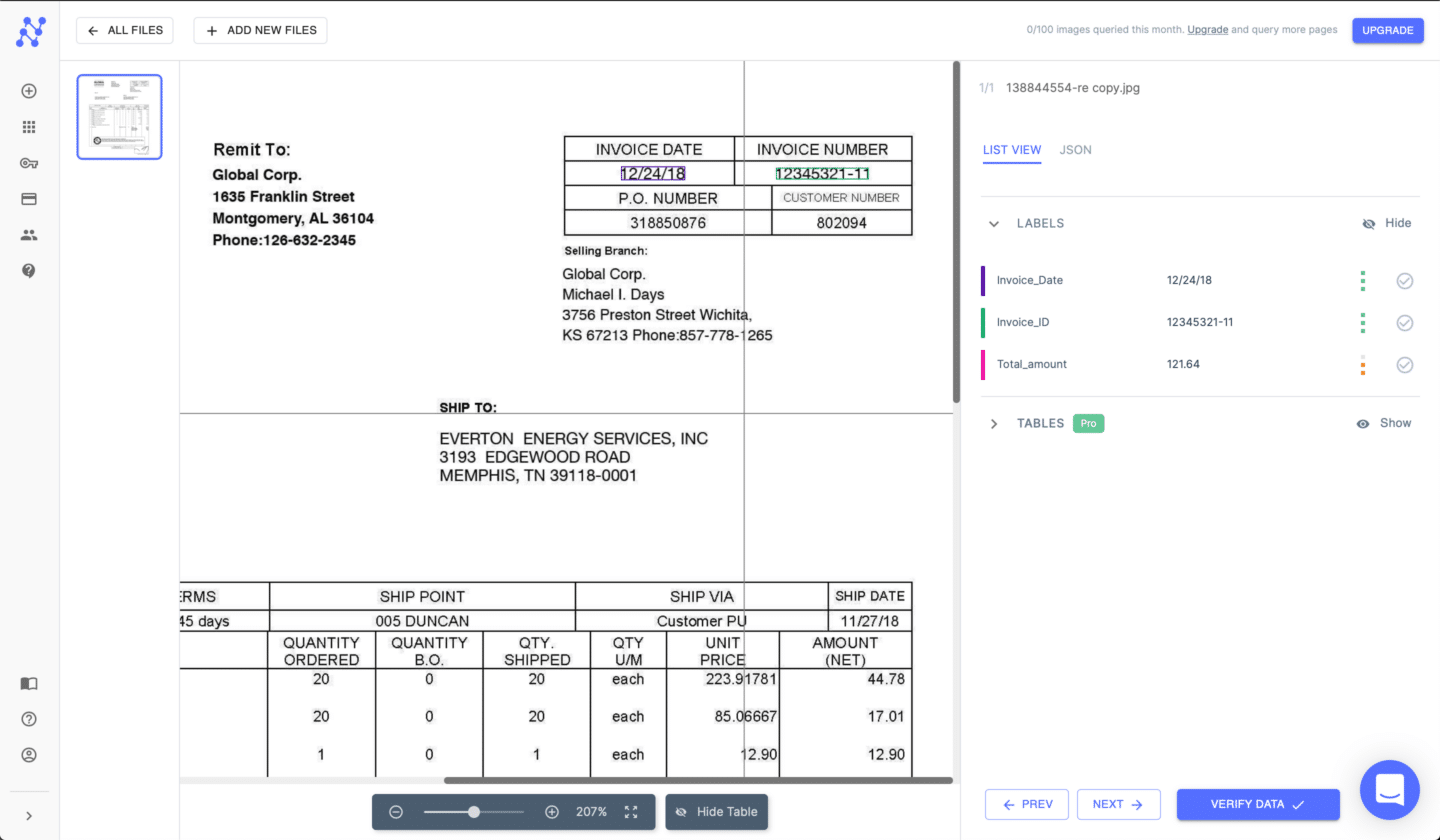
Nanonets is an AI-driven automation platform tailored for streamlining complex business processes The platform utilizes AI to extract and convert valuable information from invoices and receipts into practical insights.
Conclusion
Automated invoice data extraction streamlines financial management by quickly and accurately capturing crucial information from invoices, such as vendor details, amounts, and dates.
This technology ensures data accuracy, enhances financial forecasting, and supports effective expense management.
By automating this process, businesses can significantly reduce errors, save time, and improve overall financial operations.
FAQs about Invoice Data Extraction
Here are some frequently asked questions about invoice data extraction:
What is the data entry process for invoices?
The data entry process for an invoice typically involves manually inputting information such as vendor details, customer information, invoice number, dates, item descriptions, and amounts into a financial system or accounting software.
Why Invoice Data Extraction Should be Automated?
Automating invoice data extraction improves accuracy, speeds up processing, reduces labor costs, and minimizes human errors. Automation also facilitates better data management and analysis, leading to more informed business decisions.
What are the steps of invoice processing?
Invoice processing generally involves the following steps: receiving the invoice, verifying details, entering data into the system, matching invoices with purchase orders, approval for payment, and finally, executing the payment.
What is the process of invoice processing?
The invoice processing process includes receiving invoices, checking and validating them against purchase orders and receipts, entering them into accounting systems, obtaining necessary approvals, and arranging payment within the stipulated payment terms.
What is the best Invoice scanner?
DocuClipper is considered the best invoice scanning software due to its specialization in financial document processing. It uses specialized OCR software tailored for high accuracy in extracting data from invoices.
How accurate is AI-based invoice data extraction?
Modern AI-based invoice data extraction systems like DocuClipper achieve accuracy rates of 95-98%, significantly higher than the 80-85% typical of traditional OCR systems. The accuracy improves over time as the AI learns from corrections and additional data processing. For most businesses, this means virtually error-free invoice processing after an initial training period.
Can invoice data extraction work with handwritten invoices?
Yes, advanced invoice data extraction solutions can process handwritten invoices, though with slightly lower accuracy (85-90%) compared to typed invoices. The technology uses specialized handwriting recognition algorithms and continuously improves through machine learning. For best results, consistent handwriting and good image quality are important when processing handwritten elements.
What’s the ROI of implementing automated invoice extraction?
Businesses typically achieve ROI within 3-6 months of implementing automated invoice extraction. A company processing 1,000 invoices monthly can save approximately $20,000-$40,000 annually in direct labor costs alone. Additional ROI comes from capturing early payment discounts (worth 2-3% of invoice value), reducing late payment penalties, and freeing staff for higher-value activities. Most organizations report 300-500% ROI within the first year.
How does invoice data extraction integrate with ERP systems?
Invoice data extraction solutions integrate with ERP systems through several methods:
- API connections that allow direct data transfer
- Pre-built connectors for popular ERPs like SAP, Oracle, and Microsoft Dynamics
- Export/import functionality using standardized formats (XML, JSON, CSV)
- Middleware solutions for complex integration scenarios
The integration typically maps extracted invoice fields to corresponding ERP fields and can be configured to trigger workflow actions such as approval routing or payment scheduling. Most modern invoice extraction systems offer “plug-and-play” integration with major ERPs, requiring minimal IT resources to implement.
How can I improve the accuracy of automated invoice data extraction?
To improve the accuracy of automated invoice data extraction:
- Use original digital invoices whenever possible rather than scanned copies
- Ensure proper image quality (300+ DPI) when scanning is necessary
- Implement a validation step to review and correct potential errors
- Train the AI system by correcting mistakes, which improves future accuracy
- Create vendor-specific templates for recurring suppliers
- Standardize invoice formats with your vendors when possible
- Use specialized invoice OCR software rather than general document scanning tools
These practices can help achieve accuracy rates exceeding 99% for most invoice processing scenarios.