In today’s digital era, as information becomes increasingly digitized, there arises a necessity for a method to convert physical information into an easily editable digital format. This is where Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology starts to play
In this article, we will discuss the fundamentals of OCR technology and its operational mechanisms. Understanding the process and recognizing its utility enables you to leverage OCR to its fullest extent for your projects, professional work, or business operations.
We’ll also provide you with the best examples of OCR tech available right now and its specialized uses.
What is OCR (Optical Character Recognition)?
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) is a game-changing tech tool in our digital world. Basically, OCR turns text from printed or handwritten documents, pictures, or scans into text that computers can read and edit.
Why is OCR Important?
OCR has been a game-changer for many, whether in companies, practices, or small businesses. OCR Data entry tasks have been significantly more efficient for numerous companies because of the time and resources saved in digitalizing data.
The latest OCR technology accuracy reaches 99% for transforming data, encompassing handwritten words, with numerous OCR software options already achieving this level of precision.
OCR can be used in sectors that handle data that are put in a variety of documents. It is primarily used in finance, accounting, education, healthcare, and statistics.
How Does OCR Work?
The process of extracting data from documents or images into machine-readable text involves a sequence of precise steps. This breakdown elucidates the workings of OCR, unraveling the intricacies from image upload to final text recognition.
Step 1: Upload Image/Document
The process begins with the user uploading an image or document containing the desired text. This could range from scanned documents, photographs, or any image containing textual information.
The quality and clarity of the input play a crucial role in determining the accuracy of the OCR output.
Clearer photos like PDFs and bank statements are likely to be more accurate during the conversion process while handwritten or typewriter documents can be less accurate.
Step 2: OCR Preprocessing
Once the image is uploaded, the OCR system initiates preprocessing. This step involves enhancing the image quality, cleaning up noise, and optimizing the document for efficient text extraction.
When an OCR system encounters a scanned document with uneven lighting conditions, preprocessing algorithms would work to normalize the lighting. It is to ensure a uniform background for better character recognition.
Additionally, if the document has varying font sizes, preprocessing techniques would standardize the text, allowing for consistent and accurate recognition.
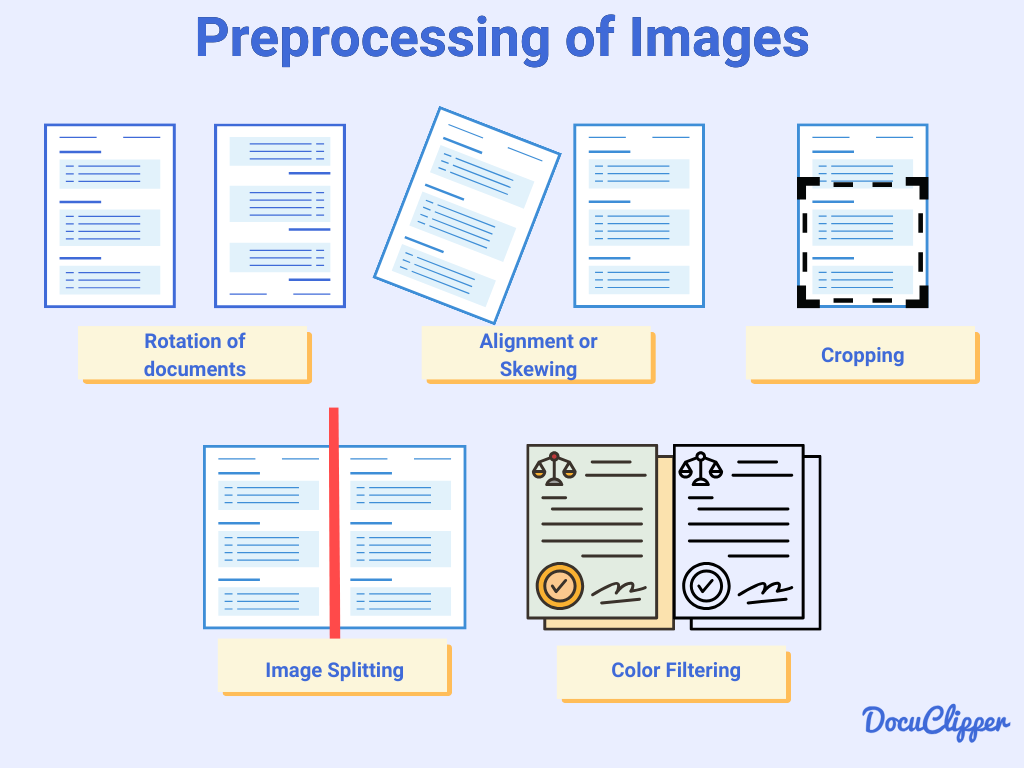
Step 3: Text Recognition
Pattern Matching
In this stage, the OCR software compares the visual patterns of the input text with a database of known characters and symbols. This matching process helps the system identify and differentiate individual characters within the image.
Imagine the OCR system handling invoices of different styles and fonts. Using pattern matching, it identifies key patterns for invoice numbers, dates, and amounts.
By consulting a database of known patterns, the OCR system accurately extracts essential information, ensuring precise OCR data extraction from various document layouts.
Feature Extraction
OCR systems often employ sophisticated algorithms to extract distinctive features from each character, such as line thickness, curvature, and spatial relationships. These features aid in refining character recognition and minimizing errors.
In a scenario where an OCR system is tasked with recognizing handwritten characters in a medical prescription. Feature extraction algorithms would analyze the unique characteristics of each handwritten character, such as the slant, loop shapes, and intersections, to enhance the accuracy of recognition.
Step 4: Postprocessing
Postprocessing involves error correction, contextual analysis, and the assembly of recognized characters into coherent words and sentences. This stage is essential for addressing any inaccuracies or misinterpretations that may have occurred during the preceding steps.
Beyond document processing, OCR advancements have paved the way for innovative tools such as AI video generators, which can transform text-based data into dynamic visual content, enhancing accessibility and engagement.
As an example, if the OCR system encounters ambiguous characters in a legal document, postprocessing algorithms would analyze the context of surrounding words to correct any misinterpretations.
6 Types of OCR Technology
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology has various approaches that cater to diverse needs. Here, we explore six types of OCR technology, each tailored to specific applications, contributing to the efficiency and precision of text extraction in various contexts.
Pattern Recognition OCR
Pattern Recognition OCR stands at the forefront of OCR technology, using advanced algorithms to identify and match visual patterns in characters. This excels in recognizing and deciphering textual content, ideal for high-precision applications like legal documents and financial reports.
Feature Extraction OCR
Feature Extraction OCR goes beyond basic character recognition by analyzing specific features of each character, such as line thickness, curvature, and spatial relationships. Its ability to handle diverse fonts and styles makes it superior in scenarios where traditional OCR systems fail.
Intelligent Character Recognition (ICR)
Intelligent Character Recognition (ICR) specializes in deciphering handwritten characters, going beyond the capabilities of standard OCR. It’s effective for tasks involving human input like form processing and personalized correspondence like individual handwriting styles.
Optical Mark Recognition (OMR)
Designed to recognize and interpret human-marked data, Optical Mark Recognition (OMR) focuses on processing marked fields on documents. Used in survey forms, multiple-choice exams, and questionnaires, it efficiently identifies and interprets checkboxes and bubbles.
OWR Word Recognition (OWR)
Optical Word Recognition (OWR) technology recognizes whole words in documents, improving context understanding in machine-printed texts like newspapers. This enhances content extraction and comprehension efficiency.
Mobile OCR
Mobile OCR allows users to digitize documents on the go by capturing text through smartphone cameras, making it an essential tool for field professionals and researchers who need immediate data extraction without extra equipment.
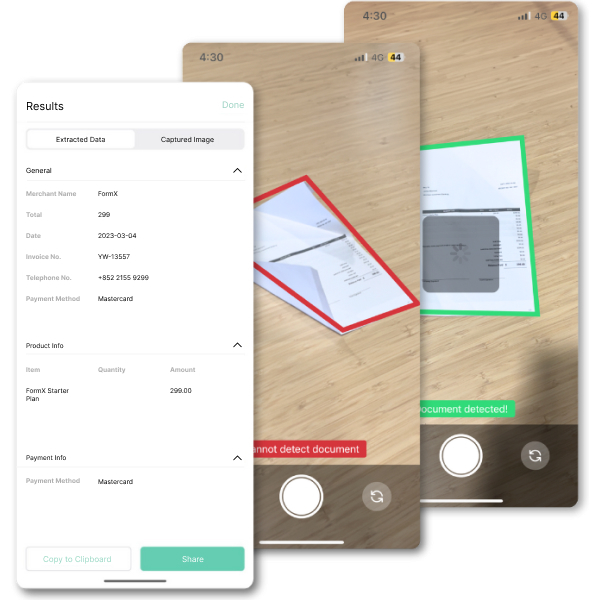
Benefits of Using OCR
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology brings a multitude of advantages, enhancing various aspects of business operations and service delivery.
Improve Operational Efficiency
OCR significantly boosts operational efficiency by automating data entry processes. This eliminates the need for manual data entry, reducing the time and resources traditionally spent on such tasks.
Save Money
OCR contributes to cost savings for businesses by streamlining processes and diminishing the dependence on manual data entry personnel.
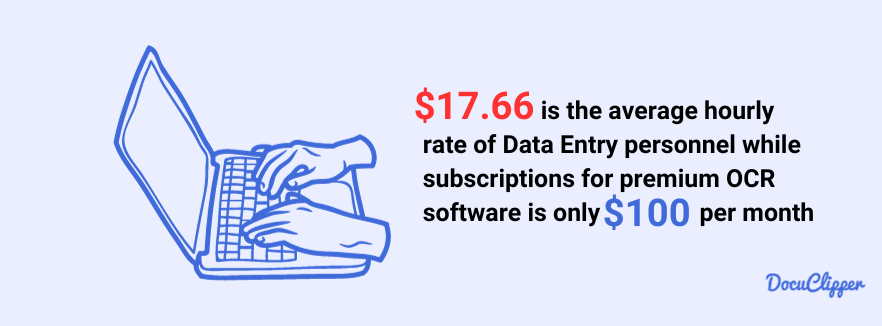
The expenses associated with OCR subscriptions are minimal compared to the salaries of multiple employees.
On average, the hourly rate for data entry personnel is $17.66 per hour while monthly subscriptions for OCR software are around $20. The automated efficiency of OCR results in substantial cost savings for businesses.
Reduce Time Data Entry
OCR accelerates data entry processes, considerably reducing the time required for tasks that would otherwise be time-consuming if done manually. This time efficiency contributes to overall productivity gains. What might take days for conversion can be completed within a matter of hours.
Improve Human Error
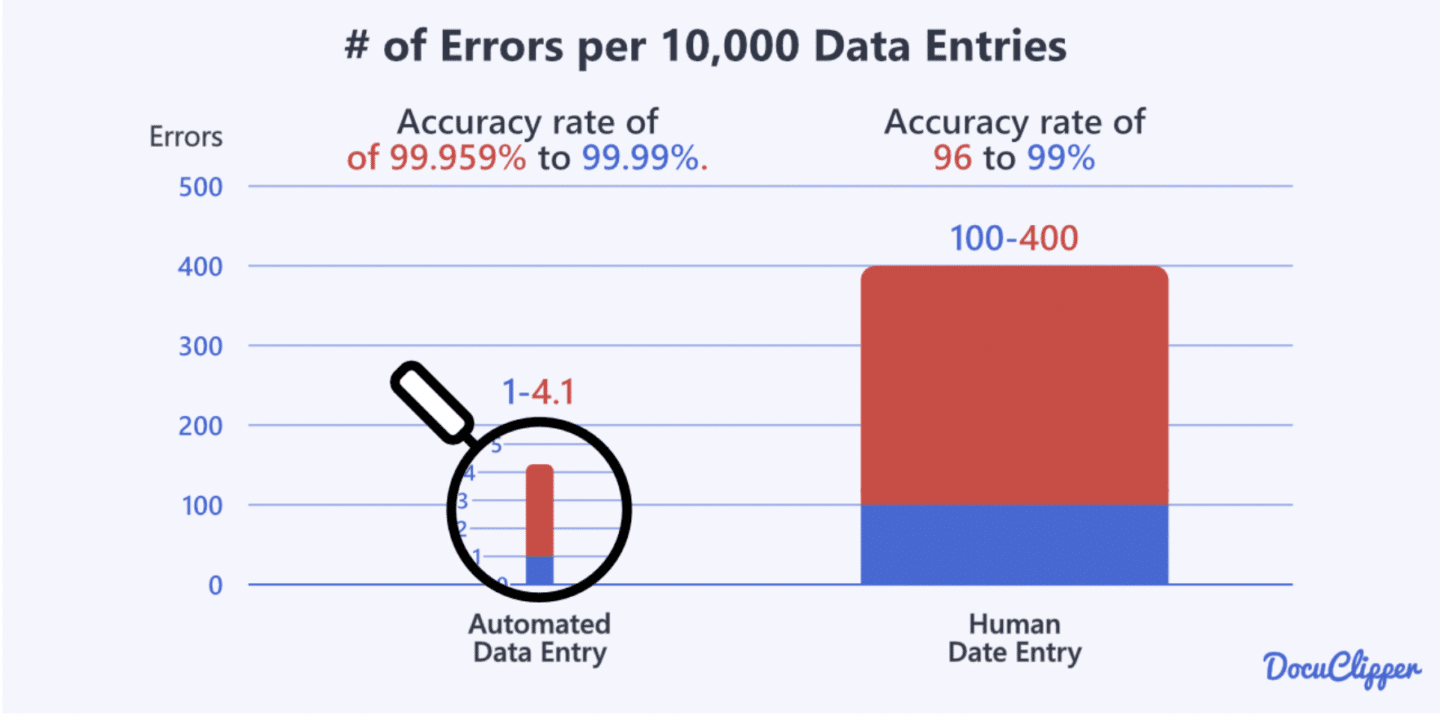
Automated data entry with OCR significantly reduces the chances of errors. OCR demonstrates a remarkable accuracy rate between 99.959% and 99.99%, surpassing the accuracy rates of human data entry, which usually fall between 96% and 99%.
To illustrate, when processing 10,000 documents, OCR systems encounter errors in only 1 to 4 documents, whereas human data entry personnel may have errors ranging from 100 to 400 documents.
Improve Your Services
Accounting and bookkeeping companies can elevate their services by implementing OCR, ensuring accurate and efficient data processing. Industries with customer-facing environments can use OCR to expedite processing times, leading to heightened customer satisfaction.
Overall using OCR to automate data entry from manual data entry will benefit your operation almost in every aspect, especially when scaling.
Typical OCR Use Cases
The applications of OCR span across various industries, bringing efficiency, accuracy, and automation to diverse workflows. It has become a major step for industries that tackle high-volume information processing.
Banking and Finance
OCR tech is necessary for streamlining processes, particularly in analyzing bank statements. Financial institutions can efficiently digitize and extract essential information, expediting document processing when using an OCR bank statement converter.
This technology not only enhances the speed and accuracy of data extraction but also facilitates advanced bank statement analysis, allowing for the swift categorization of transactions.
Healthcare
The healthcare sector benefits significantly from OCR’s ability to convert handwritten medical records, prescriptions, and administrative documents into digital formats. OCR facilitates efficient data management, accelerates medical billing processes, and improves patient care by ensuring accurate and accessible documentation. Partnering with a reliable EHR vendor can further streamline these processes, ensuring seamless integration, compliance, and optimized workflow management for your business.
Legal
Legal professionals can swiftly digitize vast volumes of paperwork, including contracts, court documents, and case files. OCR’s precision in recognizing printed and handwritten text streamlines document retrieval and enables legal teams to focus on critical tasks.
Retail
Retail businesses can optimize resource allocation, minimize errors, and provide a more seamless customer experience by using OCR technology. OCR transforms retail operations by automating inventory management, order processing, and customer interaction.
OCR enhances the speed and accuracy of retail workflows from scanning and recognizing product labels to automating invoice processing.
Education
Educational institutions can use OCR for their assessment of student performance from paper formats. It can make the process significantly efficient in grading exams and processing admission forms to converting textbooks into accessible digital formats.
Schools can also leverage OCR to streamline administrative tasks, improve accessibility for students, and enhance the overall learning experience.
Government
OCR is widely used in government offices for various tasks. It helps in immigration procedures, digitizing old documents, and processing accounting data. They use OCR to improve public services by efficiently extracting data from forms and automating document classification.
OCR Technology Benchmarks
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technologies play a pivotal role in transforming images into machine-readable text, yet achieving perfect accuracy remains a challenge.
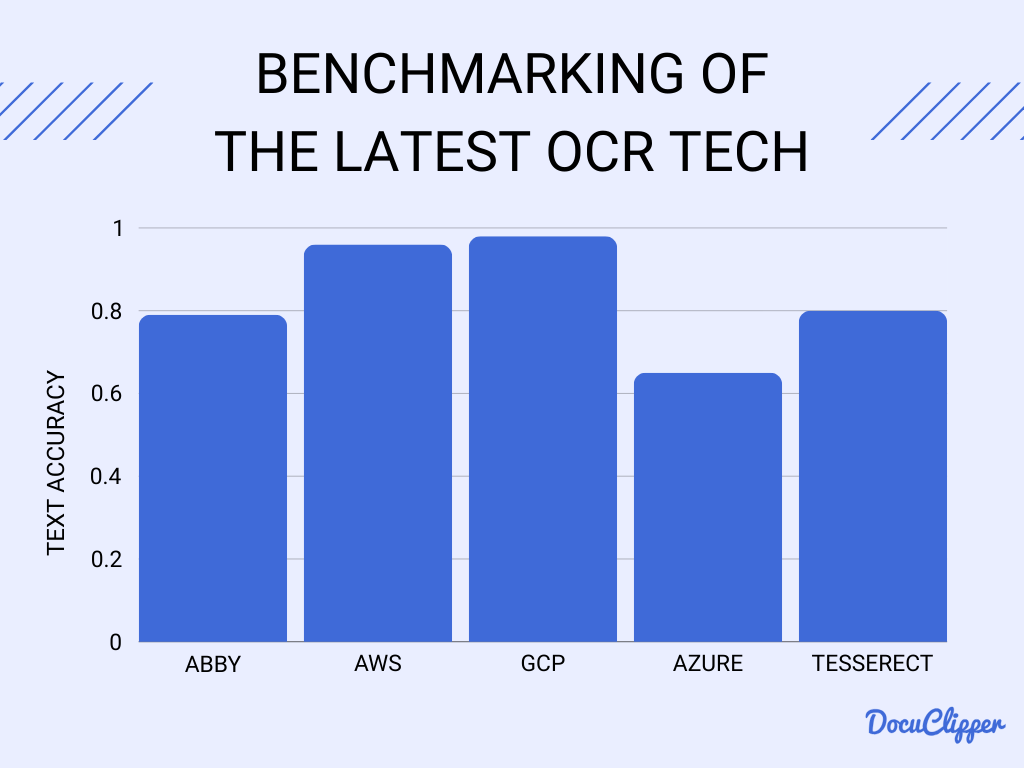
In a benchmark performed by AI Multiple, Google Cloud Platform’s Vision OCR tool emerged as the leader, showcasing a 98.0% accuracy rate across diverse image categories.
However, the inclusion of handwritten text posed challenges for some products, emphasizing the importance of understanding OCR capabilities in varying scenarios.
AWS Textract’s performance improved significantly when excluding problematic images, emphasizing the impact of specific cases on overall results.
OCR Benchmarking on Accounting Uses

The choice between generic multi-format engines and specialized solutions depends on the specific document types and tasks at hand.
DocuClipper stands out as a specialized OCR platform designed for financial documents, with an impressive 99.5% accuracy in processing bank statements.
It’s training on over 1,000,000 bank statements underscores its precision in tasks like financial analysis and bookkeeping.
Nanonets, while offering a wide range of document support, achieves an OCR accuracy level of around 95%-96%.
Valid8 Financial, a specialized solution for financial intelligence and forensic accounting, reaches a remarkable 99% accuracy, ensuring the reliability of extracted data.
Rossum focuses on invoices and receipts, achieving an OCR accuracy of up to 98%.
In essence, the dedicated OCR tools with a financial focus lead the pack with accuracy rates surpassing 99%, while more generalized multi-format solutions range between 95-98%. The choice hinges on the specific needs of financial tasks and the desired level of accuracy.

History of OCR Technology
In 1974, Ray Kurzweil revolutionized technology with the introduction of Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology. His creation, capable of recognizing text in diverse fonts, marked a significant breakthrough.
Kurzweil’s humanitarian vision materialized in a reading machine for the visually impaired, which Xerox acquired in 1980 to advance paper-to-computer text conversion.
Although OCR technology gained limited recognition until the early 1990s, its transformative impact unfolded when historians and archivists used it to digitize historical newspapers, reshaping information preservation.
Evolving significantly, OCR now achieves near-perfect accuracy, standing at the forefront of automating document processing workflows.
It eliminates manual retyping, ensuring swift and flawless digitization, and serving as an emblem of technological advancement in both personal and professional realms.
6 Best OCR Software in 2025
Here are the best OCR software for 2025 that leads in data entry and data management:
DocuClipper
DocuClipper stands out as a cloud-based solution, emphasizing its prowess in optical character recognition (OCR) for seamlessly transforming bank and credit card statements into Excel or diverse accounting software formats.
It adeptly extracts data from PDFs and various image formats using OCR technology, showcasing remarkable compatibility with an extensive array of over 10,000 bank statements globally.
DocuClipper excels in simplifying the importation of statements into accounting software. This emphasis on OCR not only ensures a rapid process but also significantly reduces the risk of errors, providing users with an efficient and accurate means to manage their financial statements.
ABBYY FineReader
ABBYY FineReader stands as a frontrunner in OCR tech because of its accuracy in different uses. it excels at transforming scanned documents and images into editable formats, setting itself apart with advanced OCR algorithms and comprehensive language support.
Businesses and professionals seeking precise and multilingual text extraction consistently favor ABBYY FineReader for its exceptional capabilities.
Image to Text
Image to Text stands out as a straightforward OCR solution, designed to quickly and accurately extract editable text from images and scanned documents. Its simplicity and ease of use make it a top choice for individuals and small businesses who need fast, no-fuss document conversion.
Global audience widely applauds Imagetotext.info’s capability of accepting 3 photos in one go for extraction, while also supporting more than 20 languages.
Adobe Scan
Adobe Scan integrates a robust OCR solution with seamless document management features. Designed for mobile use, its user-friendly interface enables users to capture, convert, and organize bank statements, receipts, and other documents effortlessly on the go.
What distinguishes Adobe Scan is its synergy with other Adobe tools, elevating overall document collaboration and workflow efficiency to unprecedented levels.
Google Lens
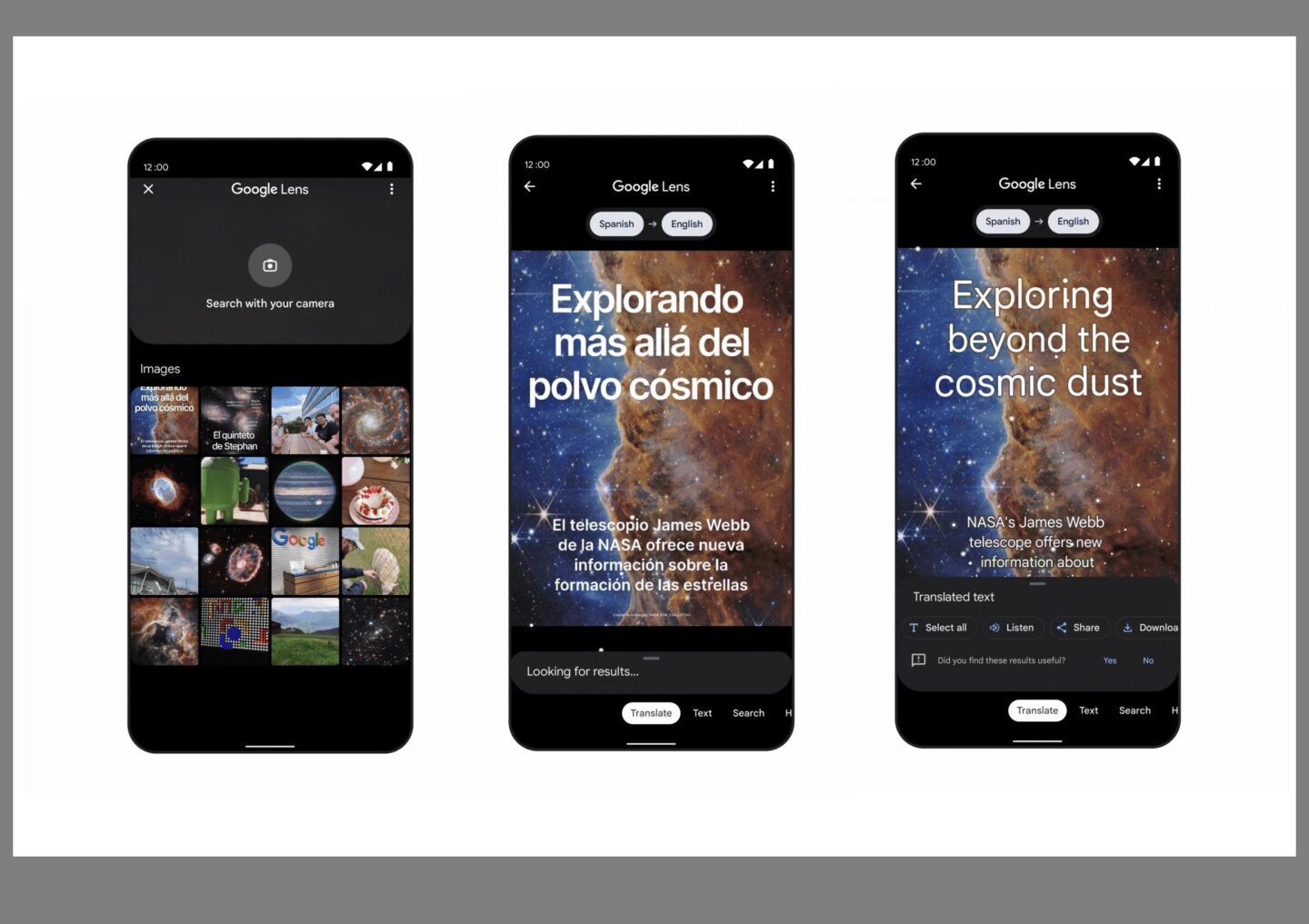
More than just a visual search tool, Google Lens emerges as a powerful OCR solution within a mobile application. Its real-time text recognition feature empowers users to extract and translate text from images.
Google Lens is versatile for applications ranging from language translation to capturing information from printed materials. The accessibility and seamless integration with mobile devices set Google Lens in the latest OCR technology.
DupliChecker
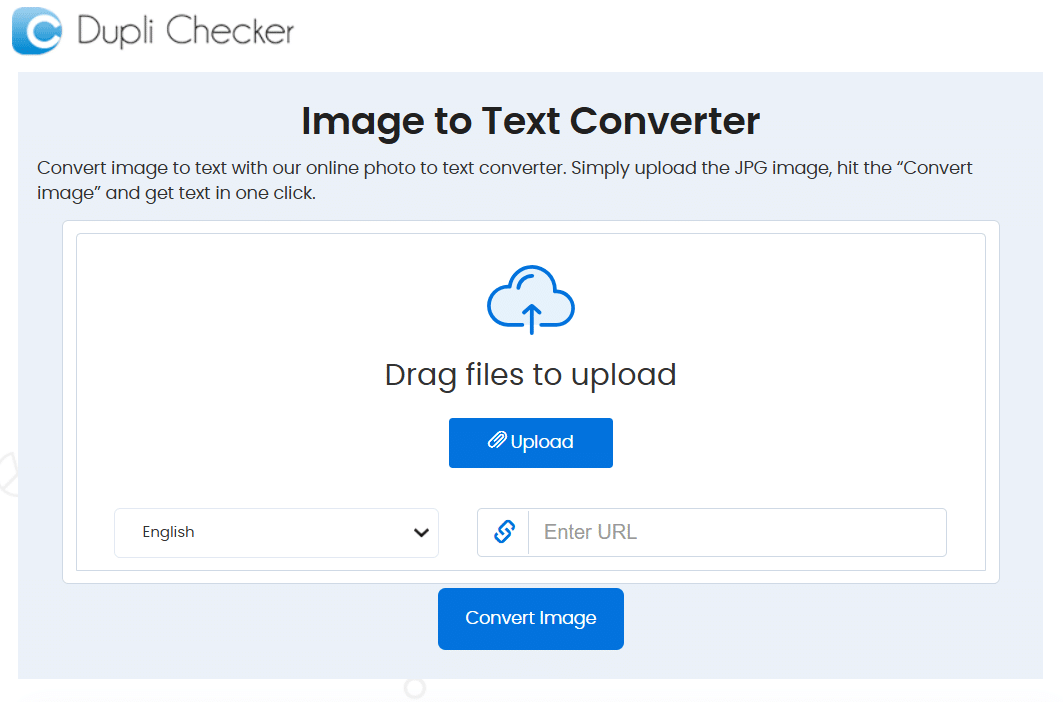
The image to text converter by DupliChecker is another web-based OCR software you can utilize for precise extraction of textual content from pictures. This advanced tool helps you swiftly convert any image to text form in a matter of seconds.
You can upload an image to this tool by browsing it from your device or entering an image URL. It also gives you the option to select the language of the text contained in your image and fetch it accurately.
CamScanner
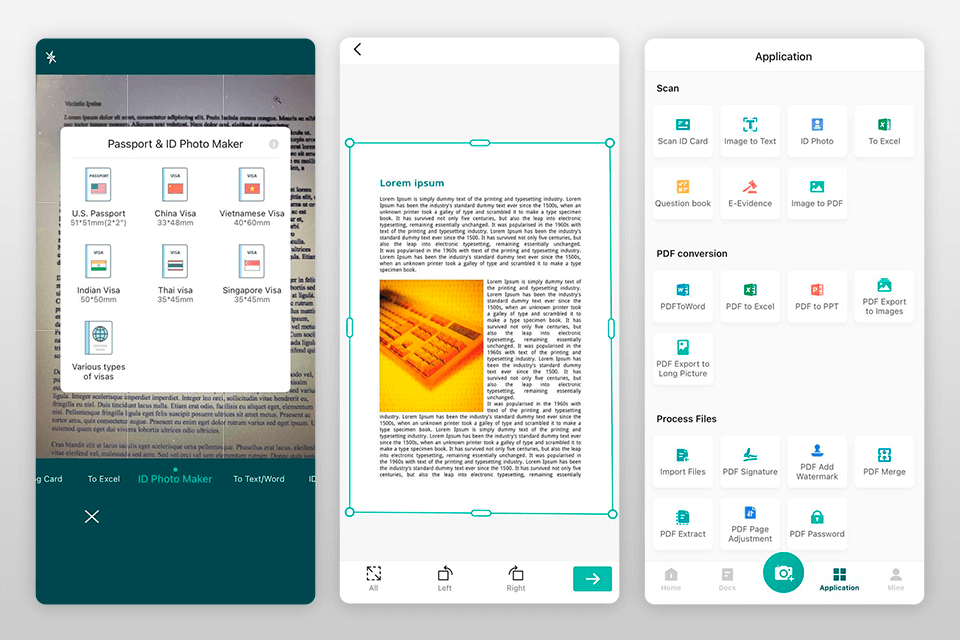
CamScanner is a top choice among mobile OCR apps, smoothly blending document scanning with effective text recognition. It lets users capture and convert images into PDF or editable text formats, standing out with features like smart cropping and image enhancement.
Its reliability and user-friendly design make it a favored OCR solution for efficient document management on mobile devices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology is a transformative force in the digital landscape, playing a crucial role in converting printed or handwritten text from various sources into machine-readable and editable formats.
This article has explored the fundamentals of OCR technology, its operational mechanisms, and its diverse applications across industries. As information becomes increasingly digitized, OCR becomes an indispensable tool for improving operational efficiency, reducing costs, and minimizing errors.
The technology’s evolution, benchmarking, and the emergence of specialized OCR solutions for specific document types, such as bank statements, highlight its versatility and impact.
FAQs about OCR
Here are the most frequently asked questions regarding OCR and its applications.
What is OCR, and how does it work?
OCR, or Optical Character Recognition, is a technology that converts printed or handwritten text from documents, images, or scanned pages into machine-readable and editable text. It involves uploading an image, preprocessing, text recognition using pattern matching and feature extraction, and postprocessing for error correction.
Why is OCR important?
OCR is crucial for efficient data entry, and saving time and resources. It has an accuracy rate of up to 99%, making it a game-changer in various sectors like finance, accounting, education, healthcare, and statistics.
How does OCR improve operational efficiency?
OCR automates data entry processes, eliminating the need for manual entry. This significantly boosts operational efficiency by saving time and resources traditionally spent on such tasks.
What are the benefits of using OCR?
OCR improves operational efficiency, saves money, reduces data entry time, minimizes human errors, and enhances services in industries like accounting, healthcare, legal, retail, education, and government.
What are the typical use cases of OCR?
OCR finds applications in banking, healthcare, legal, retail, education, and government for tasks such as analyzing bank statements, digitizing medical records, processing legal documents, optimizing retail operations, grading exams, and enhancing government services.
What are the different types of OCR technology?
There are six types of OCR technology: Pattern Recognition OCR, Feature Extraction OCR, Intelligent Character Recognition (ICR), Optical Mark Recognition (OMR), Optical Word Recognition (OWR), and Mobile OCR.
Which OCR software is recommended for bank statements?
DocuClipper is recommended for bank statements, achieving an impressive accuracy of 99.5% in processing financial documents.
What is the history of OCR technology?
OCR technology was introduced in 1974 by Ray Kurzweil. Initially developed for the visually impaired, it gained recognition in the 1990s for digitizing historical newspapers. Today, OCR stands at the forefront of document processing automation.
What factors impact the accuracy of OCR technology?
Several factors influence OCR accuracy, including the quality and clarity of the input image, preprocessing techniques, the sophistication of pattern matching and feature extraction algorithms, and the effectiveness of postprocessing for error correction. Understanding these factors is crucial for optimizing OCR performance.
What are the accuracy benchmarks for OCR technology?
OCR technologies generally demonstrate accuracy rates between 95-99%. Google Cloud Platform’s Vision OCR tool led in a benchmark with a 98.0% accuracy rate, emphasizing the importance of understanding OCR capabilities in varying scenarios.