In the tech space, many tools are readily available for businesses to exploit and take advantage of to make their processes more efficient.
These tools allow businesses to venture into automation that improves their revenue, cuts their costs, and creates higher turnover rates. Among the tools that are widely used in information processing for businesses are AI and OCR.
This blog will cover the OCR vs AI comparison and how these technologies stuck up against each other and more importantly how they work together to improve your business processes.
Key Takeaways:
- OCR is efficient for structured text and enhances document data extraction with high accuracy, cost-effectiveness, and improved searchability, but struggles with handwritten or complex texts.
- AI excels in learning, handling large data sets, and innovative problem-solving, with the ability to adapt and improve over time, but is costlier and raises ethical concerns.
- The integration of AI and OCR can significantly improve accuracy, extend OCR’s applicability, enhance data analysis, speed up processing, and reduce manual interventions.
- OCR is widely used in banking, invoice processing, healthcare record digitization, legal document analysis, and retail product information extraction.
- AI is crucial for extracting insights from social media, analyzing financial and healthcare data, real estate market analysis, and automating resume screening in HR.
What is OCR?
Optical Character Recognition, or OCR, is a technology that converts different types of documents, such as scanned paper documents, PDFs, or images captured by a digital camera, into editable and searchable data.
Most OCR software is used in different fields like accounting, finance, data analysis, and research. It is mainly known for converting bank statements into digital formats by reading and transforming the text from images or scanned documents.
What is AI?
Artificial Intelligence, or AI, refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think and learn. It encompasses a range of capabilities from basic problem-solving to complex decision-making and pattern recognition.
AI took off with the boom of ChatGPT and has been widely used in various areas such as writing, marketing, programming, data science, and gaming, especially in recent years.
Comparing OCR and AI
While both technologies aim to streamline data processing, their approaches and outcomes vary significantly. There are specific use cases for each technology based on their advantages and limitations.
OCR Advantages
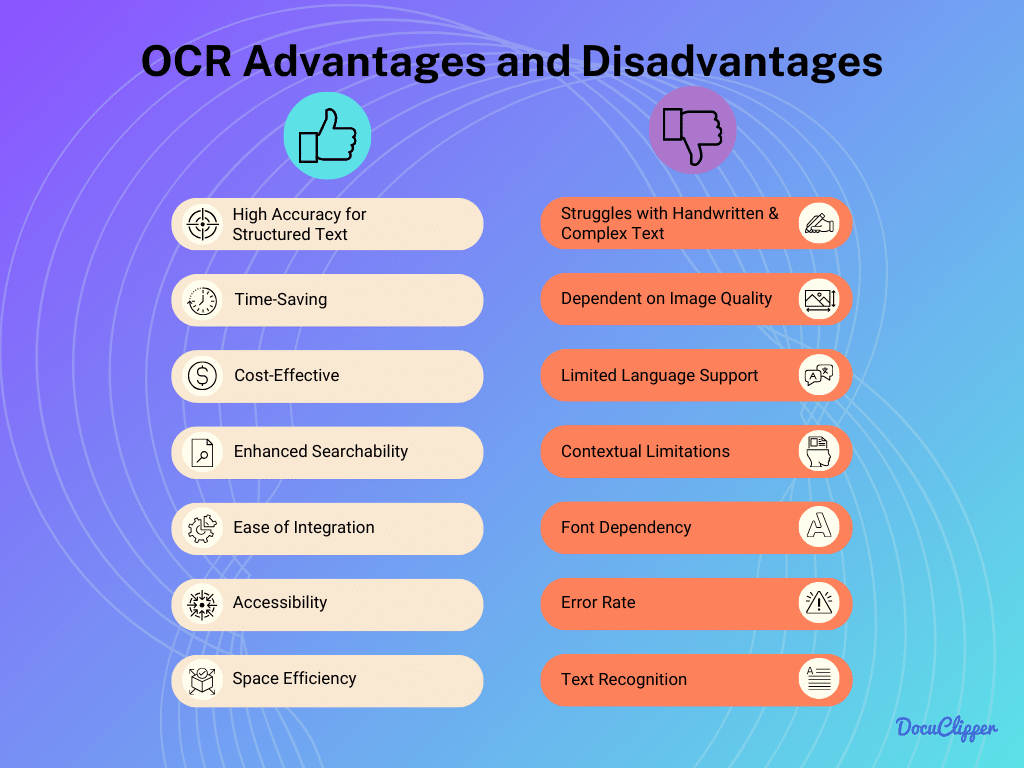
OCR has advantages over manual data entry tasks. There has been a clear-cut view of how it is applied across many fields and here are the reasons why:
- High Accuracy for Structured Text: OCR is highly efficient in accurately converting structured text, excelling with clear fonts and formats. This accuracy is crucial in environments where precise data capture is needed.
- Time-Saving: OCR technology significantly reduces the time required for data entry, streamlining document processing tasks. This efficiency leads to quicker turnaround times in business operations.
- Cost-Effective: Generally, OCR is more affordable than complex AI solutions, making it a budget-friendly option for document digitization. Its cost-effectiveness is especially beneficial for small to medium-sized enterprises.
- Enhanced Searchability: OCR makes text within images searchable, greatly improving the ability to locate information in large document sets. This feature is vital for efficient data management and retrieval.
- Ease of Integration: OCR technology can be easily integrated into existing systems, enhancing their functionality without major overhauls. This ease of integration makes it a practical choice for improving existing workflows.
- Accessibility: OCR enhances the accessibility of printed text for visually impaired users, making information more inclusive. This is a significant step towards creating barrier-free access to information.
- Space Efficiency: By digitizing documents, OCR reduces the need for physical storage space, aiding in efficient space management. This is particularly beneficial in reducing clutter and managing archival systems.
Overall OCR is commonly used to automate manual data entry as well as across many industries. For example, OCR is excellent for automating bookkeeping tasks.
OCR Limitations
OCR, which reads text from images, isn’t perfect yet and there are some OCR limitations.
But, there are ways to make it better. Let’s explore how.
- Struggles with Handwritten & Complex Text: OCR’s accuracy diminishes when processing handwritten notes or stylized fonts, limiting its scope of use. This limitation poses a challenge in situations where such text types are common.
- Dependent on Image Quality: Poor image quality can significantly reduce OCR’s accuracy, leading to errors in text recognition. This dependency requires high-quality scans or images for optimal performance.
- Limited Language Support: Some OCR systems support a limited number of languages, which can be a drawback in multi-lingual environments. This limitation can restrict its usability in global or diverse settings.
- Contextual Limitations: OCR lacks an understanding of context and semantics, focusing solely on text recognition. This limitation means it cannot interpret the meaning or intent behind the text.
- Font Dependency: OCR’s effectiveness can be hindered by specific fonts, impacting its versatility. This font dependency requires careful consideration when using OCR in varied document types.
- Error Rate: Although rare, OCR is not infallible and can make errors in text recognition. These errors, though minimal, can be significant in contexts where accuracy has to be a priority.
- Text Recognition: OCR is limited to recognizing and converting text, lacking the ability to interpret or analyze the underlying data. This limitation means it cannot provide insights or a deeper understanding of the content it processes.
AI Advantages
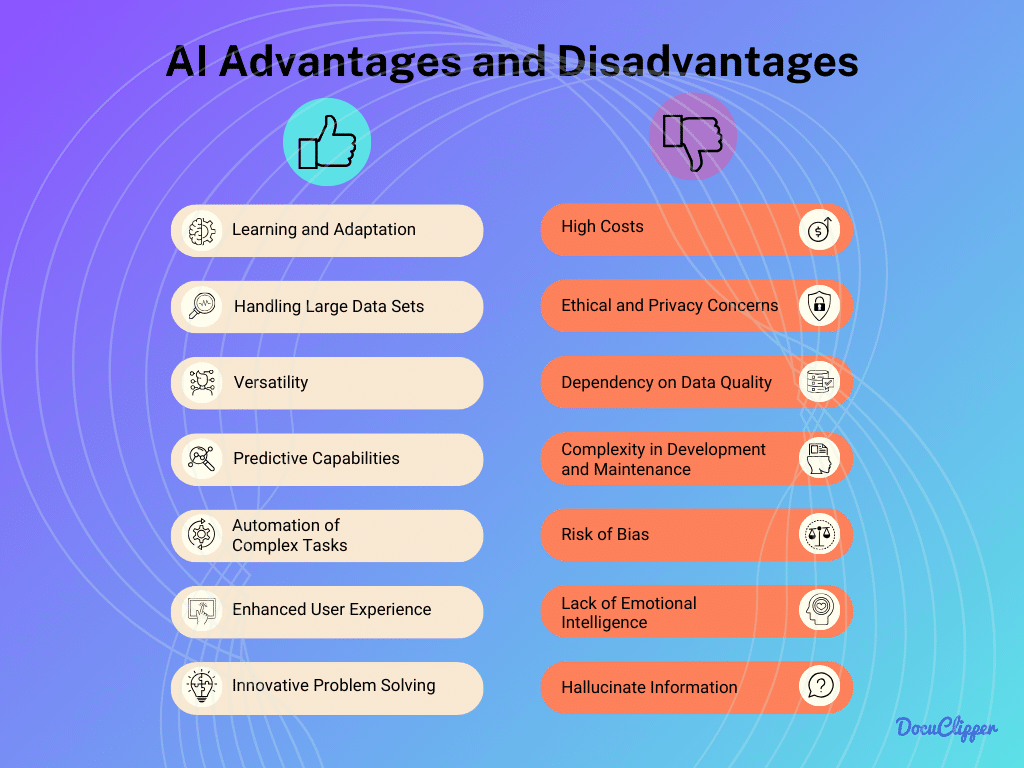
AI has distinct advantages over traditional manual data entry. It’s been effectively applied in various fields, and there are key reasons for its success. Here are its advantages:
- Learning and Adaptation: AI systems can learn and adapt over time, improving their performance and accuracy with continued use. This adaptability makes AI ideal for evolving and complex data environments.
- Handling Large Data Sets: AI excels in processing and analyzing large volumes of data, making it suitable for big data applications. Its ability to manage and interpret vast datasets is critical for data-driven decision-making.
- Versatility: AI’s versatility allows it to be applied in a wide range of tasks beyond just text recognition, including image and voice recognition. This broad applicability makes AI a powerful tool in various technological fields. For example, AI-powered tools like a sentence rephraser help refine written content, making it clearer and more engaging.
- Predictive Capabilities: AI can predict outcomes based on data analysis, providing foresight into potential future scenarios. These predictive capabilities are invaluable in fields like market analysis and risk assessment.
- Automation of Complex Tasks: AI is capable of automating complex operations, and streamlining processes that would be too intricate or time-consuming for humans. This automation leads to increased efficiency and productivity.
- Enhanced User Experience: AI can personalize user experiences, tailoring interactions and services to individual preferences. This personalization enhances user engagement and satisfaction.
- Innovative Problem Solving: AI can find solutions to complex, unstructured problems, often in ways humans might not conceive. Its ability to innovate is crucial in tackling challenging and novel issues.
AI Limitations
While AI offers many benefits, it also has its limitations. Understanding these can help in optimizing its use in business processes. Here are some of the challenges and limitations of AI to consider:
- High Costs: The development and implementation of AI technologies can be expensive, making them less accessible for smaller organizations. These high costs can limit the widespread adoption of AI solutions.
- Ethical and Privacy Concerns: AI raises important questions about data privacy and ethical use, particularly in handling sensitive information. These concerns are paramount in maintaining trust and integrity in AI applications.
- Dependency on Data Quality: The output quality of AI systems is only as good as the input data. Poor quality or biased data can lead to inaccurate or unethical results.
- Complexity in Development and Maintenance: AI systems require specialized skills for development and maintenance, making them complex to implement and manage. This complexity can be a barrier in terms of resource allocation and expertise.
- Risk of Bias: AI systems can inherit biases present in the training data, leading to skewed or unfair outcomes. Addressing these biases is essential to ensure fair and ethical AI applications.
- Lack of Emotional Intelligence: AI does not possess emotional intelligence, limiting its ability to understand or interpret human emotions. This limitation is significant in fields where emotional understanding is key.
- Hallucinate Information: AI might generate inaccurate or fabricated data. This risk underscores the need for careful monitoring and validation of AI outputs.
Summary of OCR vs AI
The major differences between OCR and AI are their functionalities and application scopes.
OCR offers high accuracy in structured text recognition, cost-effectiveness, and is time-efficient, but struggles with complex texts and image quality.
AI, on the other hand, excels in learning, adaptation, handling large data sets, and innovative problem-solving, but faces challenges like high costs, ethical concerns, and dependency on data quality.
The choice between them depends on specific task requirements and resources.
The Advantages of AI-powered OCR Systems
The combination of AI and OCR can be incredibly powerful and efficient in enhancing business processes. Here are some potential benefits you can gain from this synchronization:
- Improved Accuracy: AI significantly boosts OCR’s text recognition accuracy, even in challenging conditions. It enables the system to handle diverse fonts and layouts more effectively.
- Increasing Usefulness and Deployment: By integrating AI, OCR systems become more versatile and applicable in various industries. This integration extends OCR’s capabilities beyond traditional boundaries.
- Improve Data Analysis: AI-OCR combinations not only extract text but also analyze the data for deeper insights. They can identify patterns and trends that are invaluable for business intelligence.
- Faster Processing: AI algorithms process data much faster than traditional OCR. This speed translates to increased efficiency and productivity in data handling tasks.
- Reduced Manual Intervention: The automation provided by AI reduces the need for manual data entry and checking. This leads to fewer errors and saves valuable human resources for more complex tasks.
Use Cases of OCR for Data Extraction
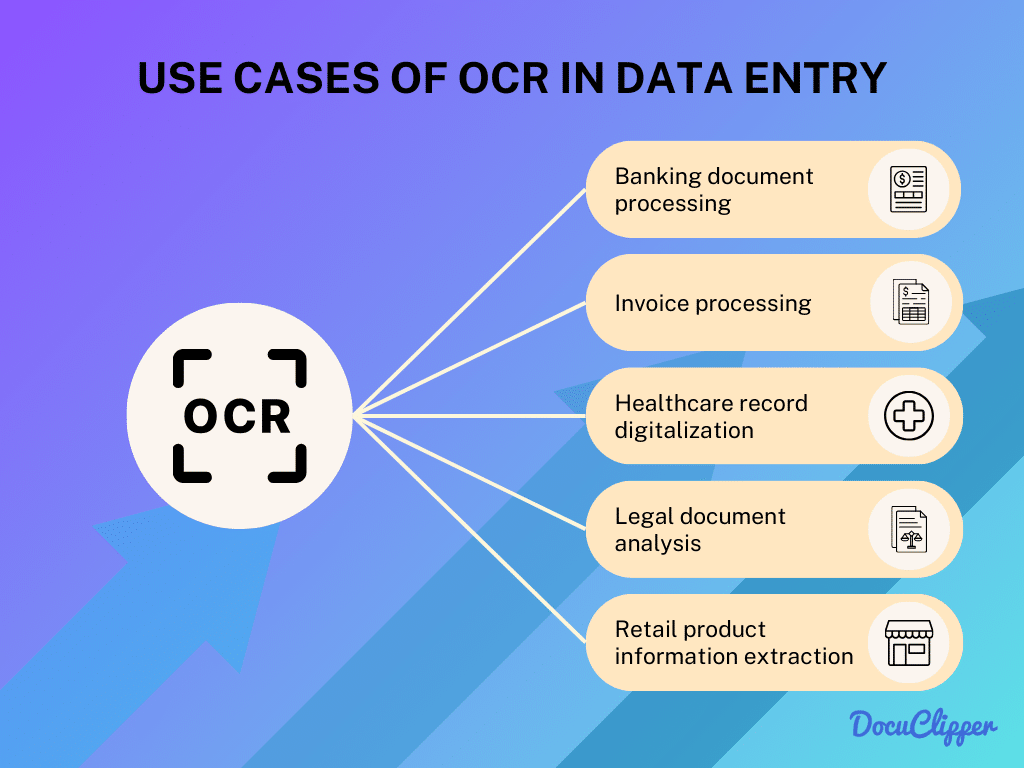
OCR technology is successfully streamlining workflows in several fields. Here are some key areas where it’s being used effectively:
- Banking Document Processing: OCR bank statement converters streamline the processing of customer forms and financial documents in banking. It ensures accurate data capture, aiding in faster customer service and compliance.
- Invoice Processing: OCR simplifies the invoice data extraction into digital formats. This digitization makes invoice management more efficient and less prone to errors.
- Healthcare Record Digitization: In healthcare, OCR aids in converting patient records into digital formats. This digitization enhances accessibility and aids in better health record management.
- Legal Document Analysis: OCR is invaluable in the legal sector for organizing and analyzing vast amounts of documents. It helps in quick retrieval and analysis of legal texts, case files, and precedents.
- Retail Product Information Extraction: Retailers use OCR to automate the extraction of product information from labels and documents. This automation improves inventory management and customer service.
Use Cases of AI for Data Extraction
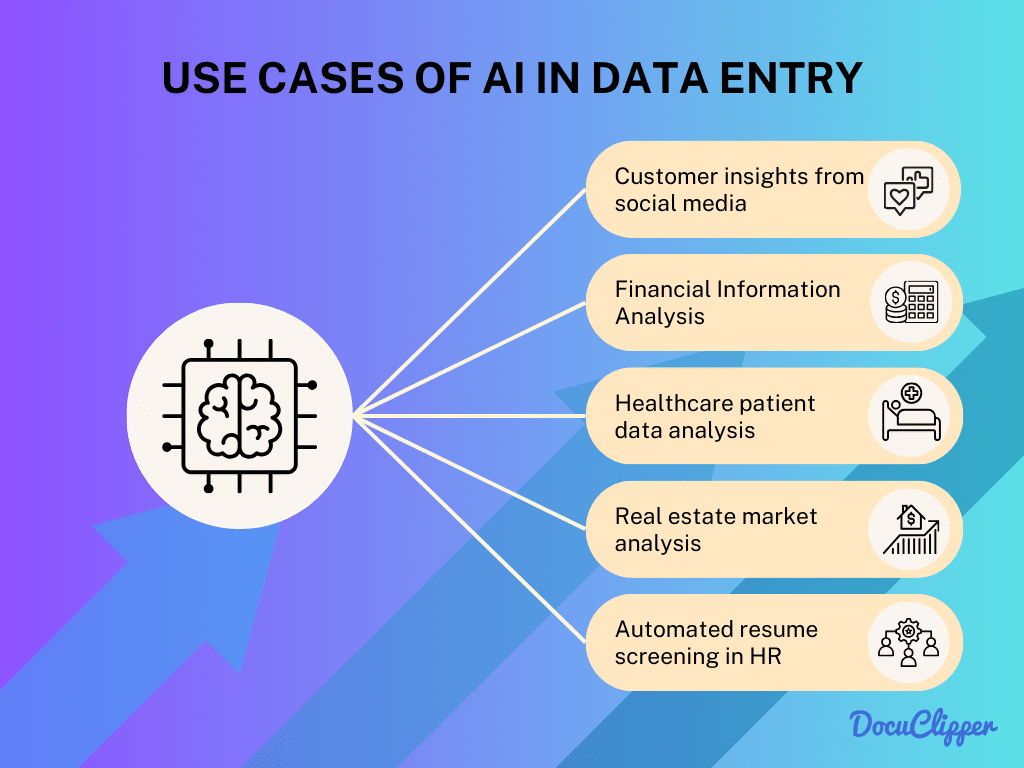
AI is widely used for data extraction in many fields. Here are some key areas where it significantly impacts:
- Customer Insights from Social Media: AI tools analyze social media data to gain insights into customer behaviors and preferences. This analysis is crucial for marketing strategies and customer engagement.
- Financial Information Analysis: AI provides detailed analysis of financial data, identifying trends and making predictions. This capability is essential for market analysis and financial planning.
- Healthcare Patient Data Analysis: In healthcare, AI analyzes patient data to assist in diagnosis and predict health outcomes. This analysis improves patient care and treatment planning.
- Real Estate Market Analysis: AI tools are used to analyze real estate market trends and property values. This analysis aids investors and realtors in making informed decisions.
- Automated Resume Screening in HR: AI streamline hiring process by screening and analyzing resumes. This automation enables HR to focus on the most suitable candidates, improving the recruitment process.
Conclusion
OCR and AI are powerful tools for businesses, each with unique strengths. OCR excels in quickly and accurately converting structured texts like bank statements, making it cost-effective for simple data entry tasks. AI, however, is better for complex tasks, offering advanced data analysis and automation capabilities.
The choice between OCR and AI depends on the specific needs of a business, whether it’s straightforward data digitization or in-depth data processing and analysis.
Try OCR with DocuClipper
If you’re looking to streamline your workflow, choose DocuClipper as a bank statement converter. It’s a top-notch OCR tool specifically designed for converting bank statements. With high OCR accuracy, it can convert PDF bank statements into formats like XSV, CSV, and QBO.
Plus, it’s compatible with various accounting software, including QuickBooks, Sage, and Xero, making financial management and OCR data capture much more efficient.